Summary
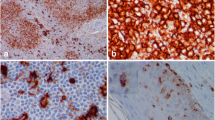
The developmental expression of C3 receptor, an important surface marker of murine epidermal Langerhans cells (LCs), was quantitatively studied using an immunohistochemical technique on epidermal sheets and then compared with developmental expression of Ia antigen and membrane ATPase. Anti-Mac-1 monoclonal antibody associated with CR3 was used for detecting C3 receptor and proved positive for LCs by immunoelectron microscopy. Mac-1 positive (Mac-1+) cells showed quite a different distribution from those of ATPase+ and Ia+ cells. Almost the same number of Mac-1+ and ATPase+ cells were present during the embryonic period. The number of Mac-1+ cells gradually decreased from day 1 to day 5 of postnatal life, after which they increased again. Using the doublelabeling technique on epidermal sheets at day 1 of postnatal life, it was shown that Ia+ cells possessed membrane ATPase activity and some Mac-1+ cells expressed Ia antigen. On days 4 and 7 of postnatal life all Mac-1+ cells expressed Ia antigen. These findings suggest that Mac-1 antigen observed during the embryonic period gradually fades after birth and is re-expressed after day 5 of postnatal life.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beller DI, Springer TA, Schreiber RD (1982) Anti-Mac-1 selectively inhibits the mouse and human type three complement receptor. J Exp Med 156:1000–1009
Fllote TJ, Springer TA, Thorbecke JG (1983) Dendritic cell and macrophage staining by monoclonal antibodies in tissue sections and epidermal sheets. Am J Pathol 111:112–124
Gelfand EW, Resch K, Prester M (1972) Antibody-mediated target cell lysis by non-immune cells. Characterization of the antibody and effector cell population. Eur J Immunol 2:419–424
Hayward AR (1981) Development of lymphocyte responses and interactions in the human fetus and newborn. Immunol Rev 57:39–60
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) A comparative study of the peroxidase-antiperoxidase method and an avidin-biotin complex method for studying polypeptide hormones with radioimmunoassay antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol 75:734–738
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin-biotin peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques. J Histochem Cytochemistry 29:577–580
Katz SI, Tamaki K, Sachs DH (1979) Epidermal Langerhans cells are derived from cells originating in bone marrow. Nature 282:324–326
Kurzinger K, Springer TA (1982) Purification and structural characterization of LFA-1, a lymphocyte function-associated antigen, and Mac-1, a related macrophage distribution antigen associated with the type three complement receptor. J Biol Chem 257:12412–12418
Mackenzie I, Squier CA (1975) Cytochemical identification of ATPase-positive Langerhans cells in EDTA-separated sheets of mouse epidermis. Br J Dermatol 92:523–533
McLean IW, Nakane PK (1974) Periodate-lysine paraformaldehyde fixative: a new fixative for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 22:1077–1083
Romani N, Schuler G, Fritsch P (1986) Ontogeny of Ia-positive and Thy-1-positive leukocytes of murine epidermis. J Invest Dermatol 86:129–133
Scalette LJ, MacCallum DK (1972) A fine structural study of divalent cation-mediated epithelial union with connective tissue in human oral mucosa. Am J Anat 133:431–454
Schweizer J, Marks F (1977) A developmental study of the distribution and frequency of Langerhans cells in relation to formation of patterning in mouse tail epidermis. J Invest Dermatol 69:198–204
Stingl G, Wolff-Schreiner EC, Pinchler WJ, Gschnait F, Knapp W, Wolff K (1977) Epidermal Langerhans cells bear Fc and C3 receptors. Nature 268:245–246
Stingl G, Katz SI, Shevach EM, Rosenthal AS, Green I (1978) Analogous functions of macrophages and Langerhans cells in the initiation of immuno response. J Invest Dermatol 71:59–64
Tamaki K, Stingl G, Gullino M, Sachs DH, Katz SI (1979) Ia antigens in mouse skin are predominantly expressed on Langerhans cells. J Immunol 123:784–787
Weiss LW, Zelickson AS (1975) Embryology of the epidermis: ultrastructural aspects. Acta Derm Venereol (Stockh) 55:431–442
Wright SD, Silverstein SC (1982) Tumor-promoting phorbol esters stimulate C3b and C3d receptor-mediated phagocytosis in cultured human monocytes. J Exp Med 156:1149–1168
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okada, T., Konishi, H., Ito, M. et al. Developmental expression of C3 receptor on murine epidermal Langerhans cells during ontogeny. Arch Dermatol Res 280, 39–44 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00412687
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00412687