Summary
-
1.
The effect of deoxycholate and cholera toxin on the transfer of water, sodium, potassium and chloride and on mucosal permeability was studied in perfusion experiments on rat colon in vivo. The influence of both secretagogues on surface morphology was assessed by scanning electron microscopy.
-
2.
Deoxycholate turned the absorption of water, sodium and chloride to secretion and enhanced potassium secretion. Cholera toxin induced water and sodium secretion, inhibited chloride absorption and enhanced potassium secretion.
-
3.
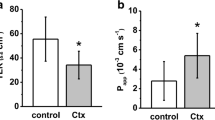
Deoxycholate increased reversibly the mucosal permeability as measured by the colonic clearance of 51CrEDTA and glucose, whereas cholera toxin decreased the colonic 51CrEDTA clearance.
-
4.
Deoxycholate caused protrusion of the luminal cell surface and an increase of exfoliation of epithelial cells. The epithelial continuity was preserved. The only change induced by cholera toxin was an enhanced mucus extrusion.
-
5.
Our results are consistent with the view that deoxycholate causes fluid secretion by filtration whereas cholera toxin enhances the secretory activity of the epithelium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aziz, K. M. S., Mohsin, A. K. M., Hare, W. K., Phillips, R. A.: Using the rat as a cholera “model”. Nature 220, 814–815 (1968)
Binder, H. J., Filburn, C., Volpe, B. T.: Bile salt alteration of colonic electrolyte transport: Role of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Gastroenterology 68, 503–508 (1975)
Binder, H. J., Dobbins, J. W., Racusen, L. C., Whiting, D. S.: Effect of propranolol on ricinoleic acid- and deoxycholic acid-induced changes of intestinal electrolyte movement and mucosal permeability. Gastroenterology 75, 668–673 (1978)
Chadwick, V. S., Gaginella, T. S., Debongie, J. C., Carlson, G. L., Phillips, S. F., Hofmann, A. F.: Mucosal epitheliolysis: A mechanism for the increased colonic permeability induced by dihydroxy bile acids. Gut 17, 816 (1976)
Chadwick, V. S., Phillips, S. F., Hofmann, A. F.: Measurement of intestinal permeability using low molecular weight polyethylene glycols (PEG 400). II. Application to normal and abnormal permeability states in man and animals. Gastroenterology 73, 247–251 (1977)
Cline, W. S., Lorenzsonn, V., Bentz, L., Bass, P., Olson, W. A.: The effects of sodium ricinoleate on small intestinal function and structure. J. Clin. Invest. 58, 380–390 (1976)
Desjeux, J. F., Tai, Y. H., Powell, D., Curran, P. F.: Effects of cholera toxin on cellular and paracellular sodium fluxes in rabbit ileum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 448, 352–367 (1976)
DiBona, D. R., Chen, L. C., Sharp, G. W. G.: A study of intercellular spaces in the rabbit jejunum during acute volume expansion and after treatment with cholera toxin. J. Clin. Invest. 53, 1300–1307 (1974)
Donowitz, M., Binder, H. J.: Effect of enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae, Escherichia coli, and Shigella dysenteriae Type 1 on fluid and electrolyte transport in the colon. J. Infect. Dis. 134, 135–143 (1976)
Donowitz, M., Charney, A. N.: Propranolol prevention of cholera enterotoxin-induced intestinal secretion in the rat. Gastroenterology 76, 482–491 (1979)
Forth, W., Rummel, W.: Activation and inhibition of intestinal absorption by drugs. In: Pharmacology of intestinal absorption: Gastrointestinal absorption of drugs. Section 39 B, Vol. 1 (W. Forth, W. Rummel, eds.), pp. 171–244. Oxford, New York, Toronto, Sydney, Braunschweig: Pergamon Press 1975
Gaginella, T. S., Phillips, S. F., Dozois, R. R., Go, V. L. W.: Stimulation of adenylate cyclase in homogenates of isolated intestinal epithelial cells from hamsters. Gastroenterology 74, 11–15 (1978)
Goerg, K. J., Gross, M.: Comparison of the secretory effects of deoxycholate and cholera toxin on the rat colon. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 297, (Suppl.) R1 (1977)
Gullikson, G. W., Cline, W. S., Lorenzsonn, V., Benz, L., Olsen, W. A., Bass, P.: Effects of anionic surfactants on hamster small intestine structure and function: Relationship to surface activity. Gastroenterology 73, 501–511 (1977)
Hendrix, T. R.: Cholera toxin and intestinal transport. In: Intestinal absorption and malabsorption (T. Z. Csaky, ed.), pp. 253–271. New York: Raven Press 1975
Lifson, N., Hakim, A. A., Lender, E. J.: Effects of cholera toxin on intestinal permeability and transport interactions. Am. J. Physiol. 222, 1479–1487 (1972)
Naftalin, R. J.: The role of the paracellular pathway in control of the direction of net electrolyte and fluid movements across rabbit ileum. Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 2, 331–332 (1978)
Nell, G., Forth, W., Rummel, W., Wanitschke, R.: Pathway of sodium moving from blood to intestinal lumen under the influence of oxyphenisatin and deoxycholate. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 293, 31–37 (1976)
Norris, H. T., Schultz, S. G., Curran, P. F., Finkelstein, R. A.: Active sodium transport across rabbit ileum in experimental cholera incuced by choleragen. J. Infect. Dis. 117, 193–196 (1967)
Parsons, D. S., Paterson, C. F.: Fluid and solute transport across rat colonic mucosa. Quart. J. Physiol. 50, 220–231 (1965)
Rummel, W.: Wirkungen von Gallensäuren und Laxantien auf den mucosalen Transfer. Bull. Schweiz. Akad. Med. Wiss. 32, 233–250 (1976)
Saunders, D. R., Hedges, J. R., Sillery, J., Esther, L., Matsumura, K., Rubin, C. E.: Morphological and functional effects of bile salts on rat colon. Gastroenterology 68, 1236–1245 (1975)
Simon, B., Czygan, P., Stiehl, A., Kather, H.: Human colonic adenylate cyclase: Effects of bile acids. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 8, 321–323 (1978)
Schales, D., Schales, S. S.: A simple and accurate method for the determination of chloride in biological fluids. J. Biol. Chem. 140, 879–884 (1941)
Taub, M., Coyne, M. J., Bonorris, G. G., Chung, A., Coyne, B., Schoenfield, L. J.: Inhibition by propranolol of bile acid and PGE1-stimulated cAMP and intestinal secretion. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 70, 129–135 (1978)
Yardley, J. H., Bayless, T. M., Luebbers, E. H., Halsted, C. H., Hendrix, T. R.: Goblet cell mucus in the small intestine. Findings after net fluid production due to choleratoxin and hypertonic solutions. J. Hopkins Med. J. 131, 1–10 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Part on the results has already been presented on the occasion of the 18th Spring meeting of the Deutsche Pharmakologische Gesellschaft, Mainz, FRG (Goerg and Gross, 1977)
Supported by a grant of the Sonderforschungsbereich 38, Membrane Research, Universität des Saarlandes
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goerg, K.J., Gross, M., Nell, G. et al. Comparative study of the effect of cholera toxin and sodium deoxycholate on the paracellular permeability and on net fluid and electrolyte transfer in the rat colon. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 312, 91–97 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00502580
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00502580