Abstract
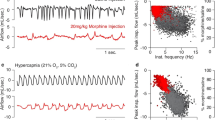
The influence of drugs which modify brain amine concentration was studied on morphine-induced respiratory depression in decerebrate cats. Resting and CO2-stimulated respiration were evaluated. The respiratory depression was partially antagonized by pretreatment with reserpine and p-chlorophenylalanine; enhanced by two monoamine oxidase inhibitors, pargyline and tranylcypromine, and, to some extent, by α-methyl-tyrosine. It was not changed by intracerebral 6-hydroxydopamine. The results show that, as with the other central actions of morphine, the presence of 5-HT is necessary for morphine activity to be complete.
The change in the level of brain amines also modified the respiratory activity in a way that suggests that the respiratory center is stimulated by adrenergic and damped by serotonergic tone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloom, F. E., Algeri, S., Gropetti, A., Revuelta, A., Costa, E.: Lesions of central norepinephrine terminals with 6-OH-dopamine: Biochemistry and fine structure. Science 166, 1284–1286 (1969).
Breese, G. R., Traylor, T. D.: Effect of 6-hydroxydopamine on brain norepinephrine and dopamine: evidence for selective degeneration of catecholamine neurons. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 174, 413–420 (1970).
Cheney, D. L., Goldstein, A.: The effect of p-chlorophenylalanine on opiate-induced running, analgesia, tolerance and physical dependence in mice. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 177, 309–315 (1971).
Conner, R. L., Stolk, J. M., Barchas, J. D., Levine, S.: Parachlorophenylalanine and habituation to repetitive auditory startle stimuli in rats. Physiol. Behav. 5, 1215–1219 (1970).
Contreras, E., Huidobro, F.: Hyposensitivity to drugs induced by morphine and some related substances in the cat. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 39, 789–797 (1970).
Day, M. D., Owen, D. A.: Role of noradrenaline in the acute pressor response to angiotensin in conscious cats. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 40, 884 (1970).
Dewey, W. L., Harris, L. S., Howes, J. F., Nuite, J. A.: The effects of various neurohumoral modulators on the activity of morphine and the narcotic antagonists in the tail-flick and phenylquinone tests. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 175, 435–442 (1970).
Dripps, R. D., Dumke, P. R.: The effect of narcotics on the balance between central and chemoreceptor control of respiration. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 77, 290–300 (1943).
Eidelberg, E., Schwartz, A. S.: Possible mechanism of action of morphine on brain. Nature (Lond.) 225, 1152–1153 (1970).
Fennessy, M. R., Lee, J. R.: Modification of morphine analgesia by drugs affecting adrenergic and tryptaminergic mechanisms. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 22, 930–935 (1970).
Fibiger, H. C., Campbell, B. A.: The effect of p-chlorophenylalanine on spontaneous locomotor activity in the rat. Neuropharmacology 10, 25–32 (1971).
Flórez, J., Borison, H. L.: Effects of central depressant drugs on respiratory regulation in the decerebrate cat. Resp. Physiol. 6, 318–329 (1969).
Flórez, J., McCarthy, L. E., Borison, H. L.: A comparative study in the cat of the respiratory effects of morphine injected intravenously and into the cerebrospinal fluid. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 163, 448–455 (1968).
Goodman, L. S., Gilman, A.: The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 4th ed. New York: The McMillam Press Co. 1970.
Goodrich, C. A.: Effect of monoamineoxidase inhibitors on 5-hydroxytryptamine output from perfused cerebral ventricles of anaesthetized cats. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 37, 87–93 (1969).
Greenberg, S., Long, J. P.: Potentiation by DMAE of the sympathetic component of the vasopressor response to angiotensin. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 174, 35–44 (1970).
Haubrich, D. R., Blake, D. E.: Modification of the hypothermic action of morphine after depletion of brain serotonin and catecholamines. Life Sci. (Part I) 10, 175–180 (1971).
Howard, J. L., Leahy, J. P., Breese, G. R.: Some physiological and behavioral consequences of acute and chronic injection of 6-hydroxydopamine. Fed. Proc. 30, 541 Abs. (1971).
Hoyland, V. J., Shillito, E. E., Vogt, M.: The effect of parachlorophenylalanine on the behaviour of cats. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 40, 659–667 (1970).
King, C. D., Jewett, R. E.: The effects of α-methyltyrosine on sleep and brain norepinephrine in cats. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 177, 188–195 (1971).
Koe, B. K., Weissman, A.: p-chlorophenylalanine. A specific depletor of brain serotonin. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 154, 499–516 (1966).
Koella, W. P., Feldstein, A., Czicman, J. S.: The effect of para-chlorophenylalanine on the sleep of cats. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 25, 481–490 (1968).
McCarthy, L. E., Borison, H. L.: Volumetric compartmentalization of the cranial cerebrospinal fluid system determined radiographically in the cat. Anat. Rec. 155, 305–314 (1966).
Muñoz, C., Paeile, C.: Changes in morphine analgesia induced by drugs which modify catecholamine content of the brain. Arch. Biol. Med. exp. 4, 63–68 (1967).
Nagatsu, T., Levitt, M., Udenfried, S.: Tyrosine hydroxylase. The initial step in norepinephrine biosynthesis. J. biol. Chem. 239, 2910–2917 (1964).
Ngai, S. H.: Effects of morphine and meperidine on the central respiratory mechanisms in the cat; the action of levallorphan in antagonizing these effects. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 131, 91–99 (1961).
Pirch, J. H.: Effect of reserpine and p-chlorophenylalanine on the electrocorticogram of unrestrained rats during short and long recording sessions. Int. J. Neuropharmacol. 8, 535–548 (1969).
Rogers, K. J., Thornton, J. A.: The interaction between monoamineoxidase inhibitors and narcotic analgesics. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 36, 470–480 (1969).
—: Role of brain monoamines in the interaction between pethidine and tranylcypromine. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 14, 86–88 (1971).
Ross, J. W., Ashford, A.: The effect of reserpine and α-methyldopa on the analgesic action of morphine in the mouse. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 19, 709–713 (1967).
Samanin, R., Gumulka, W., Valzelli, L.: Reduced effect of morphine in midbrain raphe lesioned rats. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 10, 339–343 (1970).
- Kon, S., Garattini, S.: Abolition of the morphine effect on body temperature in midbrain raphe lesioned rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. (in Press).
- Valzelli, L.: Increase of morphine-induced analgesia by stimulation of the nucleus raphe dorsalis. Europ. J. Pharmacol. (in Press).
Schneider, J. A.: Reserpine antagonism and morphine analgesia in mice. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.) 87, 614–615 (1954).
Sethy, V.H., Naik, S. R., Sheth, U. K.: The effect of drugs influencing amine synthesis on the analgesic action of tremorine. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 19, 73–80 (1971).
—, Pradhan, R. J., Mandrekar, S. S., Sheth, U. K.: Role of brain amines in the analgesic action of meperidine hydrochloride. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 17, 320–326 (1970).
Sigg, E. B., Caprio, G., Schneider, J. A.: Synergism of amines and antagonism of reserpine to morphine analgesia. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.) 97, 97–100 (1958).
Sparkes, C. G., Spencer, P. S. J.: Antinociceptive activity of morphine after injection of biogenic amines in the cerebral ventricles of the conscious rats. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 42, 230–241 (1971).
Takagi, H., Takashima, T., Kimura, K.: Antagonism of the analgesic effect of morphine in mice by tetrabenazine and reserpine. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 149, 484–492 (1964).
Tenen, S. S.: The effects of p-chlorophenylalanine, a serotonin depletor, on avoidance acquisition, pain sensitivity and related behavior in the rat. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 10, 204–219 (1967).
—: Antagonism of the analgesic effect of morphine and other drugs by p-chlorophenylalanine, a serotonin depletor. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 12, 278–285 (1968).
Vedernikov, Y. P., Afrikanov, I. I.: On the role of a central adrenergic mechanism in morphine analgesic action. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 21, 845–847 (1969).
Verri, R. A., Graeff, F. G., Corrado, A. P.: Effect of reserpine and alpha-methyltyrosine on morphine analgesia. Int. J. Neuropharmacol. 7, 283–292 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flórez, J., Delgado, G. & Armijo, J.A. Adrenergic and serotonergic mechanisms in morphine-induced respiratory depression. Psychopharmacologia 24, 258–274 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00403646
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00403646