Summary
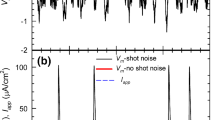
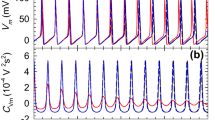
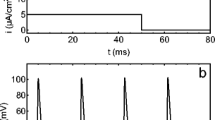
The power spectra of the spontaneous voltage fluctuations (membrane noise) of the node of Ranvier were measured in the frequency range from 0.3 to 1500 cycles per second at different levels of the membrane potential (−90 to +30 mV, inside negative). Up from about −30 mV the power spectrum shows a\(\frac{1}{{1 + \left( {2\pi f\tau } \right)^2 }}\) component, which increases with depolarization. This shot like noise component is independent of and occurs in addition to the 1/f component. The source of this shot like noise component is probably given by fluctuations in the conductance for potassium ions. With the use of a minimum parameter model which consists of channels that switch randomly in time from the closed to the open state and vice versa, independent of each other, the number of active channels per μm2 appears to be of the order of 1000. The elementary unit of the potassium system conductance is then of the order of 10−11 S per channel1 and the mean frequency of switches per second per channels is about 160.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blair, E. A., Erlanger, J.: Responses of axons to brief shocks. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.)29, 926–927 (1932).
Cole, K. S.: Membranes, Ions and Impulses. Berkeley-Los Angelos: University of California Press 1968.
DeFelice, L. J., Adair, J. R.: Electrical noise from single cells. Biophys. Soc. Abstr. (1973) (in press).
DeFelice, L. J., Michalides, J. P. L. M.: Electrical noise from synthetic membranes. J. Membrane Biol.9, 261–290 (1972).
Derksen, H. E.: Axon membrane voltage fluctuations. Acta physiol. pharmacol. neerl.13, 373–466 (1965).
Dodge, F. A.: A study of ionic permeability changes underlying excitation in myelinated nerve fibres of the frog. New York: The Rockefeller Institute 1963.
Fishman, H. M.: Excess noise from small patches of squid axon membrane. Biophys. Soc. Abstr. 119a (1972).
Fishman, H. M.: Potassium channel noise in squid axon membranes. Biophys. Soc. Abstr. (1973). (in press).
Frankenhaeuser, B.: A method for recording resting and action potentials in the isolated myelinated nervefibre of the frog. J. Physiol. (Lond.)135, 550–559 (1957).
Gordon, L. G. M., Haydon, D. A.: The unit conductance channel of alamethicin. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)255, 1014–1018 (1972).
Hill, T. L., Chen, Y.: On the theory of ion transport across the nerve membrane. IV. Noise from the open-close kinetics of K+ channels. Biophys. J.12, 948–959 (1972).
Katz, B., Miledi, R.: The statistical nature of the acetylcholine potential and its molecular components. J. Physiol. (Lond.)224, 665–699 (1972).
Keynes, R. D.: Excitable membranes. Nature (Lond.)239, 29–50 (1972).
Latorre, R., Ehrenstein, G., Lecar, H.: Ion transport through excitability-inducing material (EIM) channels in lipid bilayer membranes. J. gen. Physiol.60, 72–85 (1972).
Lee, Y. W.: Statistical theory of communication. New York: Wiley 1960.
Pecher, C.: Fluctuations indépendantes de l'excitabilité de deux fibres d'un même nerf. C. R. Soc. Biol. (Paris)124, 839–842 (1937).
Poussart, D. J. M.: Nerve membrane current noise: direct measurement under voltage clamp. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.)64, 95–99 (1969).
Poussart, D. J. M.: Membrane current noise in lobster axon under voltage clamp. Biophys. J.11, 211–234 (1971).
Rice, S. O.: Mathematical analysis of random noise. Bell Syst. Techn. J.23, 282;24, 46 (1944/1945). Reprinted in N. Wax, ed.: Selected Papers on Noise and Stochastic Processes. Dover-New York 1954.
Siebenga, E., Verveen, A. A.: The dependence of the 1/f noise intensity of the node of Ranvier on membrane potential. Proceedings of the First European Biophysics Congress, Vol. V, pp. 219–233, Wien 1971.
Stevens, C. F.: Inferences about membrane properties from electrical noise measurements. Biophys. J.12, 1028–1047 (1972).
Verveen, A. A.: Fluctuation in Excitability, Amsterdam, Central Institute for Brain Research (1961).
Verveen, A. A., Derksen, H. E.: Fluctuations in membrane potential of axons and the problem of coding. Kybernetik2, 152–160 (1965).
Verveen, A. A., Derksen, H. E.: Fluctuation phenomena in nerve membrane. Proc. IEEE56, 906–916 (1968).
Verveen, A. A., Derksen, H. E.: Amplitude distribution of axon membrane noise voltage. Acta physiol. pharmacol. neerl.15, 353–379 (1969).
Verveen, A. A.: Membrane noise and channel dynamics. Paper submitted for the 1973 International Symposium on Dynamics and Control in Physiological Systems. Rochester, August 22–24, 1973.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by a grant from the Netherlands Organization for Pure Research (Z.W.O.).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siebenga, E., Meyer, A.W.A. & Verveen, A.A. Membrane shot-noise in electrically depolarized nodes of Ranvier. Pflugers Arch. 341, 87–96 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587315
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587315