Summary
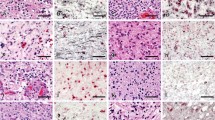
The expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and vimentin was investigated immuno-histochemically in 104 experimental gliomas induced by transplancental application of ethylnitrosourea (ENU) in CDF rats. Immunoreactivity for vimentin was prominent in many astrocytic tumor cells and especially in small glioma cells forming anaplastic medulloblastoma-like foci in many tumors. The majority of tumor cells in oligodendroglial tumors were vimentin negative, except for some of the large polymorphous oligodendrogliomas which contained intermingled vimentin positive glioma cells. GFAP immunoreactivity was detectable only in a low fraction of tumor astrocytes and in a few exceptional cases some oligodendroglial tumor cells stained positive. Immunohistochemistry with antibodies against neurofilaments and cytokeratins revealed no staining in tumor cells of ENU-induced gliomas, while all oligoden-drogliomatous tumors stained positive for HNK-1. Immunocytological and immunoblot investigations of the two rat glioma cell clones RG2 and F98, which are both derived from ENU-induced gliomas, showed a prominent expression of vimentin in monolayer cultures and in syngeneic intracerebral transplantation tumors. F98 additionally demonstrated a fraction of GFAP positive cells especially in confluent cultures and in intracerebral tumors. RG2, on the other hand, exhibited virtually no GFAP immunoreactivity in culture but showed individual GFAP positive tumor cells in intracerebral tumors. Our results revealed a more precise picture of the cellular differentiation in ENU-induced rat gliomas and in two widely used glioma cell lines. They underline the heterogeneity of experimental rat gliomas which may comprise cells at different stages of differentiation towards the oligodendroglial or astroglial phenotype.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altmannsberger M, Osborn M, Schauer A, Weber K (1981) Antibodies to different intermediate filament proteins —Cell type-specific markers on paraffin-embedded human tissues. Lab Invest 45:427–434
Backhovens H, Gheuens J, Slegers H (1987) Expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein in rat C6 glioma relates to vimentin and is independent of cell-cell contact. J Neurochem 49:348–354
Bignami A, Raju T, Dahl D (1982) Localization of vimentin, the nonspecific filament protein, in embryonal glia and in early differentiating neurons. Biol 91:286–295
Bilzer T, Reifenberger G, Wechsler W (1989) Induction of brain tumors by nitrosoureas: molecular biology, neuropathology and experimental studies. Neurotoxicol Teratol (in press)
Bissel MG, Eng LF, Herman MM, Bensch KG, Miles LEM (1975) Quantitative increase of neuroglia-specific GFA protein in rat C6 glioma cells in vitro. Nature 255:633–634
Bullon MM, Alvarez-Gago T, Fernandez-Ruiz B, Aguirre C (1984) Glial fibrillary acidic (GFA) protein in the rat spinal cord. An immunohistochemical study in semithin sections. Brain Res 309:79–83
Chiu FC, Norton WT, Fields KL (1981) The cytoskeleton of primary astrocytes in culture contains actin, glial fibrillary acidic protein, and the fibroblast-type protein, vimentin. J Neurochem 37:147–155
Choi BH, Kim RC (1985) Expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein by immature oligodendroglia and its implications. J Neuroimmunol 8:215–235
Conley FK (1979) The immunocytochemical localization of GFA protein in experimental murine tumors. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 45:9–16
Dahl D (1981) The vimentin-GFA transition in rat neuroglia cytoskeleton occurs at the time of myelination. J Neurosci Res 6:741–748
Dahl D, Rueger DC, Bignami A (1981) Vimentin, the 57000 molecular weight protein of fibroblast filaments, is the major cytoskeletal component in immature glia. Eur J Cell Biol 24:191–196
Daneels G, Moeremans M, deRaeymaeker M, deMey J (1986) Sequential immunostaining (gold/silver) and complete protein staining (AuroDye) on Western blots. J Immunol Methods 89:89–91
Duffy PE (1983) Astrocytes: normal, reactive, and neoplastic. Raven Press, New York, pp 87–99
Eng LF (1985) Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP): the major protein of glial intermediate filaments in differentiated astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol 8:203–214
Franke WW, Schmid E, Winter S, Osborn M, Weber K (1979) Widespread occurence of intermediate-sized filaments of the vimentin-type in cultured cells from diverse vertebrates. Exp Cell Res 123:25–46
Franke WW, Schiller BL, Moll R, Winter S, Schmidt E, Engelbrecht I, Denk H, Krepler R, Platzer B (1981) Diversity of cytokeratins: differentiation specific expression of cytokeratin polypeptides in epithelial cells and tissues. J Mol Biol 153:933–959
Gaboiani G, Kapanci Y, Barazzone P, Franke WW (1981) Immunochemical identification of intermediate-sized filaments in human neoplastic cells. Am J Pathol 104:206–216
Giordana Mt, Mauro A, Germano I, Giaccone G, Migheli A, Schiffer D (1984) Transplacental ENU tumors of the rat: immunohistochemical contribution to the recognition of cell types. J Neurooncol 2:270 [abstr]
Herpers MJHM, Budka H (1984) Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in oligodendroglial tumors: gliofibrillary oligodendroglioma and transitional oligoastrocytoma as subtypes of oligodendroglioma. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 64:265–272
Herpers MJHM, Ramaekers FCS, Aldeweireldt J, Moesker O, Slooff J (1986) Co-expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein-and vimentin-type intermediate filaments in human astrocytomas. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 70:333–339
Hsu SM, Raine, L, Fanger H (1981) The use of anti-avidin antibody and avidin-biotin-peroxidase-complex in immunoperoxidase techniques. Am J Clin Pathol 75:816–821
Kleihues P, Matsumoto S, Wechsler W, Zülch KJ (1968) Morphologie und Wachstum der mit Äthylnitrosoharnstoff transplazentar erzeugten Tumoren des Nervensystems. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol 52:372–379
Kleihues P, Kiessling M, Janzer RC (1987) Morphological markers in neuro-oncology. Curr Top Pathol 77:307–338
Ko L, Koestner A, Wechsler W (1980) Morphological characterization of nitrosourea-induced glioma cell lines and clones. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 51:23–31
Ko L, Koestner A, Wechsler W (1980) Characterization of cell cycle and biological parameters of transplantable glioma cell lines and clones. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 51:107–111
Kruse J, Mailhammer R, Wernecke H, Sommer I, Schachner M (1984) Neural cell adhesion molecules and myelin associated glycoprotein share a common carbohydrate moiety recognized by monoclonal antibodies L2 and HNK-1. Nature 311:153–155
Kruse J, Keilhauer G, Timpl R, Schachner M (1985) The Jl glycoprotein: a novel nervous system cell adhesion molecule of the L2/HNK-1 family. Nature 316:146–148
Lantos PL (1972) The fine structure of periventricular pleomorphic gliomas induced transplacentally byN-ethyl-N-nitrosourea in BD-IX rats. J Neurol Sci 17:443–460
Lantos PL (1974) An electron microscope study of reacting astrocytes in gliomas induced byN-ethyl-N-nitrosourea in rats. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 30:175–181
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembley of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Liwniez BH, Archer G (1982) RG2, a clone of nitrosourea-induced rat glioma, can be used for studing astrocytic differentation in vitro. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 41:368 [abstr]
Ludwin SK, Kosek JC, Eng LF (1976) The topographical distribution of S-100 and GFA proteins in the adult rat brain. An immunohistochemical study using horseradish peroxidase-labelled antibodies. J Comp Neurol 165:172–208
Mandybur TI, Alvira MM (1982) Ultrastructural findings in so-called ependymal rat tumors induced by transplacental administration of ethylnitrosourea (ENU). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 57:51–58
Maruno M, Yoshimine T, Ushio Y, Hayakawa T, Jamshidi J, Bitoh S, Mogami H (1985) Immunohistochemical study of ethylnitrosourea-induced rat gliomas with vimentin and astroprotein (GFAP). Brain Nerve Tokyo 37:1173–1179 (English abstract)
Mauro A, Giordana MT, Migheli A, Schiffer D (1983) Glial fibrillary acidic protein in rat brain tumors transplacentally induced by ethylnitrosourea (ENU). J Neurol Sci 61:349–355
Meneses ACO, Kepes JJ, Sternberger NA (1982) Astrocytic differentation of neoplastic oligodendrocytes. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 41:368 [abstr]
Mennel HD, Ivancovic S (1975) Experimentelle Erzeugung von Tumoren des Nervensystems. Handbuch Allgemeine Pathologie, Bd 6, Geschwülste III. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 33–122
Mennel HD, Simon H (1985) Morphology of early stages of ENU-induced brain tumors in rats. Exp Pathol 28:207–214
Miettinen M, Lehto VP, Virtanen I (1984) Antibodies to intermediate filament proteins in the diagnosis and classification of human tumors. Ultrastruct Pathol 7:83–107
Ogawa H, Sato Y, Takeshita I, Tateishi J, Kitamura K (1985) Transient expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein in developing oligodendrocytes in vitro. Dev Brain Res 18:133–141
Osborn M, Weber K (1983) Biology of disease. Tumor diagnosis by intermediate filament typing: a novel tool for surgical pathology. Lab Invest 48:372–394
Osborn M, Ludwig-Festl M, Weber K, Bignami A, Dahl D, Bayreuther K (1981) Expression of glial and vimentin type intermediate filaments in cultures derived from human glial material. Differentation 19:161–167
Paetau A, Virtanen I, Stenman S, Kurki P, Linder E, Vahrei A, Westermark B, Dahl D, Haltia M (1979) Glial fibrillary acidic protein and intermediate filaments in human glioma cells. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 47:71–74
Perentes E, Rubinstein LJ (1987) Recent applications of immunoperoxidase histochemistry in human neuro-oncology. An update. Arch Pathol Lab Med 111:796–812
Pixley SKR, de Vellis J (1984) Transition between immature radial glia and mature astrocytes studied with a monoclonal antibody to vimentin. Dev Brain Res 15:201–209
Quinlan RA, Franke WW (1983) Molecular interactions in intermediate-sized filaments by chemical cross-linking —Heteropolymers of vimentin and glial filament protein in cultured human glioma cells. Eur J Biochem 132:477–484
Raju TR, Bignami A, Dahl D (1980) Glial fibrillary acidic protein in monolayer cultures of C-6 glioma cells: effect of aging and dibutyryl cyclic AMP. Brain Res 200:225–230
Ramaekers FCS, Puts JJG, Kant A, Moesker O, Jap PHK, Vooijs GP (1982) Use of antibodies to intermediate filaments in the characterization of human tumors. Cold Spring Harbor Symb Quant Biol 46:331–339
Reifenberger G, Wechsler W (1989) Immunhistochemie experimenteller Gliome der Ratte. Zentralbl Allg Pathol Pathol Anat [abstr] 135:96
Reifenberger G, Mai JK, Krajewski S, Wechsler W (1987) Distribution of anti-Leu-7, anti-Leu-11a and anti-Leu-M1 immunoreactivity in the brain of the adult rat. Cell Tissue Res 248:305–313
Reifenberger G, Szymas J, Wechsler W (1987) Differential expression of glial- and neuronal-associated antigens in human tumors of the central and peripheral nervous system. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 74:105–123
Saggu H, Pilkington GJ (1986) Immunocytochemical characterization of the A15A5 transplantable brain tumor model in vivo. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 12:291–303
Schiffer D, Giordana MT, Migheli A, Giaccone G, Pezzotta S, Mauro A (1986) Glial fibrillary acidic protein and vimentin in the experimantal glial reaction of the rat brain. Brain Res 374:110–118
Schiffer D, Giordana MT, Mauro A, Migheli A, Germano I, Giaccone G (1986) Immunohistochemical demonstration of vimentin in human cerebral tumors. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 70:209–219
Schnitzer J, Franke WW, Schachner M (1981) Immunocytochemical demonstration of vimentin in astrocytes and ependymal cells of developing and adult mouse nervous system. J Cell Biol 90:435–447
Schuller-Petrovic S, Gebhardt W, Lassmann H, Rumpold H, Kraft D (1983) A shared antigenic determinant between natural killer cells and nervous tissue. Nature 306:179–181
Sharp G, Osborn M, Weber K (1982) Occurrence of two different intermediate filaments proteins in the same filament in situ within a human glioma cell line. Exp Cell Res 141:385–395
Sternberger LA (1986) Immunocytochemistry, 3rd eds. J. Wiley and Sons, New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto, pp 103–114
Townbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354
Wang E, Cairncross G, Liem RKH (1984) Identification of glial filament protein and vimentin in the same intermediate filament system in human glioma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:2102–2106
Wechsler W (1987) Experimental malignant gliomas: pathology and transplantation biology of ENU-induced rat tumors. In: Bock WJ, Wechsler W, Beck L, Grundmann E (eds) Experimental neurooncology, brain tumor and pain therapy, Cancer campaign 10. Fischer, Stuttgart New York, pp 145–168
Wechsler W, Kleihues P, Matsumoto S, Zülch KJ, Ivankovic S, Preussmann R, Druckrey H (1969) Pathology of experimental neurogenic tumors chemically induced during prenatal and postnatal life. Ann NY Acad Sci 159:360–408
Wechsler W, Teske U, Reifenberger G, Deckert M, Seitz RJ, Mies G, Paschen W, Hossmann KA (1987) Neuropathology and regional imaging of microcirculation, tissue pH, metabolites and necrosis in cerebral RG2 and F98 anaplastic rat glioma transplantation tumors. In: Chatel M, Darcel F, Pecker J (eds) Brain oncology. Martinus Nijhoff, Dordrecht, pp 187–199
Yen SH, Fields KL (1981) Antibodies to neurofilament, glial filament, and fibroblast intermediate filaments protein bind to different cell types of the nervous system. J Cell Biol 88:115–126
Yoshimine T, Ushio Y, Hayakawa T, Arita N, Horbata K, Mori T (1980) Immunoperoxidase method using antiserum against astroprotein for the diagnosis of experimental brain tumors. Brain Nerve (Tokyo) 32:107–113 (English abstract)
Yoshino T, Motoi M, Ogawa K (1985) Immunohistochemical studies on cellular character of microtumors induced by ethylnitrosourea in the rat brain utilizing anti-Leu-7 and anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein antibodies. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 66:167–169
Yung WKA, Luna M, Borit A (1985) Vimentin and glial fibrillary acidic protein in human brain tumors. J Neurooncol 3:35–38
Zülch KJ, Mennel HD (1971) Die Morphologie der durch alkylierende Substanzen erzeugten Tumoren des Nervensystems. Zentralbl Neurochir 32:225–243
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, SFB 200
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reifenberger, G., Bilzer, T., Seitz, R.J. et al. Expression of vimentin and glial fibrillary acidic protein in ethylnitrosourea-induced rat gliomas and glioma cell lines. Acta Neuropathol 78, 270–282 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687757
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687757