Abstract
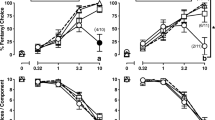
Rats were trained to discriminate between fentanyl (0.04 mg/kg) and saline in a two-lever procedure. Using a FR 10 schedule of food reinforcement, drug-induced differences between the number of reinforcers obtained under fentanyl and saline conditions were observed. The effect of eliminating these differences on the outcome of generalization tests was investigated by different manipulations. In one group (N=10), the FR 10 schedule used during saline sessions was changed to FR 6 during drug sessions. In a second group (N=12), saline sessions ended after the number of reinforcers obtained was equal to the number obtained during the preceding drug session. A control group (N=10) was trained using a FR 10 schedule under both conditions. Elimination of differences in reinforcement frequency 1) accelerated the acquisition of the discrimination, 2) diminished response bias, 3) flattened the slope and reduced the ED50 value of generalization gradients of fentanyl, morphine and sufentanil and 4) increased the ED50 value of naloxone in antagonizing 0.04 mg/kg fentanyl. It is concluded that the unconditioned effects of 0.04 mg/kg fentanyl on response rate in a FR 10 procedure lead to differences between saline and drug sessions which contribute to the apparent discriminative stimulus properties of fentanyl.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colpaert FC (1982) The pharmacological specificity of opiate drug discrimination. In: Colpaert FC, Slangen JL (eds) Drug discrimination: Applications in CNS pharmacology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 3–16
Colpaert FC, Janssen PAJ (1981) Factors regulating drug cue sensitivity: The effect of frustrative non-reward in fentanylsaline discrimination. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 254:241–251
Colpaert FC, Slangen JL (1982) Drug discrimination: Applications in CNS pharmacology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Colpaert FC, Maroli AN, Meert T (1982) Parameteric effects in the discrimination of intracranial stimulation: Some methodological and analytical issues. Physiol Behav 28: 1047–1058
Colpaert FC, Niemegeers CJE, Janssen PAJ (1976) Theoretical and methodological considerations on drug discrimination learning. Psychopharmacologia 46:169–177
Colpaert FC, Niemegeers CJE, Janssen PAJ (1980) Factors regulating drug cue sensitivity: The effect of training dose in fentanylsaline discrimination. Neuropharmacology 19:705–713
Extance K, Goudie AJ (1981) Interanimal olfactory cues in operant drug discrimination procedures in rats. Psychopharmacology 73:363–371
Koek W, Slangen JL (1982a) The role of fentanyl training dose and of the alternative stimulus condition in drug generalization. Psychopharmacology 76:149–156
Koek W, Slangen JL (1982b) Effects of reinforcement difference between drug and saline sessions on discriminative stimulus properties of fentanyl. In: Colpaert FC, Slangen JL (eds) Drug discrimination: Applications in CNS pharmacology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 343–354
Litchfield JT, Wilcoxon F (1949) A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 96:99–113
Overton DA (1982) Comparison of the degree of discriminability of various drugs using the T-maze drug discrimination paradigm. Psychopharmacology 76:385–395
Stolerman IP, D'Mello GD (1981) Role of training conditions in discrimination of central nervous system stimulants by rats. Psychopharmacology 73:295–303
Winer BJ (1971) Statistical principles in experimental design, 2nd edn. McGraw Hill, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Vry, J., Koek, W. & Slangen, J.L. Effects of drug-induced differences in reinforcement frequency on discriminative stimulus properties of fentanyl. Psychopharmacology 83, 257–261 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00464790
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00464790