Abstract
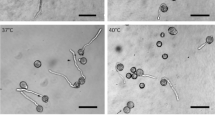
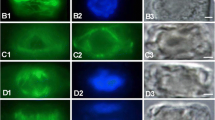
In the epidermal cells of onion (Allium cepa L.) bulb scales the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) can be subdivided into three domains: a peripheral tubular network, cisternae, and long tubular strands. The latter are the form in which the ER is moved in onion cells. During cold treatment the arrangement of the three domains changes drastically. The cisternae and long tubular strands disintegrate into short ER tubules which show rapid agitational motion. Long-distance movement is inhibited. The peripheral tubular ER network is presumably retained during cold treatment. Rewarming of previously chilled bulb scales initiates the reorganization of the ER into the three domains. The ER is partly relocated during recovery from cold treatment. Redistribution and reorganization of the ER is not affected by the microtubule-destabilizing herbicides oryzalin and trifluralin (5 μM). Cytochalasin D (2μM), however, inhibits not only the relocation of ER material, as is evident by the absence of long tubular ER strands, but also the movement of other cell organelles. The latter cluster on top of the cisternae in a manner which is characteristic of treatment with the actin-filament inhibitor. The array of actin filaments is similar in unstressed, cold-treated cells, and cells which recover from low temperatures in the presence of oryzalin or tap water alone. In the presence of cytochalasin D the actin filaments are severely fragmented. The results indicate that low temperatures most likely influence either the interaction of the force-generating system, probably myosin, with actin filaments, or the force-generating mechanism of the actomyosin-driven intracellular movement, but do not affect actin-filament integrity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DiOC6 :
-
3,3′-dihexyloxacarbocyanine iodide
- ER:
-
endoplasmic reticulum
References
Brown, S.S., Spudich, J.A. (1981) Mechanism of action of cytochalasin B: evidence that it binds to actin filament ends. J. Cell Biol. 88, 487–491
Forde, J., Steer, M.W. (1976) Cytoplasmic streaming in Elodea. Can. J. Bot. 54, 2688–2694
Girbardt, M. (1965) Lebendnachweis von Einzelelementen des endoplasmatischen Retikulums. J. Cell Biol. 27, 433–440
Goosen-de Roo, L., Burggraff, P.D., Libbenga, K.R. (1983) Microfilament bundles associated with tubular endoplasmic reticulum in fusiform cells in the active cambial zone of Fraxinus excelsior L. Protoplasma 116, 204–208
Graham, D., Patterson, B.D. (1977) Effect of chilling temperatures on the protoplasmic streaming of plants from different climates. J. Exp. Bot. 28, 736–743
Graham, D., Patterson, B.D. (1982) Response of plants to low non-freezing temperatures: proteins, metabolism and acclimation. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 33, 347–372
Harris, N. (1986) Organization of the endomembrane system. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 37, 73–92
Hensel, W. (1985) Cytochalasin B affects the structural polarity of statocytes from roots (Lepidium sativum). Protoplasma 129, 178–187
Ilker, R., Breidenbach, R.W., Lyons, J.M. (1979) Sequence of ultrastructural changes in tomato cotyledons during short periods of chilling. In: Low temperature stress in crop plants, pp. 97–125, Lyons, J.M., Raison, J.K., Steponkus, P.L., eds. Academic Press, New York
Itoh, S. (1962) Light and electronmicroscopic study of membranous cytoplasmic organelles. In: The interpretation of ultrastructure, pp. 129–148, Harris, R.J.C., ed. Academic Press, New York
Kamiya, N. (1959) Protoplasmic streaming. Protoplasmatologia VIII. 3a, 1–199
Lloyd, C.W. (1987) The plant cytoskeleton: The impact of fluorescence microscopy. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 38, 119–139
Lyons, J.M., Raison, J.K., Steponkus, P.L. (1979) The plant membrane in response to low temperature: an overview. In: Low temperature stress in crop plants, pp. 1–24, Lyons, J.M., Raison, J.K., Steponkus, P.L., eds. Academic Press, New York
McCully, M.E., Canny, B.C. (1985) The stabilization of labile configurations of plant cytoplasm by freeze sustitution. J. Microsc. Oxford 139, 27–33
Minorsky, P.V. (1985) A heuristic hypothesis of chilling injury in plants: a role for calcium as the primary physiological transducer of injury. Plant Cell Environ. 8, 75–94
Palevitz, B.V., Hodge, L.D. (1984) The endoplasmic reticulum in the cortex of developing guard cells: coordinate studies with chlorotetracycline and osmium ferricyanide. Dev. Biol. 101, 147–159
Parthasarathy, M.V., Perdue, T.D., Witztum, A., Alvernaz, J. (1985) Actin network as a normal component of the cytoskeleton in many vascular plant cells. Am. J. Bot. 72, 1318–1323
Pryme, I.F., Hesketh, J.E. (1987) Cytochalasin B binding and actin content of endoplasmic reticulum subfractions isolated from L-929 cells. Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 11, 615–623
Quader, H., Schnepf, E. (1986) Endoplasmic reticulum and cytoplasmic streaming: Fluorescence microscopical observations in adaxial epidermis cells of onion bulb scales. Protoplasma 131, 250–253
Quader, H., Hofmann, A., Schnepf, E. (1987a) Shape and movement of the endoplasmic reticulum in onion bulb epidermis cells: possible involvement of actin. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 44, 17–26
Quader, H., Hofmann, A., Schnepf, E. (1987b) Circumstantial evidence for the involvement of actin in ER distribution in plant cells. (Abstr.) Eur. J. Cell Biol. 43 Suppl. 17, 45
Terasaki, M., Song, J., Wong, J.R., Weiss, M.J., Chen, L.B. (1984) Localization of endoplasmic reticulum in living and glutaraldehyde-fixed cells with fluorescent dyes. Cell 83, 101–108
Tominaga, Y., Shimmen, T., Tazawa, M. (1983) Control of cytoplasmic streaming by extracellular Ca2+ in permeabilized Nitella cells. Protoplasma 116, 75–77
Tucker, E.B., Allen, N.S. (1986) Intracellular particle motions (cytoplasmic streaming) in staminal hairs of Setcreasea purpurea: effect of azide and low temperature. Cell Motil. Cytoskel. 6, 305–313
Url, W. (1967) Das endoplasmatische Retikulum von Desmidiaceen im Phasenkontrast. Protoplasma 64, 26–48
Williamson, R.E. (1979) Filaments associated with the endoplasmic reticulum in the streaming cytoplasm of Chara corallina. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 20, 177–183
Williamson, R.E. (1986) Organelle movement along actin filaments and microtubules. Plant Physiol. 82, 631–634
Woods, C.M., Reids, M.S., Patterson, B.D. (1984a) Response to chilling stress in plant cells. I. Changes in cyclosis and cytoplasmic structure. Protoplasma 121, 8–16
Woods, C.M., Polito, V.S., Reid, M.S. (1984b) Response to chilling stress in plant cells. II. Redistribution of intracellular calcium. Protoplasma 121, 17–24
Wulf, E., Deboben, A., Bautz, F.A., Faulstich, H., Wieland, Th. (1979) Fluorescent phallotoxin, a tool for visualization of cellular actin. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 76, 4498–4502
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quader, H., Hofmann, A. & Schnepf, E. Reorganization of the endoplasmic reticulum in epidermal cells of onion bulb scales after cold stress: Involvement of cytoskeletal elements. Planta 177, 273–280 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392816
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392816