Abstract
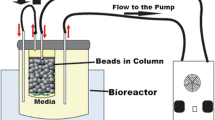
When the immobilized cells are employed in packed-bed bioreactors several problems appear. To overcome these drawbacks, a new bioreactor based on the use of pulsed systems was developed [1]. In this work, we study the glucose fermentation by immobilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae in a packed-bed bioreactor. A comparative study was then carried out for continuous fermentation in two packed-bed bioreactors, one of them with pulsed flow. The determination of the axial dispersion coefficients indicates that by introducing the pulsation, the hydraulic behaviour is closer to the plug flow model. In both cases, the residence time tested varied from 0.8 to 2.6 h. A higher ethanol concentration and productivity (increases up to 16%) were achieved with the pulsated reactors. The volumes occupied by the CO2 were 5.22% and 9.45% for fermentation with/without pulsation respectively. An activity test of the particles from the different sections revealed that the concentration and viability of bioparticles from the two bioreactors are similar. From the results we conclude that the improvements of the process are attributable to a mechanical effect rather than to physiological changes of microorganisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D m2/s:
-
dispersion coefficient
- K is l/g:
-
inhibition substrate constant
- K ip l/g:
-
inhibition ethanol constant
- K s g/l:
-
Apparent affinity constant
- P g/l:
-
ethanol concentration
- q p g/(gh):
-
specific ethanol productivity
- Q p g/(lh):
-
overall ethanol productivity
- q s g/(gh):
-
specific glucose consumption rate
- Q s g/(lh):
-
glucose consumption rate
- S g/l:
-
residual glucose concentration
- S(in0) g/l:
-
initial glucose concentration
- V max g/(lh):
-
maximum rate
- Y p/s g/g:
-
yield in product
References
Sanromán, A.; Chamy, R.; Nuñez, M. J.; Lema, J. M.: Enzymatic hydrolysis of starch in a fixed-bed pulsed flow reactor. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 28/29 (1991) 527–538
Roca, E.; Sanromán, A.; Núñez, M. J.; Lema, J. M.: Determination of axial dispersion coefficients in a fixed packed-bed pulsed flow bioreactor. 5th Mediterranean Congress on Chemical Engineering. Barcelona. P4.525 (1990) 564–565
Lema, J. M.; Nuñez, M. J.; Sanromán, A.; Roca, E.: Dispositivo de pulsación para ser acoplado a equipos de fermentación, reactores enzimáticos o reactores químicos. Spanish Patent: P 9200315. (1991)
Chamy, R.; Nuñez, M. J.; Lema, J. M.: Optimization of hardening treatment of S. cerevisiae bioparticles. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 12 (1990) 749–754
Bernfeld, P. D.: Enzymes of starch degradation and synthesis. Adv. Enzymol. 12 (1951) 379–427
Veiga, M. C.; Soto, M.; Mendez, R.; Lema, J. M.: A new device for measurement and control of gas production by bench scale anaerobic digesters. Wat. Res. 24 (1990) 1551–1554
Levespiel, O.: Chemical Reaction Engineering. New York. Wiley 1983
Bouzas, S.; Casares, J. J.; Lema, J. M.: Análisis de reactores de flujo no ideal. II. Ajuste a modelos de un solo parámetro. Ingeniería Química. 235 (1988) 115–120
Daugulis, A. J.; Swaine, D. E.: Examination of substrate and product inhibition kinetics on the production of ethanol by suspended and immobilized cell reactors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 29 (1987) 639–645
Bunday, B. D.: Basic Optimization Methods. London. E. Arnold Pu. 1984
Dourado, A.; Goma, G.; Albuquerque, U.; Sevely, Y.: Modelling and static optimization of the ethanol production in a cascade reactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 29 (1987) 187–194
Ghose, T. K.; Tyagy, R. D.: Rapid ethanol fermentation of cellulose hydrolysate. I. Batch versus continuous systems. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 21 (1979) 1387–1400
Ghose, T. K.; Tyagy, R. D.: Rapid ethanol fermentation of cellulose hydrolysate. II. Product and substrate inhibition and optimization of fermenter design. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 21 (1979) 1401–1420
Gòdia, F.; Casas, C.; Solà, C.: Mathematical modelling of a packed-bed reactor performance with immobilized yeast for ethanol fermentation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 30 (1987) 836–843
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanromán, A., Roca, E., Núñez, M.J. et al. A pulsing device for packed-bed bioreactors: II. Application to alcoholic fermentation. Bioprocess Engineering 10, 75–81 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393389
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393389