Abstract
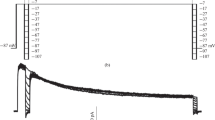
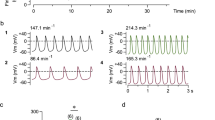
The fully activated I–V relation (ĪK) for the potassium current (IK) in the Ranvier node was obtained in two ways: (a) by measuring IK values on stepping to various potentials, at the end of a depolarizing clamp pulse which fully activated IK; (b) by dividing the time dependent change in IK seen on depolarizing to a certain potential, by the time dependent change in IK seen on repolarizing from that potential to the holding potential. In solutions of high external [K+], the true ĪK curve (method a) and the current ratio ĪK curve (method b) were similar. At low external [K+], the current ratio ĪK curve was greatly distorted from the true ĪK curve. This discrepancy is attributed to K+ accumulation and depletion just outside the nodal membrane.
Using the true ĪK curves, we calculated the distortion of the current ratio ĪK curves expected on the basis of extra-cellular [K+] changes. The magnitude of diffusion barrier between the nodal membrane and the bulk solution which was necessary to give the observed distortion, is attributable to the position of the nodal membrane between the paranodal myelin.
These data support the idea that extra-cellular [K+] changes are an important determinant of the magnitude and time course of IK.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attwell, D., Cohen, I., Eisner, D. A., Ohba, M., Ojeda, C.: The steady state TTX-sensitive (“window”) sodium current in cardiac Purkinje fibres. Pflügers Arch.379, 137–142 (1979)
Baumgarten, C. M., Isenberg, G.: Depletion and accumulation of potassium in the extracellular clefts of cardiac Purkinje fibres during voltage clamp hyperpolarization and depolarization. Pflügers Arch.368, 19–31 (1977)
Baumgarten, C. M., Isenberg, G., McDonald, T. F., ten Eick, R. E.: Depletion and accumulation of potassium in the extracellular clefts of cardiac Purkinje fibres during voltage clamp hyperpolarization and depolarization.Experiments in sodium free bathing media. J. Gen. Physiol.70, 149–169 (1977)
Bromm, B., Esslinger, H.: Ionic permeability at resting potential of Ranvier node. Proceedings of the International Union of Physiological Sciences. 26th Int. Congress.II, 149 (1974)
Cohen, I., Daut, J., Noble, D.: An analysis of the actions of low concentrations of ouabain on membrane currents in Purkinje fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)260, 75–93 (1976)
Drouin, H., Neumcke, B.: Specific and unspecific charges at the sodium channel of nerve membrane. Pflügers Arch.351, 207–229 (1974)
Dubois, J. M., Bergman, C.: Potassium accumulation in the perinodal space of frog myelinated axons. Pflügers Arch.358, 111–124 (1975)
Dubois, J. M., Bergman, C.: The steady state potassium conductance of the Ranvier node at various external K concentrations. Pflügers Arch.370, 185–194 (1977)
Frankenhaeuser, B.: A quantitative description of potassium currents in myelinated fibres ofXenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.)169, 424–430 (1963)
Frankenhaeuser B., Huxley, A. F.: The action potential in the myelinated nerve fibre ofXenopus laevis as computed on the basis of voltage clamp data. J. Physiol. (Lond.)171, 302–315 (1964)
Hille, B.: Voltage clamp studies on myelinated nerve fibres. In: Biophysics and physiology of excitable membranes, Chapter 12 (W. J. Adelman ed.), pp. 242–243. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold 1971
Hille, B.: Potassium currents in myelinated nerve. Selective permeability to small cations. J. Gen. Physiol.61, 669–686 (1973)
Kline, R., Morad, M.: Potassium efflux and accumulation in heart. Evidence from K+ electrode studies. Biophys. J.16, 367–372 (1976)
Maughan, D. N.: Some effects of prolonged depolarization on membrane currents in bullfrog atrial muscle. J. Membr. Biol.11, 331–352 (1973)
McDonald, T. F., Trautwein, W.: The potassium current underlying delayed rectification in cat ventricular muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)274, 217–246 (1978)
Noble, D., Tsien, R. W.: The kinetics and rectifier properties of the slow potassium current in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J. Physiol (Lond.)195, 185–214 (1968)
Noble, D., Tsien, R. W.: Outward membrane currents activated in the plateau range of potentials in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)200, 205–231 (1969)
Noble, S. J.: Potassium accumulation and depletion in frog atrial muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)258, 579–613 (1976)
Nonner, W.: A new voltage clamp method for Ranvier nodes. Pflügers Arch.309, 176–192 (1969)
Stämpfli, R.: Is the resting potential of Ranvier nodes a potassium potential? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.81, 265–284 (1959)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attwell, D., Dubois, JM. & Ojeda, C. Fully activated potassium current-voltage relationship in the Ranvier node. Pflugers Arch. 384, 49–56 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00589513
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00589513