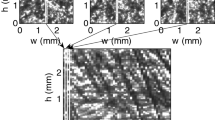
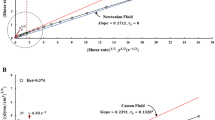
Summary
Employing both microscopic and photometric methods the rheology of pathological red cell aggregation was studied in model experiments. Suspensions of washed human red blood cells in dextran solutions containing rising concentrations of dextrans (M.W. 40000, 70000, 110000, 250000, 500000) were used. At low concentrations (<500 mg-%) of high molecular weight dextrans (>70000)red cell suspensions formed aggregates similar to the ones found in normal human blood. At higher concentrations, the aggregates were similar to those observed in pathological human blood. The aggregates were studied under the condition of stasis, slow flow and at shear rate of their hydrodynamic dispersion. Besides, the flow behavior of the dispersed cells at high shear rates was studied. We found:
-
1.
In all samples the rate of spontaneous aggregate re-formation in stasis (following hydrodynamic desaggregation) rose with rising dextran concentration up to 5.0 g-%.
-
2.
The shear resistance of the aggregates, as measured by the shear stress necessary to keep them dispersed, rose up to concentrations of 2.5 g-%, but fell at higher concentrations.
-
3.
Only with dextran of a molecular weight above 110000 coarse agglomerates could be produced at high concentrations. Loose elastic meshes were rapidly produced at high concentrations of Dx 70.
-
4.
When subjected to steady state low shear (7 sec−1) only the agglomerates, but not the meshes rapidly grew in size.
Most of the aggregation kinetics recorded by photometry and microscopy evaded detection by viscometry.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benis, A. M., Lacoste, J.: Study of erythrocyte aggregation by blood viscometry at low shear rates using a balance method. Circulat. Res.22, 29–41 (1968)
Berman, H. J., Fuhro, R. I.: Quantitative red blood cell aggregometry of human and hamster bloods. Proc. VIIth Conference on Microcirculation, Aberdeen, 1972, pp. 117–125. Basel: Karger 1973
Bingham, E. C., Roepke, R. R.: The rheology of blood III. J. gen. Physiol.28, 79–93 (1944)
Brinkman, R., Zijlstra, W. G., Jansonius, N. J.: Quantitative evaluation of the rate of rouleaux formation of erythrocytes by measuring light reflection (“Syllectometry”). Proc. Kon. Ned. Akad. Wet., Ser. C66, 236–248 (1963)
Brooks, D. E., Seaman, G. V. F.: Some effects of dextran on human erythrocyte interaction. Proc. VIIth Conference on Microcirculation, Aberdeen, 1972, pp. 272–281. Basel: Karger 1973
Chien, S.: The present state of blood rheology. In: Hemodilution, theoretical basis and clinical application. K. Messmer and H. Schmid-Schönbein, eds., pp. 1–40. Basel: Karger 1972
Chien, S., Luse, S. A., Jan, K.-M., Usami, S., Miller, L. H., Fremount, H.: Effects of macromolecules on the rheology and ultrastructure of red cell suspension. In: Proc. 6th Europ. Conf. on Microcirculation, Ditzel and Lewis, eds., pp. 29–84. Basel: Karger 1971
Chien, S., Usami, S., Dellenback, R. J., Gregersen, M. I.: Blood viscosity: Influence of erythrocyte deformation. Science157, 827–829 (1967)
Cokelet, G. R., Merrill, E. W., Gilliland, E. R., Shin, H., Britten, A., Wells, R. E., Jr.: The rheology of human blood, measurements near and at zero shear rate. Trans. Soc. Rheol.7, 303–317 (1963)
Dintenfass, L.: Molecular and rheological considerations of the red cell membrane in view of the internal fluid of the red cell. Acta haemat. (Basel)32, 299–313 (1964)
Dintenfass, L.: Blood microrheology-viscosity factors in blood flow, ischemia and thrombosis. London: Butterworths 1971
Frimberger, F.: Die Druckabhängigkeit der Viskositätswerte des Blutes und ihre Ursachen. Folia haemat. (Lpz.)60, 237–242 (1938)
Gelin, L. E.: Intravascular aggregation and capillary flow. Acta chir. scand.113, 463–465 (1957)
Gregersen, M. I., Usami, S., Peric, B., Chang, C., Sinclair, D., Chien, S. Blood viscosity at low shear rates. Effects of low and high molecular dextrans. Biorheology1, 247–253 (1963)
Reference deleted
Jan, K., Chien, S.: Role of the electrostatic repulsive force in red cell interactions. Proc. VIIthe Conference on Microcirculation, Aberdeen, 1972, pp. 281–289, Basel: Karger 1973
Klose, H. J., Volger, E., Brechtelsbauer, H., Heinich, L., Schmid-Schönbein, H.: Microrheology and light transmission of blood. I. The photometric effects of red cell aggregation and red cell orientation. Pflügers Arch.333, 126–139 (1972)
Knisely, M. H.: Intravascular erythrocyte aggregation (blood sludge). In: Handbook of physiology, Sect. 2, Vol. III W. F. Hamilton and P. Dow, eds., pp. 2249–2292. American Physiological Society, Washington 1965
Knisely, M. H., Block, E. H., Eliot, T. S., Warner, L.: Sludged blood. Science106, 431–440 (1947)
Meiselman, H. J.: In vivo viscometry: Effect of hemodilution. In: Hemodilution theoretical basis and clinical application. K. Messmer and H. Schmid-Schönbein, eds., pp. 143–156. Basel: Karger 1972
Meiselman, H. J., Merrill, E. W., Gilliland, E. R., Pelletier, G. A., Salzman, E. W.: Influence of plasma osmolarity on the rheology of human blood. J. app. Physiol.22, 772–781 (1967)
Meiselman, H. J., Merrill, E. W., Salzman, E. M., Gilliland, E. R., Pelletier, G. A.: Effect of dextran on the rheology of human blood: low shear viscometry. J. appl. Physiol.22, 480–486 (1967)
Merrill, E. W.: Rheology of blood. Physiol. Rev.49, 863–888 (1969)
Merrill, E. W., Gilliland, E. R., Cokelet, G., Shin, H., Britten, A., Wells, R. E.: Rheology of human blood, near and at zero flow. Effects of temperature and hematocrit level. Biophys. J.3, 199–233 (1963)
Ponder, E.: Hemolysis and related phenomena. New York: Grune and Stratton 1948
Schmid-Schönbein, H.: Hemodynamic significance of red cell fluidity. Proc. 6th Europ. Conf. Microcirculation. Ditzel and Lewis, eds., pp. 2–7. Basel: Karger 1971
Schmid-Schönbein, H.: A simple device allowing blood viscometry at low rates of shear with the Wells-Brookfield viscometer. Res. exp. Med.161, 49–57 (1973)
Schmid-Schönbein, H.: Red cell aggregation in flow. Klin. Wschr. (in press) (1974)
Schmid-Schönbein, H., Gaehtgens, P., Hirsch, H.: On the shear dependence of red cell aggregation in vitro. J. clin. Invest.47, 1447–1454 (1968)
Schmid-Schönbein, H., Gallasch, G., Volger, E., Klose, H. J.: Microrheology and protein chemistry of pathological red cell aggregation (blood sludge) studied in vitro. Biorheology10, 213–227 (1973)
Schmid-Schönbein, H., Goldstone, J., Wells, R. E.: Red cell deformation and red cell aggregation: their influence on blood rheology in health and disease. In: Theoretical and clinical hemorheology. Proc. 2nd. Intern. Conf. Hemorheology, Heidelberg 1969
Schmid-Schönbein, H., v. Gosen, J., Heinich, L., Klose, H. J., Volger, E.: A counter-rotating “rheoscope chamber” for the study of the microrheology of blood cell aggregation by microscopic observation and microphotometry. Microvasc. Res.6, 366–376 (1973)
Schmid-Schönbein, H., Kline, K. A., Heinich, L., Volger, E., Fischer, T.: Microrheology and light transmission of blood. III. The velocity of red cell aggregate formation. Pflügers Arch.354, 299–317 (1975)
Schmid-Schönbein, H., Klose, H. J., Volger, E.: Effect of colloidal plasma substitutes on microrheology of human blood. In: Hemodilution theoretical basis and clinical application. K. Messmer and H. Schmid-Schönbein, eds., pp. 66–78. Basel: Karger 1972
Schmid-Schönbein, H., Volger, E., Klose, H. J.: Microrheology and light transmission of blood. II. The photometric quantification of red cell aggregates formation and dispersion of flow. Pflügers Arch.333, 140–155 (1972)
Schmid-Schönbein, H., Wells, R. E.: Fluid drop-like transition of erythrocytes under shear. Science165, 288–291 (1969)
Schmid-Schönbein, H., Wells, R. E.: Rheological properties of human erythrocytes and their influence upon the “anomalous” viscosity of blood. Ergebn. Physiol.63, 146–219 (1971)
Thorsen, G., Hint, H.: Aggregation, sedimentation and intravascular sludging of erythrocytes. Acta chir. scand., Suppl.154, 1–50 (1950)
Usami, S., Chien, S.: Optical reflectometry of red blood cell aggregation under shear flow. Proc. VIIth Conference on Microcirculation, Aberdeen 1972, pp. 91–98. Basel: Karger 1973
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Grants from Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Schm 84/1-5)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volger, E., Schmid-Schönbein, H., Gosen, J.v. et al. Microrheology and light transmission of blood. Pflugers Arch. 354, 319–337 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587850
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587850