Abstract
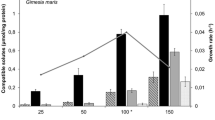
The intracellular concentrations of low-molecular weight carbohydrates and quaternary ammonium compounds present in 26 axenic isolates of unicellular cyanobacteria have been studied over a range of external salinity from freshwater up to 300% seawater (100%=35‰ S). In all cases, a single carbohydrate, either sucrose or glucosylglycerol, was identified as the principal organic osmoticum, showing major variation in response to the external salt concentration; quaternary ammonium compounds were present in osmotically insignificant amounts. Glucosylglycerol was accumulated as primary osmoticum by nine of the isolates from saline habitats and by five of the freshwater isolates; trace amounts of sucrose were also prsent. The remaining twelve freshwater strains accumulated sucrose as sole osmoticum. Glucosylglycerol-accumulating strains grew over the widest salinity range (up to 200 to 250% seawater), whether isolated from saline or non-saline habitats. Sucrose-accumulating strains were more stenohaline, growing only in up to 50 to 100% seawater and showing no sustained growth in hypersaline media (>100% seawater). The data suggest that (1) glycosylglycerol accumulation is not unique to marine cyanobacteria, and (2) the upper salinity limit for growth may be linked to organic solute accumulation, rather than habitat, with glucosylglycerol-accumulating isolates having a greater potential for growth in salt-stressed conditions than sucrose accumulators.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Ben Amotz, A. and M. Avron: Accumulation of metabolites by halotolerant algae and its industrial potential. A. Rev. Microbiol. 37, 95–119 (1983)
Bisson, M. A. and G. O. Kirst: Osmotic adaptation in the marine alga Griffithsia monilis (Rhodophyceae): the role of ions and organic compounds. Aust. J. Pl. Physiol 6, 523–538 (1979)
Bisson, M. A. and G. O. Kirst: Lamprothamnium, a euryhaline charophyte. II. Time course of turgor regulation. J. exp. Bot. 31, 1237–1244 (1980)
Blumwald, E., R. J. Mehlhorn and L. Packer: Studies of osmoregulation in salt adaptation of cyanobacteria with ESR spinprobe techniques. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. USA. 80, 2599–2602 (1983)
Blumwald, E. and E. Tel-Or: Osmoregulation and cell composition in salt-adaptation of Nostoc muscorum. Archs Microbiol. 132, 168–172 (1982)
Borowitzka, L. J.: Solute accumulation and regulation of cell water activity. In: The physiology and biochemistry of drought resistance in plants, pp 97–130 Ed. by L. G. Paleg and D. Aspinall. London: Academic Press 1981
Borowitzka, L. J., S. Demmerle, M. A. Mackay and R. S. Norton: Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance study of osmoregulation in a blue-green alga. Science, N.Y. 210, 650–651 (1980)
Bouillard, L. and D. Le Rudulier: Nitrogen fixation under osmotic stress: enhancement of nitrogenase biosynthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae by glycine betaine. Physiologie vég. 21, 447–457 (1983)
Brown, A. D.: Microbial water stress. Bact. Rev. 40, 803–846 (1976)
Brown, A. D.: Halophilic prokaryotes. In: Encyclopedia of plant physiology, Vol. 12C. pp 137–162. Ed. by O. L. Lange, P. S. Nobel, C. B. Osmond and H. Ziegler. Berlin: Springer-Verlag 1983
Brown, A. D. and J. R. Simpson: Water relations of sugar-tolerant yeasts: the role of intracellular polyols. J. gen. Microbiol. 72, 589–591 (1972)
Brown, A. D. and J. A. Hellebust: The contribution of organic solutes to osmotic balance in some green and enstigmatophyte algae. J. Phycol. 16, 265–270 (1980)
Carr, N. G. and B. A. Whitton (Eds.): The biology of Cyanobacteria, 688 pp. Oxford: Blackwell 1982
Craigie, J. S.: Storage products. In: Algal physiology and biochemistry, pp 206–235. Ed. by W. D. P. Stewart. Oxford: Blackwell 1974
Craigie, J. S. and J. McLachlan: Glycerol as a photosynthetic product in Dunaliella tertiolecta Butcher. Can. J. Bot. 42, 777–778 (1964)
Cram, W. J.: Negative feedback regulation of transport in cells. The maintenance of turgor, volume and nutrient supply. In: Encyclopedia of plant physiology, Vol 2A. pp 284–326. Ed. by U. Luttge and M. G. Pitman. Berlin: Springer-Verlag 1976
Dickson, D. M., J. Davenport and R. G. Wyn Jones: Steady state osmotic adaptation in Ulva lactuca. Planta 150, 158–165 (1980)
Erdmann, N.: Organic osmoregulatory solutes in blue-green algae. Z. PflPhysiol. 110 147–155 (1983)
Fogg, G. E., W. D. P. Stewart, P. Fay and A. E. Walsby: The blue-green algae, 459 pp. London: Academic Press 1973
Hellebust, J. A.: Osmoregulation. A. Rev. Pl. Physiol. 27, 485–507 (1976)
Hinton, R. H., M. L. E. Burge and G. C. Hartman: Sucrose interference in the assay of enzymes and protein. Analyt. Biochem. 29, 248–256 (1969)
Holligan, P. M. and E. A. Drew: Routine analysis by gas-liquid chromatography of soluble carbohydrates in extracts of plant tissues. II. Quantitative analysis of standard carbohydrates, and the separation and estimation of soluble sugars and polyols from a variety of plant tissues. New Phytol. 70, 271–297 (1971)
Kauss, H.: Isofloridosid und Osmoregulation bei Ochromonas malhamensis. Z. PflPhysiol 56, 453–465 (1967)
Kauss, H.: α-Galaktosylglyzeride und Osmoregulation in Rotalgen. Z. PflPhysiol. 58, 428–433 (1968)
Kauss, H.: Osmotic regulation in algae. Prog. Phytochem. 5, 1–27 (1978)
Kirst, G. O.: The cell volume of the unicellular alga Platymonas subcordiformis Hazen.: effect of the salinity of the culture medium and of osmotic stresses. Z. PflPhysiol. 81, 386–394 (1977)
Kirst, G. O. and M. A. Bisson: Regulation of turgor in marine algae: ions and low-molecular weight organic compounds. Aust. J. Pl. Physiol. 6, 539–556 (1979)
Kremer, B. P.: Aspects of carbon metabolism in marine macroalgae. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 19, 41–94 (1981)
Mackay, M. A., R. S. Norton and L. J. Borowitzka: Marine bluegreen algae have a unique osmoregulatory system. Mar. Biol. 73, 301–307 (1983)
Mackay, M. A., R. S. Norton and L. J. Borowitzka: Organic osmoregulatory solutes in cyanobacteria. J. gen. Microbiol. 130, 2177–2191 (1984)
Miller, D. M., J. H. Jones, J. H. Yopp, D. R. Tindall and W. E. Schmid: Ion metabolism in a halophilic blue-green alga, Aphanothece halophytica. Archs Microbiol 111, 145–149 (1976)
Mohammad, F. A. A., R. H. Reed and W. D. P. Stewart: The halophilic cyanobacterium Synechocystis DUN52 and its osmotic responses. Fedn eur. microbiol. Soc. (FEMS) Lett. 16, 287–290 (1983)
Parsons, T. R.: Coulter counter for phytoplankton. In: Handbook of phycological methods, pp 345–358. Ed. by J. R. Stein. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1973
Pollard, A. and R. G. Wyn Jones: Enzyme activities in concentrated solutions of glycine betaine and other solutes. Planta 144, 291–298 (1979)
Reed, R. H.: Taxonomic implications of osmoacclimation in Cyanidium caldarium (Tilden) Geitler. Phycologia 22, 351–354 (1983a)
Reed, R. H.: Measurement and osmotic significance of β-dimethylsulphoniopropionate in marine macroalgae. Mar. Biol. Lett. 4, 173–181 (1983b)
Reed, R. H.: Osmoacclimation in Bangia atropurpurea (Rhodophyta, Bangiales): the osmotic role of floridoside. Br. phycol. J. 20 (In press). (1985)
Reed, R. H., J. C. Collins and G. Russell: The effects of salinity upon galactosyl-glycerol content and concentration of the marine red alga Porphyra purpurea (Roth) C. Ag. J. exp. Bot. 31, 1539–1554 (1980)
Reed, R. H., J. A. Chudek, R. Foster and W. D. P. Stewart: Osmotic adjustment in cyanobacteria from hypersaline environments. Archs Microbiol. 138, 333–337 (1984a)
Reed, R. H., D. L. Richardson and W. D. P. Stewart: Na+ uptake and extrusion in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC 6714 in response to hypersaline treatment: evidence for transient changes in membrane permeability. Biochim. biophys. Acta 814, 347–355 (1985)
Reed, R. H., D. L. Richardson, S. R. C. Warrand W. D. P. Stewart: Carbohydrate accumulation and osmotic stress in cyanobacteria. J. gen. Microbiol. 130, 1–4 (1984b)
Reed, R. H. and W. D. P. Stewart: Physiological responses of Rivularia atra to salinity: osmotic adjustment in hyposaline media. New Phytol. 95, 595–603 (1983)
Richardson, D. L., R. H. Reed and W. D. P. Stewart: Synechocystis PCC 6803: a euryhaline cyanobacterium. Fedn eur. microbiol. Soc. (FEMS) Lett. 18, 99–102 (1983)
Rippka, R. and G. Cohen-Bazire: The Cyanobacteriales: a legitimate order based on the type strain Cyanobacterium stanieri? Annls Inst. Pasteur, Paris (Microbiol.) 134 B 21–36 (1983)
Rippka, R., J. Deruelles, J. B. Waterbury, M. Herdman and R. Y. Stanier: Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J. gen. Microbiol. 111, 1–61 (1979)
Setter, T. L. and H. Greenway. Growth and osmoregulation of Chlorella emersonii in NaCl and neutral osmotica. Aust. J. Pl. Physiol. 6, 47–60 and (Corrigendum) 569-572 (1979)
Warr, S. R. C., R. H. Reed, J. A. Chudek, R. Foster and W. D. P. Stewart: Osmotic adjustment in Spirulina platensis. Planta 163, 424–429 (1985a)
Warr, S. R. C., R. H. Reed and W. D. P. Stewart: Physiological responses of Nodularia harveyana to osmotic stress. Mar. Biol. 79, 21–26 (1984a)
Warr, S. R. C., R. H. Reed and W. D. P. Stewart: Osmotic adjustment of cyanobacteria: the effects of NaCl, KCl, sucrose, and glycine betaine on glutamine synthetase activity in a marine and a halotolerant strain. J. gen. Microbiol. 130, 2169–2175 (1984b)
Warr, S. R. C., R. H. Reed and W. D. P. Stewart: Carbohydrate accumulation in osmotically stressed cyanobacteria (bluegreen algae): interactions of temperature and salinity. New Phytol. (In press) (1985b)
Wetherall, D. F.: Osmotic equilibration and growth of Scenedesmus obliquus in saline media. Physiologia Pl. 16, 82–91 (1963)
Wyn Jones, R. G. and J. Gorham: Osmoregulation. In: Encyclopedia of plant physiology, Vol. 12C. pp 35–58. Ed. by O. L. Lange, P. S. Nobel, C. B. Osmond and H. Ziegler. Berlin: Springer-Verlag 1983
Yopp, J. H., D. M. Miller and D. R. Tindall: Regulation of intracellular water potential in the halophilic blue-green alga Aphanothece halophytica (Chroococcales). In: Energetics and structure of halophilic microorganisms, pp 619–624 Ed. by S. R. Caplan and M. Ginzburg. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1978
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reed, R.H., Stewart, W.D.P. Osmotic adjustment and organic solute accumulation in unicellular cyanobacteria from freshwater and marine habitats. Mar. Biol. 88, 1–9 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393037
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393037