Abstract
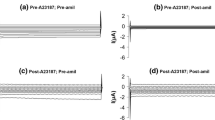
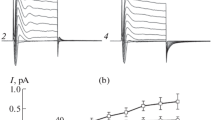
Voltage-gated Ca2+-current was identified in single isolated cells of the zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex and its properties were studied by the “tight-seal” whole cell recording technique. The Ca2+-channel current was dissected from the net current by dialyzing the cells with CsCl. The identified Ca2+-current was found to be activated by a relatively small depolarization only when the cells were held at a large negative holding potential, but it was inactivated within 10–30 ms. The time course of activation and inactivation was voltage-dependent and became faster when the amplitude of depolarization was increased. The transmembrane potential of the glomerulosa cells was highly sensitive to [K+]e, the slope of the potential change per tenfold change in [K+]e being 48 mV. An increase in [K+]e from 4.7 to 10 mM induce a membrane depolarization by 15 mV, which was sufficient to cause the membrane to reach the threshold potential (−60 mV) for activation of the Ca2+-current at physiological concentration of [Ca2+]e (2.5 mM −CaCl2). The observed properties of the Ca2+-current and K+-dependence of the membrane potential may give reasonable explanation for the mechanism of Ca2+-uptake and consequent aldosterone secretion induced by a small increase in [K+]e, which is known to be one of the major stimulations for aldosterone secretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera G, Catt KJ (1979) Loci of action of regulators of aldosterone biosynthesis in isolated glomerulosa cells. Endocrinology 104:1046–1052
Armstrong CM, Matteson DR (1985) Two distinct populations of calcium channels in a clonal line of pituitary cells. Science 277:65–67
Fakunding JL, Chow R, Catt KJ (1979) The role of calcium in the stimulation of aldosterone production by adrenocorticotropin, angiotensin II, and potassium in isolated glomerulosa cells. Endocrinology 105:327–333
Farese RV, Larson RE, Sabir MA, Gomez-Sanchez CE (1983) Effects of angiotensin II, K+, adrenocorticotropin, serotonin, adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate, A23187, and EGTA on aldosterone synthesis and phospholipid metabolism in the rat adrenal zone glomerulosa. Endocrinology 113:1377–1386
Fenwick EM, Marty A, Neher E (1982) Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol 331:599–635
Hagiwara S (1983) Membrane potential-dependent ion channels in cell membrane. Raven Press, New York, p 559
Hagiwara S, Ohmori H (1982) Studies of calcium channels in rat clonal pituitary cells with patch electrode voltage clamp. J Physiol 331:231–252
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth F (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Kojima I, Kojima K, Rasmussen H (1985) Characteristics of angiotensin II-, K+-and ACTH-induced calcium influx in adrenal glomerulosa cells. J Biol Chem 260:9171–9176
Kojima K, Kojima I, Rasmussen H (1984) Dehydropyridine calcium agonist and antagonist effects on aldosterone secretion. Am J Physiol 247:E645–E650
Marty A, Neher E (1983) Tight-seal whole-cell recording. In: Sakmann B, Neher E (eds) single-channel recording. Plenum Press, New York, pp 107–121
Maryuama Y, Petersen OH, Flanagan P, Pearson GT (1983) Quantification of Ca2+-activated K+ channels under hormonal control in pig pancreatic acinar cells. Nature 305:228–232
Nowycky MC, Fox AP, Tsien RW (1985) Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature 316:440–443
Petersen OH (1980) The electrophysiology of gland cells. Academic Press, New York
Saruta T, Cook R, Kaplan MN (1972) Adrenocortical steroidgenesis: studies on the mechanism of action of angiotensin and electrolytes. J Clin Invest 51:2239–2245
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsunaga, H., Maruyama, Y., Kojima, I. et al. Transient Ca2+-channel current characterized by a low-threshold voltage in zona glomerulosa cells of rat adrenal cortex. Pflugers Arch. 408, 351–355 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00581128
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00581128