Abstract
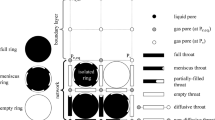
Today's practice of interpreting Hg capillary pressure curves — a widespread method in porosimetry — is generally unsatisfactory. This has already been demonstrated by Fatt. First, the saturation branch of such a curve is interpreted using the concept of a pore space model in which essential features of a network structure are disregarded. Second, the data provided by the desaturation branch are not used. Distributions of radii of capillaries within porous materials derived by this technique are usually incorrect in that the frequencies of occurrence of the greater radii turn out too small, those of the smaller radii too large.
We present a more reliable approach which constrains radii frequency ranges for the Hg saturated pore space and for both the part of the pore space that desaturates and the part that traps mercury when Hg pressure is released. The pore space may be of an arbitrary geometrical structure, the radii distribution may be continuous. Also, the Hg desaturation may enable one to distinguish experimentally between structural and contact angle hysteresis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
actual cross-section of a capillary
- a″:
-
hydrostatic equivalent circular crosssection of a capillary
- c :
-
circumference ofa
- des:
-
desaturation process, index
- i :
-
index denoting radii, radii numbers, and radii frequencies
- j :
-
number of saturated capillaries
- k :
-
upper boundary fori
- k″, k 0 ″ :
-
(mean) hydrostatic shape factor of the capillary cross-section
- T, δl :
-
mean capillary lengths
- n i :
-
number of radii of sizer i
- p c s :
-
capillary pressure of capillaries with radiusr s
- (-) δp c s :
-
difference in capillary pressure between capillaries with radiusr s ,r s-1
- \(p_j^{n_i } \) :
-
(Hg/vacuum) path probability
- r i :
-
capillary radius
- r″:
-
radius ofa″
- s :
-
index denoting the state of the capillary pressure experiment
- sat:
-
satuation process, index
- BCT:
-
bundle of capillary tubes model
- CTM:
-
chain-type model
- D:
-
dimensional
- Hg:
-
mercury
- M :
-
number of meshes within a network
- M s :
-
measured value
- N :
-
number of capillaries (radii) in a network
- N b :
-
number of border capillaries of a network in direct contact with the external Hg reservoir
- N i :
-
number of capillaries inside a network without direct contact with the external Hg reservoir
- NS:
-
network structure
- P:
-
point of intersection (indicated by ‘sat’ or ‘des’)
- ℝk :
-
k-D space of representation
- RD:
-
radii distribution
- RP:
-
radii placement
- S :
-
number of nodes (sites) within a network
- SHN:
-
single hexagonal network model
- SMN:
-
square mesh network model
- V,\(\bar V\) :
-
measured (expected) network volume during saturation or desaturation, respectively (indicated by ‘Hg’, ‘sat’, ‘2’, or ‘des’)
- V por :
-
pore volume of a network or a porous material
- Β :
-
network constant
- ε :
-
network constant (mesh density)
- η :
-
network constant (node density)
- σ :
-
surface tension of mercury
- θ:
-
contact angle of mercury
- σ,\(\bar \Sigma \) :
-
(expected) saturation/desaturation belonging toV (\(\bar V\))
- 2:
-
index denoting vacuum
References
Van Brakel, J., Modry, S.; and Svata, M., 1981, Mercury porosimetry: State of the art,Powder Technol. 29, 1–12.
Drake, L. C. and Ritter, H. L., 1945, Pore-size distribution in porous materials; Macropore-size distributions in some typical porous substances,Ind. Eng. Chem., Anal. Ed. 17, 782–791.
Fatt, I., 1956, The network model of porous media: I. Capillary pressure characteristics,Trans. AIME 207, 144–159.
Good, R. J., Mikhail, R. Sh., 1981, The contact angle in mercury intrusion porosimetry,Powder Technol. 29, 53–62.
Jonas, M., 1988, überlegungen graphentheoretisch-kombinatorischer Natur zur Berechnung mittlerer wahrscheinlicher Kapillardruckkurven von Netzwerkmodellen und die Lösung des radiellen Inversionsproblems, Clausthaler Geowissenschaftliche Dissertationen (ISSN 0172-3804),34.
Kadlec, O., 1984, The general equation of the high pressure mercury porosimetry,Ads. Sci. Technol. 1, 177–182.
Kloubek, J., 1981, Hysteresis in porosimetry,Powder Technol. 29, 63–73.
Pape, H., Riepe, L., and Schopper, J. R., 1981, A solution attempt to the ‘coastline of Britain problem’,Proc. 3rd Eur. Symp. Stereol., inStereol. Yugosl. 3/Suppl. 1, 331–336.
Pape, H., Riepe, L. and Schopper, J. R., 1983, Conversion between specific surface measurements of different resolution power with the aid of pigeon-hole model theory,Proc. RILEM/CNR Int. Symp., Paper 20, also in Haynes, J. M. and Rossi-Doria, P., eds.Principles and Applications of Pore Structural Characterization, 1985, Arrowsmith, London.
Pohl, A., 1981, Geohydrodynamische Erkundung — 5: Kapillareigenschaften, die Bestimmung von Kapillardruck-bzw. Saugspannungskurven und deren Auswertung,Zeitschrift für angewandte Geol.,27, 273–284.
Rybarczyk, G., 1982, Untersuchungen zur effektiven Porenradienverteilung in Sedimentgesteinen mittels Kapillardruckkurven, Diplomarbeit (Thesis), Technische UniversitÄt Clausthal, Inst. f. Geophysik.
Schopper, J. R., 1966, A theoretical investigation on the formation factor/permeability/porosity relationship using a network model,Geophys. Prospect. 14, 301–341.
Schopper, J. R., 1972, Theoretische Untersuchung elektrischer, hydraulischer und anderer physikalischer Eigenschaften poröser Gesteine mit Hilfe statistischer Netzwerkmodelle, Habilitationsschrift (Thesis submitted for the certificate of habilitation), Technische UniversitÄt Clausthal.
Swanson, B. F. and Yuan, H. H., 1989, Resolving pore-space characteristics by rate-controlled porosimetry,SPE Form. Eval. 4, 17–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jonas, M., Schopper, J.R. The radii inversion problem associated with the Hg capillary pressure experiment. Transp Porous Med 14, 33–72 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00617027
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00617027