Abstract
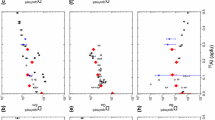
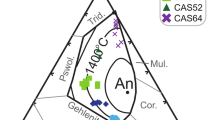
The addition of phosphorus to H2O-saturated and initially subaluminous haplogranitic (Qz−Ab−Or) compositions at 200 MPa(H2O) promotes expansion of the liquidus field of quartz, a marked decrease of the solidus temperature, increased solubility limits of H2O in melt at low phosphorus concentrations, and fractionation of melt out of the haplogranite plane (projected along an Or28 isopleth) toward a peralkaline, silica-poor but quartz-saturated minimum composition. The partition coefficient for P2O5 between aqueous vapor and melt with an ASI (aluminum saturation index, mol Al/[mol Na+K])=1 is negligible (0.06), and consequently so are the effects of phosphorus on other melt-vapor relations involving major components. Phosphorus becomes more soluble in vapor, however, as the concentration of a NaPO3 component increases via the fractionation of melt by crystallization of quartz and feldspar. The experimental results here corroborate existing concepts regarding the interaction of phosphorus with alkali aluminosilicate melt: phosphorus has an affinity for alkalis and Al, but not Si. Phosphorus is incorporated into alkali feldspars by the exchange component AlPSi-2. For subaluminous compositions (ASI=1), the distribution coefficient of phosphorus between alkali feldspar and melt, D[P]Af/m, is 0.3. This value increases to D[P]Af/m=1.0 at a melt ASI value of 1.3. The increase in D[P]Af/m with ASI is expected from the fact that excess Al promotes the AlPSi-2 exchange. With this experimental data, the P2O5 content of feldspars and whole rocks can reveal important facets of crystallization and phosphorus geochemistry in subaluminous to peraluminous granitic systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowen NL (1913) The melting phenomena of the plagioclase feldspars. Am J Sci 4th Ser, 35:577–599
Corbridge DEC (1990) Phosphorus: an outline of its chemistry, biochemistry, and technology (4th ed). Elsevier Science Publishers BV. New York
Dingwell DB (1985) The structure and properties of fluorine-rich melts: implications for granite petrogenesis. In:Taylor RP, Strong DF (eds) Granite-related mineral deposits. Can Inst Mining Geol Div, Halifax, Nova Scotia, pp 72–81
Gan H, Hess PC (1992) Phosphate speciation in potassium aluminosilicate glasses. Am Mineral 77:495–506
Hess PC (1991) The role of high field strength cations in silicate melts. In: Perchuk LL, Kushiro I (eds) Physical chemistry of magmas. Advances in physical chemistry 9. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 153–191
Holtz F, Dingwell DB (1991) Water solubility in boron-rich silicate melts (Abstr). EOS 72:533
Holtz F, Berhens H, Dingwell DB, Taylor RP (1992) Water solubility in aluminosilicate melts of haplogranite composition at 2 kbar. Chem Geol 96:289–302
Kogarko LN, Krigman LD, Krot TV (1988) The solubility and geochemistry of phosphorus in magmas. Geochem Int 25:1–12
London D (1987) Internal differentiation of rare-elment pegmatites: effects of boron, phosphorus, and fluorine. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 51:403–420
London D (1990) Internal differentiation of rare-element pegmatites; a synthesis of recent research. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap 246:35–50
London D (1992a) Phosphorus in S-type magmas: the P2O5 content of feldspars from peraluminous granites, pegmatites, and rhyolites. Am Mineral 77:126–145
London D (1992b) The application of experimental petrology to the genesis and crystallization of granitic pegmatites. In: Martin Cerny P (eds) Granitic pegmatites. Can Mineral 30:499–540
London D, Burt DM (1982) Chemical models for lithium aluminosilicate stabilities in pegmatites and granites. Am Mineral 67:494–509
London D, Hervig RL, Morgan GB VI, (1988) Melt-vapor solubilities and elemental partitioning in peraluminous granite-pegmatite systems: experimental results with Macusani glass at 200 MPa. Contrib Mineral Petrol 99:360–373
London D, Morgan GB VI, Hervig RL (1989) Vapor-understurated experiments in the system macusanite-H2O at 200 MPa, and the internal differentiation of granitic pegmatites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 102:1–17
London D, Cerny P, Loomis JL, Pan JJ (1990a) Phosphorus in alkali feldspars of rare-element granitic pegmatites. Can Mineral 28:771–786
London D, Loomis JL, Huang W, Morgan GB VI (1990b) Behavior and effects of phosphorus in the system Ab−Or−Qz−H2O at 200 MPa(H2O). (Abstr) Geol Soc Am Abstr with Prog 22:A302
Manning DAC (1981) The effect of fluorine on liquidus phase relationships in the system Qz−Ab−Or with excess water at 1 kbar. Contrib Mineral Petrol 76:206–215
Morgan GB VI, London D, Kirkpatrick RJ (1990) Reconnaissance spectroscopic study of hydrous sodium aluminum borosilicate glasses. (Abstr) Geol Soc Am Abstr Prog 22:A167
Mysen BO, Virgo D (1985) Structure and properties of fluorine-bearing aluminosilicate melts: the system Na2O−Al2O3−SiO2−F at 1 atm. Contrib Mineral Petrol 91:205–220
Mysen BO, Ryerson FJ, Seifert FA (1981) The structural role of phosphorus in silicate melts. Am Mineral 66:106–117
Pichavant M (1987) Effects of B and H2O on liquidus phase relations in the haplogranite system at 1 kbar. Am Mineral 72:1056–1070
Pichavant M, Montel J-M, Richard LR (1992) Apatite solubility in peraluminous liquids: experimental data and an extension of the Harrison-Watson model. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:3855–3861
Raimbault L, Azencott C (1987) Géochimie des éléments majeurs et traces du granite à métaux rares de Beauvoir (sondage GPF, Echassières). Geol Fr 2–3:189–198
Ryerson FJ, Hess PC (1980) The role of P2O5 in silicate melts. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 44:611–624
Schaller T, Dingwell DB, Keppler H, Knoller W, Merwin L, Sebald A (1992) Fluorine in silicate glasses: a multinuclear nuclear magnetic resonance study. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:701–707
Simpson DR (1977) Aluminum phosphate variants of feldspar. Am Mineral 62:351–355
Sorapure R, Hamilton DL (1984) The solubility of water in melts of albite composition with varying additions of fluorine. In: Henderson CMB (ed) Progress in experimental petrology. Nat Environ Res Council Pub Ser D 25:28–30
Tomascak PB, Cerny P (1992) Mineralogy and geochemistry of phosphorus in the Aylmer Lake pegmatite field, NWT. (Abstr) Mineral Assoc Canada Abstr Vol 17:A110
Tuttle OF, Bowen NL (1958) Origin of granite in the light of experimental studies in the system NaAlSi3O8−KAlSi3O8−SiO2−H2O. Geol Soc Am Mem 74
Visser W, Koster van Groos AF (1978) Effects of P2O5 and TiO2 on liquid immiscibility in the system K2O−FeO−Al2O3−SiO2. Am J Sci 279:970–989
Watson EB (1976) Two liquid partition coefficients: experimental data and geologic implications. Contrib Mineral Petrol 56:119–134
Watson EB, Capobianco CJ (1981) Phosphorus and the rare earth elements in felsic magmas: an assessment of the role of apatite. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45:2349–2358
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
London, D., Morgan, G.B., Babb, H.A. et al. Behavior and effects of phosphorus in the system Na2O−K2O−Al2O3−SiO2−P2O5−H2O at 200 MPa(H2O). Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 113, 450–465 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00698315
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00698315