Abstract
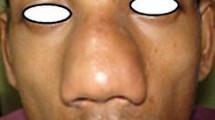
A case of rhinofacial zygomycosis with of years duration, caused by Conidiobolus coronatus is described. The patient, a 72-years-old woman, presented with a bilateral distortion of the subcutaneous tissue and disfigurement of the face. Treatment with ketoconazole and potasium iodide did not prevent several relapses. At present she is still under treatment with fluconazole with clinical healing. Histopathological and mycological examination confirmed the dermatological diagnosis. An increasing number of cases of zygomycosis caused by fungi of the order Entomophthorales have also been reported in the Northern and Northeastern States of Brazil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
King DS. Entomophthorales. In: Howard DH, Howard LF, eds. Fungi Pathogenic for Humans and Animals, Part A: Biology. New York: Marcel Dekker 1983: 61–72.
Humber RA, Brown CC. The first report of Conidiobolus lamprauges from a vertebrate rhinoconidiobolomycosis. Mycol Soc Am Abstracts 1987; 6; 11.
Drechsler, C. Widespread distribution of Delacroixia coronata and other saprophytic Entomophthoraceae in plant detritus. Science 1952; 115: 575–6.
King DS. Systematics of Conidiobolus (Entomophthorales) using numerical taxonomy. I: biology and cluster analysis. Can J Bot 1976; 54: 45–65.
King DS. Systematics of Conidiobolus (Entomophthrales) using numerical taxonomy, III: descriptions of recognized species. Can J Bot 1977; 55; 718–29.
Praserthon S. Conidial formation in Entomophthora coronata (Costantin) Kevorkian. J Insect Pathol 1963; 5: 318–35.
Porto E, Milanez AI. Basidiobolus isolados de répteis e anfícios no Brasil. Rev Inst Med trop São Paulo 1979; 21: 237–45.
Porto E, Melo NT, Heins-Vaccari EM, Lacaz C da S, Assis CM. Isolamento de Conidiobolus coronatus (Costantin) Batko 1964, de amostras de terra com e sem detritus vegetais. An bras Dermatol 1987; 62: 303–7.
Johnston MJ, Soerensen B, Saliba AM, Lacaz C da S, Bela Neto J, Cruz JM. Isolamento de Entomophthora coronata. Arq Inst Biol. 1967; 34: 51–8.
Towersey, L, Wanke B, Estrella RR, Londero AT, Mendonça AMN, Neves RG. Conidiobolus coronatus infection treated with ketoconazole. Arch Dermatol 1988; 124: 1392–6.
Fonseca APM, Fonseca WSM, Leal MJS, Araújo RC. Rinoentomoftoromicose: relato quatro casos. An bras Dermatol 1989; 64: 261–5.
Bittencourt AL. Entomoftoromicose. Revisão. Med Cut ILA 1988; 16: 93–100.
Rippon JW. Zygomycosis. In: Rippon JW. Medical Mycology: The Pathogenic Fungi and the Pathogenic Actinomycetes, 3rd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Company 1988: 687–699.
Porto E, Takahashi N, Heins EM, Lacas C da S. Nuevo metodo para microcultivo de hongos. Rev Arg Micologia 1981; 4: 24–9.
Bras G, Gordon CC, Emmons CW, Brendegast KM, Sugar M. A case of phycomycosis observed in Jamaica: infection with Entomophthora coronata. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1965; 14: 141–5.
King DS. Systematics of fungi causing entomophthoromycosis. Mycologia 1979; 71: 731–45.
Taylor GD, Sehkon AS, Tyrrell DLJ, Goldsand G. Rhinofacial zygomycosis caused by Conidiobolus coronatus: a case report including in vitro sensitivity to antimycotic agents. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1987; 36: 398–401.
Williams AO. Pathology of phycomycosis due to Entomophthora and Basidiobolus species. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1969; 87: 13–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, A.R., Porto, E., Pegas, J.R.P. et al. Rhinofacial zygomycosis caused by Conidiobolum coronatus . Mycopathologia 115, 1–8 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00436414
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00436414