Summary
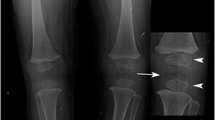
The epiphyseal growth plate of femora (proximal and distal), tibiae, radii and ulnae of seven uremic children were studied to clarify the histopathogenesis of epiphyseolysis. Epiphyseolysis was found to be result of three different processes: (1) growth arrest, (2) excessive erosion of the growth cartilage and of the trabeculae of metaphyseal spongiosa and (3) disturbance of vascularisation of hypertrophic cartilage. By resorptive destruction, secondary hyperparathyroidism causes loss of the chondro-osseous continuity. The ordered trajectoral pattern of the trabeculae in the primary spongiosa is transformed into a dense lace of mechanically inferior trabeculae consisting of woven bone. Impairment of primary mineralization could not be demonstrated. Intensive subperiosteal osteoclastic resorption leads to a reduction of metaphyseal width and to fractures of the unsupported lateral parts of the growth cartilage. There were notable differences between the growth plates in different localisations: in growth plates subjected to axial compression (distal femur, tibia) signs of growth arrest prevailed (reduction of hypertrophic cartilage, occlusion of the growth plate by a transverse plate of bone); in growth plates subjected to shearing forces (upper femur, radius, ulna) epiphyses were seen to slip sideway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber, M.: Renal dwarfism. Quart. J. Med. 14, 205–213 (1921)
Brailsford, J. F.: Slipping of the epiphysis of the head of the femur. Lancet 1933, 16–19
Brockman, E. P.: Some observations on the bone changes in renal rickets. Brit. J. Surg. 14, 634–645 (1926)
Cattell, M. S., Levin, S., Kopits, St., Lyne, E. D.: Reconstructive surgery in children with azotemic osteodystrophy. J. Bone Jt Surg. A 53, 216–228 (1971)
Fletcher, M.: Case of infantilism with polyuria and chronic renal disease. Proc. Roy. Soc. Med. 4, 95 (1911)
Follis, R. M.: Renal rickets and osteitis fibrosa in children and adolescents. Bull. Johns Hopk. Hosp. 78, 593–615 (1950)
Hamperl, H., Wallis, U.: Über renale Rachitis und renalen Zwergwuchs. Virchows Arch. path. Anat. 288, 119–145 (1933)
Harris, H. A.: Bone growth in health and disease. London: Oxford medical publications 1933
Harris, W. R.: The endocrine basis for slipping of the upper femoral epiphysis. J. Bone Jt Surg. A 33, 371–381 (1951)
Kirkwood, J. R., Ozonoff, M. B., Steinbach, M. L.: Epiphyseal displacement after metaphyseal fracture in renal osteodystrophy. Amer. J. Roentgenol. 115, 547–554 (1972)
Kluge, E.: Neue Beiträge zur Kenntnis des renalen Zwergwuchses und der renalen Rachitis. Virchows Arch. path. Anat. 298, 406–429 (1937)
Köhn, G., Gelinski, G.: Nephrofibrosis cystica congenita (sog. chronische-interstitielle Nephritis) bei renaler Rachitis und Ostitis fibrosa. Beitr. path. Anat. 106, 263–288 (1942)
Krempien, B., Mehls, O., Ritz, E., Schüler, H., Schärer, K.: Osteopathy in children with longstanding renal insufficiency. Pediat. Res. 7, 46 (1973)
Krempien, B., Ritz, E.: Experimental renal osteopathy. Israel J. med. Sci. 7, 522–524 (1971)
Krempien, B., Ritz, E., Ditzen, K., Hudelmeier, G.: Über den Einfluß der Niereninsuffizienz auf Knochenbildung und Knochenresorption. Virchows Arch. Abt. A 355, 354–366 (1972 a)
Krempien, B., Ritz, E., Schmidt, G.: Experimentelle autoradiographische Untersuchungen zum Kollagenstoffwechsel des Knochens in der Urämie. Z. Orthop. 110, 25–34 (1972 b)
Lacroix, P., Verbrugge, J.: Slipping of the upper femoral epiphysis. J. Bone Jt Surg. A 33, 371–381 (1951)
Mehls, O., Krempien, B., Ritz, E., Schärer, K., Schüler, H. W.: Renal osteodystrophy in children on maintenance hemodialysis. Proc. EDTA 1973, Vienna
Mehls, O., Ritz, E., Krempien, B., Willich, E., Schärer, K.: Roentgenological signs in the skeleton of uremic children. An analysis of the anatomical principals underlying the roentgenological changes. Pediat. Radiol. (in the press)
Park, E. A.: The imprinting of nutritional disturbances on the growing bone. Pediatrics 33 (Suppl.), 815–862 (1964)
Pauwels, P.: Gesammelte Abhandlungen zur funktionellen Anatomie des Bewegungsapparates. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1965
Ponseti, I.: Legg-Perthes disease. J. Bone Jt Surg. A 38, 739–750 (1956)
Price, N. L., Davie, T. B.: Renal rickets. Brit. J. Surg. 24, 548–569 (1936/37)
Ritz, E., Krempien, B., Mehls, O., Malluche, H., Strobel, Z., Zimmermann, M.: Skeletal complications of renal insufficiency and maintenance haemodialysis. Nephron 10, 195–207 (1973)
Schinz, H. R., Baensch, W. E., Friedl, W., Uehlinger, E.: Lehrbuch der Röntgendiagnostik. Bd. II, Teil II. Stuttgart: Thieme 1952
Shea, D., Mankin, M. J.: Slipped capital epiphysis in renal rickets. J. Bone Jt Surg. A 48, 349–355 (1966)
Stanbury, S. W.: Azotaemic renal osteodystrophy. Brit. med. Bull. 13, 57–60 (1957)
Sutro, Ch. J.: Slipping of the capital epiphysis of the femur in adolescence. Arch. Surg. 31, 345–360 (1935)
Taillard, W.: Anatomie und Physiopathologie der Epiphysiolysis capitis femoris. Documenta Geigy. Acta rheum. (Amst.) 21, 15–55 (1964)
Welz, A.: Renaler Zwergwuchs. Veröffentlichungen konst. Wehrpath. 9, 1–56 (1936)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With support of Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. Presented in part at the Annual Meeting of the European Society for Pediatric Research, Heidelberg 1972.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krempien, B., Mehls, O. & Ritz, E. Morphological studies on pathogenesis of epiphyseal slipping in uremic children. Virchows Arch. A Path. Anat. and Histol. 362, 129–143 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00432391
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00432391