Summary
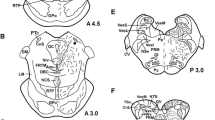
The location of the neuropeptides methionine-enkephalin (ME), neurotensin (NT), neuropeptide Y (NPY) and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) within the amygdaloid complex of healthy human individuals, schizophrenics and patients suffering from Huntington's chorea was studied qualitatively by means of immunohistochemistry. VIP-like immunoreactivity (IR) was present predominantly in a dense cluster of fibers and terminals in the central amygdaloid nucleus. ME-IR was observed in fibers, terminals and cell bodies in the same subnucleus, exhibiting a characteristical distribution pattern. NT-positive cell bodies were situated within the center of the central amygdaloid nucleus, fibers and terminals being encountered mainly at the periphery. NPY-IR was found to be evenly distributed throughout the amygdala. Distribution and staining intensity of ME, NPY and NT in the amygdala showed no qualitatively recognizable difference between the normal and schizophrenic specimens, whereas VIP-IR appeared to be slightly increased in the central amygdaloid nucleus of schizophrenics. In the choreic cases, the considerably shrunken amygdala exhibited only very low staining intensity of the four investigated neuropeptides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian TE, Allen JM, Bloom SR, Ghatei MA, Rossor MN, Roberts GW, Crow TJ, Tatemoto K, Polak JM (1983) Neuropeptide Y distribution in human brain. Nature 306:584–586
Allen YS, Adrian TE, Allen JM, Tatemoto K, Crow TJ, Bloom SR, Polak JM (1983) Neuropeptide Y distribution in the rat brain. Science 221:877–879
Aronin N, Cooper PE, Lorenz LJ, Bird ED, Sagar SM, Leeman SE, Martin JB (1983) Somatostatin is increased in the basal ganglia in Huntington's disease. Ann Neurol 13:519–526
Biggins JA, Perry EK, McDermott JR, Smith AI, Perry RH, Edwardson JA (1983) Post-mortem levels of thyrotropinreleasing hormone and neurotensin in the amygdala in Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia and depression. J Neurol Sci 58:117–122
Bogerts B (1984) Zur Neuropathologie der Schizophrenien. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr 52:428–437
Bogerts B, Meertz E, Schönfeld-Bausch R (1985) Basal ganglia and limbic system pathology in schizophrenia: a controlled post-mortem study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 42:784–791
Bouras C, Taban CH, Constantinidis J (1984) Mapping of enkephalins in human brain. An immunohistofluorescence study on brains of patients with senile and presenile dementia. Neuroscience 12:179–190
Buck SH, Burks TF, Brown MR, Yamamura HI (1981) Reduction in basal ganglia and substantia nigra substance P levels in Huntington's disease. Brain Res 209:464–469
Chronwall BM, DiMaggio DA, Massari VJ, Pickel VM, Ruggiero DA, O'Donohue TL (1985) The anatomy of neuropeptide Y-containing neurons in rat brain. Neuroscience 15:1159–1181
Cooper PE, Fernstrom MH, Rorstad OP, Leeman SE, Martin JB (1981) The regional distribution of somatostatin, substance P and neurotensin in human brain. Brain Res 218:219–232
Curran RC, Gregory J (1977) The unmasking of antigens in paraffin sections of tissue by trypsin. Experientia 33:1400–1401
Dawbarn D, Hunt SP, Emson PC (1984) Neuropeptide Y: regional distribution, chromatographic characterization and immunohistochemical demonstration in post-mortem human brain. Brain Res 296:168–173
Eiden LE, Hökfelt T, Brownstein MJ, Palkovits M (1985) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide afferents to the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the rat: An immunohistochemical and biochemical study. Neuroscience 15: 999–1013
Emson PC, Fahrenkrug J, Spokes EGS (1979) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP): distribution in normal human brain and in Huntington's disease. Brain Res 173:174–178
Emson PC, Arregui A, Clement-Jones V, Sandberg BEB, Rossor M (1980) Regional distribution of methionineenkephalin and substance P-like immunoreactivity in normal human brain and in Huntington's disease. Brain Res 199:147–160
Fahrenkrug J, Schaffalitzky de Muckadel OB (1978) Distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in the porcine central nervous system. J Neurochem 31:1445–1451
Ferrier IN, Crow TJ, Roberts GW, Johnstone EC, Owens DGC, Lee Y, Baracese-Hamilton A, McGregor G, O'Shaughnessy D, Polak J, Bloom SR (1983) Alterations in neuropeptides in limbic lobe in schizophrenia. Life Sci 33:475–483
Gale JS, Bird ED, Spokes EG, Iversen IL, Jessel T (1978) Human brain substance P: distribution in controls and Huntington's chorea. J Neurochem 30:633–634
Gray TS, Cassell MD, Kiss JZ (1984) Distribution of proopiomelanocortin-derived peptides and ekephalins in the rat central nucleus of amygdala. Brain Res 306:354–358
Gray TS, Cassell MD, Nilaver G, Zimmerman E, Williams TH (1984) The distribution and ultrastructure of VIP-immunoreactivity in the central nucleus of the rat amygdala. Neuroscience 11:399–408
Gros C, Pradelles P, Humbert J, Dray F, LeGal La Salle G, Ben-Ari Y (1978) Regional distribution of met-enkephalin within the amygdaloid complex and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Neurosci Lett 10:193–196
Haber S, Elde R (1981) Correlation between met-enkephalin and substance P immunoreactivity in the primate globus pallidus. Neuroscience 6:1291–1297
Haber S, Elde R (1982) The distribution of enkephalin immunoreactive fibers and terminals in the monkey central nervous system: A immunohistochemical study. Neuroscience 7:1049–1095
Haber S, Nauta WJH (1983) Ramifications of the globus pallidus in the rat as indicated by patterns of immunohistochemistry. Neuroscience 9:245–260
Hökfelt T, Elde R, Johansson O, Terenius L, Stein L (1977) The distribution of enkephalin-immunoreactive cell bodies in the rat central nervous system. Neurosci Lett 5:25–31
Hökfelt T, Johansson O, Ljungdahl A, Lundberg JM, Schultzberg M (1980) Peptidergic neurons. Nature 284: 515–521
Hong JS, Yang H-YT, Fratta W, Costa E (1977) Determination of methionine-enkephalin in discrete regions of rat brain. Brain Res 134:383–389
Kanazawa I, Birg E, O'Connell R, Powell D (1977) Evidence for a decrease in substance P content of substantia nigra in Huntington's chorea. Brain Res 120:387–392
Lindberg I, Smythe SJ, Dahl JL (1979) Regional distribution of enkephalin in bovine brain. Brain Res 168:200–204
Lorén I, Emson PC, Fahrenkrug J, Björklund A, Alumets J, Hakanson R, Sundler F (1979) Distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the rat and mouse brain. Neuroscience 4:1953–1976
Manberg PJ, Nemeroff CB, Iversen LL, Rossor MN, Kizer JS, Prange AJ (1982) Human brain distribution of neurotensin in normals, schizophrenics and Huntington's choreics. Ann NY Acad Sci 400:354–367
MacDonald A (1985) Morphology of peptide-containing neurons in the rat basolateral amygdaloid nucleus. Brain Res 338:186–191
Roberts GW, Woodhams PL, Bryant MG, Crow TJ, Bloom SR, Polak JM (1980) VIP in the rat brain: evidence for a major pathway linking the amygdala and hypothalamus via the stria terminalis. Histochemistry 65:103–109
Roberts GW, Woodhams PL, Crow TJ, Polak JM (1980) Loss of immunoreactive VIP in the bed nucleus following lesions of the stria terminalis. Brain Res 195:471–475
Roberts GW, Polak JM, Crow TJ (1981) The peptidergic circuitry of the amygdaloid complex. In: Ben-Ari (ed) The amygdaloid complex. Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, pp 185–195
Roberts GW, Woodhams PL, Polak JM, Crow TJ (1982) Distribution of neuropeptides in the limbic system of the rat: the amygdaloid complex. Neuroscience 7:99–131
Roberts GW, Ferrier IN, Lee Y, Crow TJ, Johnstone EC, Owens DG, Baracese-Hamilton AJ, McGregor G, O'Shaughnessey D, Polak JM, Bloom SR (1983) Peptides, the limbic lobe and schizophrenia. Brain Res 288:199–211
Sar M, Stumpf WE, Miller RJ, Chang K-J, Cuatrecasas P (1978) Immunohistochemical localization of enkephalin in rat brain and spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 182:17–38
Simantov R, Kuhar MJ, Pasternak GW, Snyder SH (1976) The regional distribution of a morphine-like factor in monkey brain. Brain Res 106:189–197
Simantov R, Kuhar MJ, Uhl GR, Snyder SH (1977) Opioid peptide enkephalin: immunohistochemical mapping in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:2167–2171
Sims KB, Hoffman DL, Said SI, Zimmerman EA (1980) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in mouse and rat brain: an immunohistochemical study. Brain Res 186:165–183
Spindel ER, Wurtman RJ, Bird ED (1980) Increased TRH content of the basal ganglia in Huntington's disease. N Engl J Med 303:1235–1236
Sternberger LA, Hardy PH, Cuculis JJ, Meyer HG (1970) The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry. Preparation and properties of soluble antigenantibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem 18:315–333
Tater D, Charpentier G, Besson G, Rosselin G, Bercovici J-P (1983) VIP removes DA-induced PRL-decrease in women with a prolactinoma. C R Acad SC Paris 297:331–334
Uhl GR, Kuhar MJ, Snyder SH (1977) Neurotension: immunohistochemical localization in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:4059–4063
Uhl GR, Kuhar MJ, Snyder SH (1978) Enkephalin-containing pathway: amygdaloid efferents in the stria terminalis. Brain Res 149:223–228
Uhl GR, Snyder SH (1976) Regional and subcellular distribution of brain neurotensin. Life Sci 19:1827–1832
Uhl GR, Snyder SH (1979) Neurotensin: a neuronal pathway projecting from amygdala through stria terminalis. Brain Res 161:522–526
Wamsley JK, Young WS, Kuhar MJ (1980) Immunohistochemical localization of enkephalin in rat forebrain. Brain Res 190:153–174
Wray S, Hoffman G (1983) Organization and interrelationship of neuropeptides in the central amygdaloid nucleus of the rat. Peptides (Fayetteville) 4:525–541
Zech M, Bogerts B (1985) Methionine-enkephalin and substance P in the basal ganglia of normals, Parkinson patients, Huntington patients, and schizophrenics: a qualitative immunohistochemical study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 68: 32–38
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zech, M., Roberts, G.W., Bogerts, B. et al. Neuropeptides in the amygdala of controls, schizophrenics and patients suffering from Huntington's chorea: An immunohistochemical study. Acta Neuropathol 71, 259–266 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688048
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688048