Abstract
-
1.
The isolated midgut of a lepidopteran larva (Manduca sexta), 5th instar was investigated with voltageclamp and fluctuation analysis techniques.
-
2.
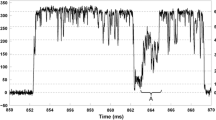
With high K+ insect saline on both sides the outward-directed short-circuit current (I sc) was carried by K+ (I K) from serosal to mucosal compartment.I K could be blocked, in a dose-dependent manner by serosal Ba2+ ions. There was no current with serosal Na+.
-
3.
Noise analysis ofI K revealed a Lorentzian component in the power spectrum when Ba2+ was present in the serosal solution. The Ba2+/receptor kinetics show pseudo-first order characteristics only at low [Ba2+]s. For [Ba2+]s>K Ba, the apparrent Ba2+ association rate decreases with a hyperbolic course as a function of serosal [Ba2+] which could indicate some “substrate-inhibition”-like interaction of Ba2+ at its receptor site.
-
4.
It is concluded that the serosal membranes of the K+-secreting intestinal cells contain the common type of Ba2+-blockable K+ channel which provides the serosal pathway for K+ during secretion which is ultimately driven by the mucosally-located electrogenic K+-ATPase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blankenmeyer JT, Harvey WR (1978) Identification of active cell in potassium transporting epithelium. J Exp Biol 77:1–13
Dow JAT (1984) A model linking electrogenic potassium ATPase to carbonate secretion in a specialised cavity can explain the generation of pH 12, the highest known in biology. 1st Congr Comp Physiol Biochem (Section of Internat Union of Biol Sci), Liege (Belgium), p B100
Dow JAT, Gupta BL, Hall TA, Harvey WR (1984) X-ray microanalysis of elements in frozen-hydrated sections of an electrogenic K+-transport system: The posterior midgut of tobacco hornworm (Manduca sexta) in vivo and in vitro. J Membr Biol 77:223–241
Giordana B, Sacchi FV, Hanoret GM (1982) Intestinal amino acid absorption in lepidopteran larvae. Biochem Biophys Acta 692:81–88
Hanrahan JW, Wills NK, Philipps JE, Lewis SA (1986) Basolateral K+ channels in an insect epithelium: channel density, conductance, and block by barium. J Gen Physiol 87:443–466
Harvey WR (1980) Water and ions in the gut. In: Locke M, Smith DS (eds) Insect biology in the future VBW 80. Academic Press, London, pp 105–124
Harvey WR, Cioffi M, Wolfersberger MG (1983) Chemiosmotic potassium ion pump of insect epithelia. Am J Physiol 244: R163-R175
Harvey WR, Nedergaard S (1964) Sodium-independent active transport of potassium in the isolated midgut ofHyalophora cecropia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 51:757–765
Helman SI, Cox TC, Van Driessche W (1983) Hormonal control of apical membrane Na transport in epithelia. J Gen Physiol 82:201–220
Jungreis A, Vaughan GL (1977) Insensitivity of lepidopteran tissues to ouabain: absence of ouabain binding and Na+−K+ ATPase in larval and adult midgut. J Insect Physiol 23:503–509
Li JH-Y, Lindemann, B (1983) Competitive blocking of epithelial sodium channels by organic cations: the relationship between macroscopic and microscopic inhibition constants. J Membr Biol 76:235–251
Moffet DF, Hudson RL, Moffet SB, Ridgway RL (1982) Intracellular K+ activities and cell membrane potentials in a K+-transporting epithelium, the midgut of tobacco hornworm (Manduca sexta) J Membr Biol 70:59–68
Van Driessche W, Gögelein H (1980) Attenuation of current and voltage noise signals recorded from epithelia. J Theor Biol 86:629–648
Van Driessche W, Hillyard SD (1985) Quinidine blockage of K+ channels in the basolateral membrane of larval bullfrog skin. Pflügers Arch 405:S77-S82
Van Driessche W, Wills NK, Hillyard SD, Zeiske W (1981) K+ channels in an epithelial “single-membrane preparations’ Arch Int Physiol Biochim 90:p12-p14
Van Driessche W, Zeiske W (1980) Ba2+-induced conductance fluctuations of spontaneously fluctuating K+ channels in the apical membrane of frog skin (Rana temporaria) J Membr Biol 56:31–42
Van Driessche W, Zeiske W (1985) Ionic channels in epithelial cell membranes. Physiol Rev 65:833–903
Wieczorek H, Cioffi M, Harvey WR, Kubler G, Wolfersberger MG (1984) KCl-stimulated ATPase activity in purified goblet cell apical membranes fromManduca sexta larval midgut. In: 1st Congress Comp Physiol Biochem (Section of Internat Union of Biol Sci) Liege, Belgium, p B101
Zeiske W, Machen TE, Van Driessche W (1983) Cl− and K+-related fluctuations of ionic current through oxyntic cells in frog gastric mucosa. Am J Physiol 245:G797-G807
Zeiske W, Van Driessche W (1979) Saturable K+-pathway across the outer border of frog skin (Rana temporaria): kinetics and inhibition by Cs+ and other cations. J Membr Biol 47:77–96
Zeiske W, Van Driessche W (1983) The interaction of “K+-like” cations with the apical K+ channel in frog skin. J Membr Biol 76:57–72
Zeiske W, Wills NK, Van Driessche W (1982) Na+ channels and amiloride-induced noise in the mammalian colon epithelium. Biochim Biophys Acta 688:201–210
Ziegler R (1984) developmental changes in the response of the fat body ofManduca sexia to injections of corpora cardiaca extracts. Gen Comp Endocrinol 54:51–58
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeiske, W., Van Driessche, W. & Ziegler, R. Current-noise analysis of the basolateral route for K+ ions across a K+-secreting insect midgut epithelium (Manduca sexta). Pflugers Arch. 407, 657–663 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582648
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582648