Conclusions
The features of the pneumotexturizing process for synthetic yarns have been examined in comparison with mechanical crimping. A mechanism has been suggested for crimp formation on elementary filaments in pneumotexturizing.
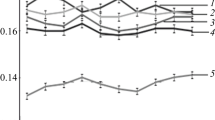
Experimental dependences of the properties of the yarns obtained on the temperature of the working air stream have been given.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. A. Volkhonskii, in: Improvement in Equipment for Texturizing Synthetic Fibres [in Russian], TsNIITÉIlegpischemash, Moscow (1971), pp. 3–15.
I. Taylor and D. Brattacharya, Text. Recorder, No. 954, 58–61 (1962).
A. P. Barabanov, A. A. Volkhonskii, S. G. Lev, and V. A. Usenko, in: The Technology of Twisting and Texturizing Man-Made Fibres and Yarns [in Russian], MTI, Moscow (1980), pp. 32–38.
Additional information
Translated from Khimicheskie Volokna, No. 1, pp. 18–19, January–February, 1984.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volkhonskii, A.A., Lev, S.G. Texturizing synthetic fibres with a stream of hot gas. Fibre Chem 16, 1–4 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00543161
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00543161