Summary
In antidiuretic rats plasma urea concentration (P u )was elevated up to 35 mM by intravenous urea loading. In renal cortical tissue (T) water content and unlabeled (u) and 14-C-urea (u *) were determined.
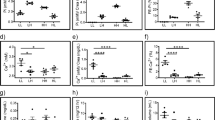
Water content of total renal cortex and of superficial and juxtamedullary layers were not significantly different and were not changed by the elevation ofP u .
In the control group (P u <10 mM), bothT/P u (3.06±0.71;n=29) and plasma specific activity were significantly higher than values forT/P u * (2.20±0.57;n=12) and tissue specific activity, respectively.T/P u andT/P u * were decreased significantly to the same level (1.68±0.35;n=20 and 1.51±0.21;n=7, respectively) atP u >20 mM and plasma and tissue specific activity became equal.
Deproteination of tissue homogenates did not depress 14-C-activity.
JuxtamedullaryT/P u was significantly higher than superficialT/P u .The difference was independent ofP u .
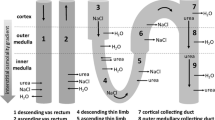
The data suggest, that renal cortical tissue urea concentration is determined (i) by distal tubular fluid urea concentration, which is inversely correlated withP u and (ii) by a constant amount of urea in an extraluminal compartment not readily exchanging.
The mechanism by which urea concentration in this extraluminal compartment is maintained independent ofP u might be urea neogenesis or urea binding to cellular structures or proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armsen, T., Schad, H., Reinhardt, H. W.: Die Konzentrierung des Harnstoffs in der Niere. II. Mikropunktionsuntersuchungen an der Ratte. Pflügers Arch.313, 222 (1969)
Beale, R. N., Croft, D.: A sensitive method for the colorimetric determination of urea. J. clin. Path.14, 418 (1961)
Carlisky, N. J., Brodsky, W. A., Huang, K. C.: Biosynthesis of urea by the kidney in relation to the mechanism of urea excretion. Fed. Proc.21, 427 (1962)
O'Dell, R. M., Schmidt-Nielsen, B.: Retention of urea by frog and mammalian kidney slices in vitro. J. cell. comp. Physiol.57, 211 (1961)
Kleinman, L. J., Radford, E. P.: Urea synthesis by rat kidney. Physiologist7, 179 (1964)
Kriz, W.: Der architektonische und funktionelle Aufbau der Rattenniere. Z. Zellforsch.82, 495 (1967)
Rabinowitz, L.: In: Urea and the kidney, p. 340. Editor: B. Schmidt-Nielsen. Excerpta Medica ICS 195 (1970)
Reinhardt, H. W., Schad, H., Armsen, T.: Zur Frage der Harnstoffkonzentrationen in den Kompartimenten der Nierenrinde (Ratte). Tissue slice-study of urea concentration in structures of the renal cortex (rat). Pflügers Arch.307, R74 (1969)
Roch-Ramel, F., Chométy, F., Peters, G.: Urea concentrations in tubular fluid and in renal tissue of nondiuretic rats. Amer. J. Physiol.215, 429 (1968)
Roch-Ramel, F., Diézi, J., Chométy, F., Michoud, P., Peters, G.: Disposal of large urea overloads by the rat kidney: a micropuncture study. Amer. J. Physiol.218, 1524 (1970)
Roch-Ramel, F., Diézi, J., Chométy, F., Michoud, P., Peters, G.: Urea concentrations in tubular fluid and in renal tissue of rats overloaded with urea or with saline solutions. In: Urea and the kidney, p. 333. Editor: B. Schmidt-Nielsen. Excerpta Medica ICS 195 (1970)
Roch-Ramel, F., Peters, G.: Intrarenal urea and electrolyte concentrations as influenced by water diuresis and by hydrochlorothiazide. Europ. J. Pharmacol.1, 124 (1967)
Saikia, T. C.: Composition of the renal cortex and medulla of rats during water diuresis and antidiuresis. Quart. J. exp. Physiol.50, 146 (1965)
Schmidt-Nielsen, B., O'Dell, R.: Structure and concentrating mechanism in the mammalian kidney. Amer. J. Physiol.200, 1119 (1961)
Truniger, B., Schmidt-Nielsen, B.: Intrarenal distribution of urea and related compounds: effects of nitrogen intake. Amer. J. Physiol.207, 971 (1964)
Truniger, B., Schmidt-Nielsen, B.: Intrarenal distribution and transtubular movement of urea and related compounds. In: Urea and the kidney, p. 314. Editor: B. Schmidt-Nielsen. Excerpta Medica ICS 195 (1970)
Ullrich, K. J., Rumrich, G., Baldamus, C. A.: Mode of urea transport across the mammalian nephron. In: Urea and the kidney, p. 175. Editor: B. Schmidt-Nielsen. Excerpta Medica ICS 195 (1970)
Valtin, H.: Sequestration of urea and non-urea solutes in renal tissues of rats with hereditary hypothalamic diabetes insipidus: effect of vasopressin and dehydration on the counter current mechanism. J. clin. Invest.45, 337 (1966)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schad, H., Reinhardt, H.W. & Armsen, T. Analysis of cortical urea sequestration in rat renal tissue slices. Pflugers Arch. 346, 31–38 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00592648
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00592648