Abstract
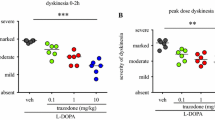
Tiapride, a selective D2 dopaminergic receptor blocking agent from the substituted benzamide class, was evaluated in a blind video-controlled trial in 10 psychiatric patients with tardive dyskinesia. There was a significant decrease in dyskinesia with a parallel increase in parkinsonism. This relationship between two opposite effects on movement suggests a common pathophysiological basis lying on a reciprocal hyper- and hypoactivity of the dopaminergic striatal system. Nevertheless, other mechanisms may be involved, for the evolution of individual parkinsonian and dyskinesia scores is not necessarily opposite: the tiapride-induced parkinsonism was generally acceptable and in two cases, the dyskinesia scores were reduced without an increase in parkinsonism. Therefore, more dyskinetic patients have to be evaluated in long-term studies with tiapride, before this drug could be recommended in tardive dyskinesia, when dyskinetic movements become intolerable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes TRE, Kidger T, Gore SM (1983) Tardive dyskinesia: a 3 year follow up study. Psychol Med 13:71–81
Bartholini G (1976) Differential effect of neuroleptic drugs on dopamine turn-over in the extrapyramidal disorders. J Pharm Pharmacol 28:429–433
Borenstein P, Champion C, Cujo P, Gekiere F, Olivenstein C, Kramarz P (1969) Un psychotrope original: le Sulpiride. Sem Hôp Paris, 45:1301–1314
Casey DE, Gerlach J (1980) Oxiperomide in tardive dyskinesia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 43:264–267
Casey DE, Gerlach J, Simmelsgaard H (1979) Sulpiride in tardive dyskinesia. Psychopharmacology 66:73–77
Claveria LE, Teychenne PF, Calne DB, Haskayne L, Petrie A, Pallis CA, Lodge-Patch IC (1975) Tardive dyskinesia treated with pimozide. J Neurol Sci 24:393–401
Corsini GU, Del Zompo M, Cianchetti C, Mangoni A (1976) Therapeutical efficacy of a combination of apomorphine with sulpiride or metoclopramide in parkinsonism. Psychopharmacology 47:169–173
Costall B, Naylor RJ (1977) Démonstration neuropharmacologique de l'effect antidyskinétique du Tiapride. Sem Hôp Paris 53:73–76
Gerlach J, Simmelsgaard H (1978) Tardive dyskinesia during and following treatment with haloperidol, haloperidol+biperiden, thioridazine and clozapine. Psychopharmacology 59:105–112
Jenner P, Marsden CD (1981) Substituted benzamide drugs as selective neuroleptic agents. Neuropharmacology 20:1285–1293
Kazamatsuri H, Chien CP, Cole JO (1972) Treatment of tardive dyskinesia. II. Short-term efficacy of dopamine-blocking agents. Arch Gen Psychiatry 27:100–103
Kebabian JW, Calne DB (1979) Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature 277:93–96
Klawans HL (1973) The pharmacology of tardive dyskinesias. Am J Psychiatry 130:82–86
Lavy S, Melamed E, Penchas S (1978) Tardive dyskinesias associated with metoclopramide. Br Med J 1:77–78
Lees AJ, Lander CM, Stern GM (1979) Tiapride in levodopa-induced involuntary movements. J Neurol neurosurg Psychiatry 42:380–383
Lhermitte F, Agid Y, Feuerstein C, Serre F, Signoret JL, Studler JM, Bonnet AM (1977a) Mouvements anormaux provoqués par la L-dopa dans la maladie de Parkinson. Corrélations avec les concentrations plasmatiques de dopa et de O-méthoxy-dopa. Rev Neurol 133:445–454
Lhermitte F, Signoret JL, Agid Y (1977b) Etude des effects d'une molécule originale, le Tiapride, dans le traitement des mouvements anormaux d'origine extra-pyramidale. Sem Hôp Paris 53:9–15
Niemegeers CJE, Janssen PAJ (1979) A systematic study of the pharmacological activities of dopamine antagonists. Life Sci 24:2201–2216
Pollak P, Gaio JM, Hommel M, Pellat J, Perret J, Chateau R (1982) Modifications de symptômes extra-pyramidaux par l'apomorphine associée à différents antagonistes dopaminergiques. Rev Neurol 138:409–413
Schachter M, Bedard P, Debono AG, Jenner P, Marsden CD, Price P, Parkes JD, Keeman J, Smith B, Rosenthaler J, Horowqki R, Dorow R (1980) The role of D1 and D2 receptors. Nature 286:157–159
Simpson GM, Lee JH, Shrivastava RK (1979) Clozapine in tardive dyskinesia. Psychopharmacology 64:171–179
Sokoloff P, Martres MP, Schwartz JC (1980) Three classes of dopamine-receptors (D-2, D-3, D-4) identified by binding studies with 3H-apomorphine and 3H-domperidone. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 315:89–102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pollak, P., Gaio, JM., Hommel, M. et al. Effects of tiapride in tardive dyskinesia. Psychopharmacology 85, 236–239 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428422
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428422