Abstract
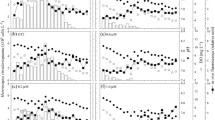
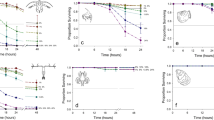
The interactive effects of copper and zinc on two estuarine planktonic ciliates, Favella sp. and Balanion sp., were determined in seawater media in which the free metal ion activities were controlled by nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) trace metal ion buffer systems. Cupric ion activities of 10-10 M caused abnormal motility in both ciliates in shortterm (5 h) tests, and cupric ion activities as low as 10-12.8 M decreased the growth rates of both species in longer-term experiments. In the short-term tests, zinc ion activity by itself did not affect the motility of the ciliates, but there were significant interactions between copper and zinc. In the longer-term experiments, the growth of Favella sp. was optimal at the lowest cupric ion activity (10-13 M) and the two lowest zinc ion activities (10-12 and 10-13 M) and the two lowest zinc ion activities (10-12 and 10-11 M), and copper and zinc inhibited growth at activities above these values. By contrast, optimal growth rate of Balanion sp. occurred at the highest zinc ion activity (10-10 M) and the lowest cupric ion activities (10-13 to 10-12 M) and growth rate was reduced at zinc ion activities ≦10-11 M. There was an antagonism between copper and zinc which was particularly pronounced in Balanion sp.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Anderson, D. M., J. S. Lively and R. F. Vaccaro: Copper complexation during spring phytoplankton blooms in coastal waters. J. mar. Res. 42, 677–695 (1984)
Anderson, D. M. and F. M. M. Morel: Copper sensitivity of Gonyaulax tamarensis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 23, 283–295 (1978)
Anderson, M. A., F. M. M. Morel and R. R. L. Guillard: Growth limitation of a coastal diatom by low zinc ion activity. Nature, Lond. 276, 70–71 (1978)
Beers, J. R. and G. L. Stewart: Micro-zooplankton in the euphotic zone at five locations across the California current. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 24, 2053–2068 (1967)
Beers, J. R. and G. L. Stewart: Micro-zooplankton and its abundance relative to the larger zooplankton and other seston components. Mar. Biol. 4, 182–189 (1969)
Beers, J. R. and G. L. Stewart: Numerical abundance and estimated biomass of micro-zooplankton. Bull. Scripps Inst. Oceanogr. 17, 67–87 (1970)
Beers, J. R. and G. L. Stewart: Micro-zooplankters in the plankton communities of the upper waters of the eastern tropical Pacific. Deep-Sea Res. 18, 861–883 (1971)
Beers, J. R., G. L. Stewart and K. D. Hoskins: Dynamics of micro-zooplankton populations treated with copper: controlled ecosystem pollution experiment. Bull. mar. Sci. 27, 66–79 (1977)
Borgman, U.: Determination of free metal ion concentration using bioassays. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 38, 999–1002 (1981)
Brand, L. E., W. G. Sunda and R. R. L. Guillard: Limitation of marine phytoplankton reproductive rates by zinc, manganese, and iron. Limnol. Oceanogr. 28, 1182–1198 (1983)
Brand, L. E., W. G. Sunda and R. R. L. Guillard: Reduction of marine phytoplankton reproduction rates by copper and cadmium. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. (In press)
Capriulo, G. M. and E. J. Carpenter: Abundance, species composition and feeding impact of tintinnid micro-zooplankton in central Long Island Sound. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 10, 277–288 (1983)
Davies, A. G. and J. A. Sleep: Inhibtion of carbon fixation as a function of zinc uptake in natural phytoplankton assemblages. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 59, 937–949 (1979)
Guillard, R. R. L.: Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates, pp 29–70. In: Culture of marine invertebrate animals. Ed. by W. L. Smith and M. H. Chanley, New York Plenum Publishing Corp. 1975
Harrison, G. I. and F. M. M. Morel: Antagonism between cadmium and iron in the marine diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii. J. Phycol. 19, 495–507 (1983)
Hart, B. A., P. E. Bertram and B. D. Scaife: Cadmium transport by Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Envir. Res. 18, 327–335 (1979)
Hasle, G. R.: The inverted microscope method, pp 88–96, In: Phytoplankton manual. Monogr. Oceanogr. Method. Vol. 6 UNESCO 1978
Heinbokel, J. F. and J. R. Beers: Studies on the functional role of tintinnids in the southern California Bight. III. Grazing impact of natural assemblages. Mar. Biol. 52, 23–32 (1979)
Hering, J. G., F. M. M. Morel, W. G. Sunda and R. L. Ferguson: Copper complexation in the New York Bight: a comparison of bacterial bioassay and fixed-potential amperometry. Mar. Chem. (In press)
Huntsman, S. A. and W. G. Sunda: The role of trace, metals in regulating phytoplankton, growth with emphasis on Fe, Mn and Cu, pp 285–328. In: The physiological ecology of phytoplankton. Ed. by I. Morris, Berkely: Univ. of California Press 1980
Jackson, G. A. and J. J. Morgan: Trace metal-chelator interactions and phytoplankton growth in seawater media: theoretical analysis and comparison with reported observations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 23, 268–282 (1978)
Martell, A. E. and R. M. Smith: Critical stability constants, vol. 1, 469 pp. Amino acids. New York: Plenum Press 1974
Morel, F. M. M. and N. M. L. Morel-Laurens: Trace metals and plankton in the oceans: facts and speculations, pp 841–869. In: Trace metals in seawater. Ed. by C. S. Wong, E. Boyle, K. W. Bruland, J. D. Burton and E. D. Goldberg: Proc. NATO Advanced Research Institute, New York: Plenum Press 1983
Oakden, J. M., J. S. Oliver and A. R. Flegal: EDTA chelation and zinc antagonism with cadmium in sediment: effects on the behavior and mortality of two infaunal amphipods. Mar. Biol. 84, 125–130 (1984)
Price, C. A. and J. W. Quigley: A method for determining quantitative zinc requirements for growth. Soil Sci. 101, 11–16 (1966)
Rueter, J. G. Jr. and F. M. M. Morel: The interaction between zinc deficiency and copper toxicity as it affects the silicic acid uptake mechanisms in Thalassiosira pseudonana. Limnol. Oceanogr. 26, 67–73 (1981)
Sokal, R. R. and F. J. Rohlf: Biometry (second ed), 859 pp, San Francisco: W. H. Freeman and Co. 1981
Stoecker, D. K., T. L. Cucci, E. M. Hulburt and C. M. Yentsch: Selective feeding by Balanion sp. (Ciliata: Balanionidae) on phytoplankton that best support its growth. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 95 (In press)
Stoecker, D., L. H. Davis and D. M. Anderson: Fine scale spatial correlations between planktonic ciliates and dinoflagellates. J. Plank. Res 6, 829–842 (1984)
Stoecker, D. and G. T. Evans: Effects of protozoan herbivory and carnivory in a microplankton food web. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 25, 159–167 (1985)
Stoecker, D., R. R. L. Guillard and R. M. Kavee: Selective predation by Favella ehrenbergii (Tintinnina) on and among dinoflagellates. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 160, 136–145 (1981)
Sunda, W. G.: Relationship between cupric ion activity and the toxicity of copper to phytoplankton, 168 pp. Ph.D. Thesis, M.I.T. 1975
Sunda, W. G. and R. L. Ferguson: Sensitivity of natural bacterial communities to additions of copper and to cupric ion activity: a bioassay of copper complexation in seawater, pp 871–891: In: Trace metals in seawater. Ed. by C. S. Wong, E. Boyle, K. W. Bruland, J. D. Burton and E. D. Goldberg. Proc. NATO Advanced Research Institute. New York: Plenum Press 1983
Sunda, W. G. and P. A. Gillespie: The response of a marine bacterium to cupric ion and its use to estimate cupric ion activity in seawater. J. mar. Res. 37, 761–777 (1979)
Sunda, W. G. and R. R. L. Guillard: The relationship between cupric ion activity and the toxicity of copper to phytoplankton. J. mar. Res. 34, 511–529 (1976)
Sunda, W. G. and S. A. Huntsman: Effect of competitive interactions between manganese and copper on cellular manganese and growth in estuarine and oceanic species of the diatom Thalassiosira. Limnol. Oceanogr. 28, 924–934 (1983)
Sunda, W. G. and S. A. Huntsman: Regulation of cellular manganese and manganese transport rates in the unicellular alga Clamydomonas. Limnol. Oceanogr. 30, 71–80 (1985)
Sunda, W. G., P. A. Tester and S. A. Huntsman: Effects of cupric and zinc ion activities on the survival and reproduction of copepods. (Unpublished manuscript)
Willis, J. N. and W. G. Sunda: Relative contributons of food and water in the accumulation of zinc by two species of marine fish. Mar. Biol. 80, 273–279 (1984)
Zamuda, C. D. and W. D. Sunda: Bioavailability of dissolved copper to the American oyster Crassostrea virginica I. Importance of chemical speciation. Mar. Biol. 66, 77–82 (1982)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Shick, Orono
Contribution No. 5871 from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stoecker, D.K., Sunda, W.G. & Davis, L.H. Effects of copper and zinc on two planktonic ciliates. Marine Biology 92, 21–29 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392741
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392741