Abstract
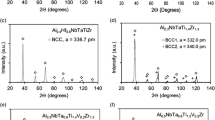
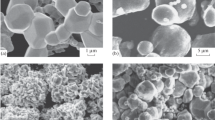
Commercial stainless steel alloys have been made into amorphous, or glassy, states by adding nearly 10 at % of refractory metals, such as W or Ti, via high-rate sputter deposition. The formation of these stable amorphous stainless steel alloys required alloy compositions beyond the equilibrium b c c solid solution phase field. For the amorphous alloys containing W, the crystallization temperature increased from 760 to 1035 K as the W content was increased from 11 at% W to 23 at % W. The high crystallization temperatures were attributed to the high resistence to crystallization of the complex intermediate χ and Μ phases, which occurred at 11 and 23 at % W respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Masumoto and R. Maddin, Acta Metal. 19 (1971) 725.
J. J. Gilman, J. Appli. Phys. 46 (1975) 1629.
M. Naka, K. Hasimoto and T. Masumoto, Corrosion 32 (1976) 146.
T. Masumoto and K. Hashimoto, Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci. 8 (1978) 215.
K. Hashimoto and T. Masumoto, in “Rapidly Quenched Metals” edited by N. J. Grant and B. C. Giessen (MIT Press, Mass., 1975) p. 285.
T. M. Devine, J. Electrochem. Soc. 124 (1977) 38.
M. Naka, K. Hashimoto and T. Masumoto, Corrosion Eng. 36 (1980) 679.
S. D. Dahlgren, Met. Trans, 1 (1970) 3095.
M. D. Merz, private communications (1980).
J. Niewiarowski and H. Matyja, in “Rapidly Quenched Metals III” Vol. 1 (The Metals Society, London, 1978) p. 193.
P. J. Grundy and J. M. Marsh, J. Mater. Sci. 13 (1978) 677.
S. D. Dahlgren, in “Rapidly Quenched Metals III” Vol. 2 (The Metals Society, London, 1978) p. 36.
R. Wang, M. D. Merz, J. L. Brimhall and S. D. Dahlgren, in “Rapidly Quenched Metals III” Vol. 1 (The Metals Society, London, 1978) p. 420.
R. Wang, M. D. Merz and J. L. Brimhall, Script. Metal 12 (1978) 1037.
R. Wang, in “Theory of Alloy Phase Formation” edited by L. H. Bennett (American Institute of Mechanical Engineers, Conference Proceedings of The Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1980) p. 472.
M. Hansen, “Constitution of Binary Alloys” (McGraw Hill Book Co., New York, 1958).
R. P. Elliot, “Constitution of Binary Alloys, First Supplement” (McGraw Hill Book Co, New York, 1965).
W. B. Pearson, “A Handbook of Lattice Spacings and Structures of Metals and Alloys” (Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1958).
W. P. Sykes, Trans. ASST 10 (1926) 839.
Idem. Idid. 10 (1926) 1035.
T. Tkai and T. Murakami, ibid. 16 (1929) 339.
J. G. McMullin, S. F. Reiter and D. G. Ebeling, Trans. Amer. Soc. Metal 46 (1954) 799.
N. G. Boriskina and I. I. Kornilov, Zh. Neorg. Khim. 4 (1959) 2171.
H. Hughes and D. T. Llewelyn, J. Iron Steel Inst. (London) 192 (1959) 170.
J. L. Brimhall, L. A. Charlot and H. E. Kissinger, J. Mater. Sci. 17 (1982) 1149.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Operated for the Department of Energy by Battelle Memorial Institute under contract number DE-AC06-76-RLO 1830.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R. Refractory-metal stabilized amorphous stainless steel. J Mater Sci 17, 1142–1148 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00543534
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00543534