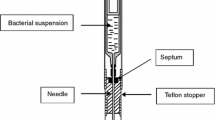
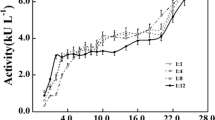
Summary
Enrichment methods — modified penicillin-techniques — were employed for Serratia marcescens HY and CV/rc 3. This was done because Serratia is highly resistant to penicillin. the incubation of HY cells under growth conditions in the presence of 0.04 mg colistin/ml for 8 hrs was found to be effective in inactivating the population to more than 10-2. Auxotrophic mutants under nongrowth conditions were not affected by the antibiotic. The mutant yield of a mutagenized HY culture (NG for 15 min; nearly 80% survival) was increased from 1% to 37–70% after 8 hrs of colistin treatment. Spheroplast formation was not caused by the enrichment procedure.
Nearly the same enrichment method was elaborated for CV/rc 3 with flavomycin, a new antibiotic produced by some strains of Streptomyces, which interacts with cell wall biosynthesis: 9 hrs of incubation in minimal-medium with 0.2 mg flavomycin/ml and following dilution in dest. H2O rose the mutant yield from 6% to 32% after NG treatment of CV/rc 3. Dilution in buffer-saline after flavomycin treatment was less effective because the spheroplasts produced by flavomycin are osmotically fragile.
Four monoauxotrophic HY mutants were tested for selective enrichment after colistin treatment. Selection could not be recognized. Some experiments which are only preliminary show that selection may occur after flavomycin treatment.
Zusammenfassung
Es wurden Anreicherungsmethoden für die penicillinresistenten Serratia-Stämme HY und CV/rc 3 entwickelt. 0,04 mg Colistin/ml Mi-Medium inaktiviert wachsende HY-Zellen auf ca. 10-2 in 8 Std, auxotrophe Zellen werden nicht getötet. Der Anteil auxotropher Zellen in einer Mischung mit Prototrophen wurde durch 8stündige Colistinbehandlung von 1% auf 35–70% gesteigert. Ähnliche Resultate wurden mit Flavomycin an CV/rc 3 gewonnen: 9stündige Behandlung mit 0,2 mg Flavomycin/ml Mi-Medium und anschließende Verdünnung in dest. H2O steigerten den Auxotrophenanteil von 6 auf 32%. Flavomycin erzeugt osmotisch sensible Sphäroplasten, Colistin dagegen nicht.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bliss, E. A., Chandler, C. A., Schoenbach, E. B.: In vitro studies of polymyxin. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 51, 944–951 (1949).
Few, A. V.: Electron microscopy of disrupted bacteria treated with polymyxin E. J. gen. Microbiol. 10, 304–308 (1954).
—: The interaction of polymyxin E with bacterial and other lipids. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 16, 137–145 (1955).
Huber, G., Nesemann, G.: Moenomycin, an inhibitor of cell wall synthesis. Biochim. biophys. Res. Commun. 30, 7–13 (1968).
Huber, G., Schacht, U., Weidenmüller, H. L., Schmidt-Thomé, J., Duphorn, J., Tschesche, R.: Moenomycin, a new antibiotic. II. Characterization and chemistry. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemother. 1965, 737–742 (1966).
Hugo, W. B., Furr, J. R.: Action of penicillin on Serratia marcescens. Antonie v. Leeuwenhoek 33, 265–273 (1967).
Kaplan, R. W.: Dose-effect curves of s-mutation and killing in Serratia marcescens. Arch. Mikrobiol. 24, 60–79 (1956).
—: Studien über die UV-Mutabilität verschiedener Stämme von Serratia und über die Natur der Färbungsmutationen. Arch. Mikrobiol. 32, 138–160 (1959).
Laderberg, J., Lederberg, E. M.: Replica plating and indirect selection of bacterial mutants. J. Bact. 63, 399–406 (1952).
Newton, B. A.: Mechanisms of antibiotic action. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 19, 209–240 (1965).
Reh, M., Schlegel, H. G.: Anreicherung und Isolierung auxotropher Mutanten von Hydrogenomonas H 16. Arch. Mikrobiol. 67, 99–109 (1969).
Schlegel, H. G., Jannasch, H. W.: Enrichment culture. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 21, 49–70 (1967).
—, Schuster, E., Reh, M., Metz, H.: Die Abtötung wachsender Hydrogenomonas-Zellen durch Colistin. Zbl. Bakt., II. Abt. 119, 225–231 (1965).
Szybalski, W., Bryson, V.: Genetic studies on microbial cross resistance to toxic agents. J. Bact. 64, 489–499 (1952).
Wahn, K., Lutsch, G., Rockstroh, T., Zapf, K.: Morphological and physiological investigations on the action of Polymyxin B on Escherichia coli. Arch. Mikrobiol. 63, 103–116 (1968).
Wallhäusser, K. H., Nesemann, G., Präve, P., Steigler, A.: Moenomycin, a new antibiotic. I. Fermentation and isolation. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemother. 1965, 734–736 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stamminger, G., Schwager, M. & Kaplan, R.W. Anreicherung auxotropher Mutanten von Serratia marcescens mittels Antibiotica. Arch. Mikrobiol. 73, 231–237 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00410624
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00410624