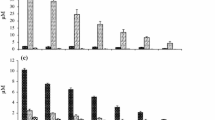
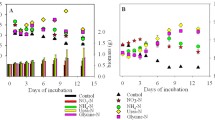
Abstract
The responses of natural summer coastal plankton communities to low-level additions (10-5 to 10-7 M) of arginine and glutamic acid has been followed by in vivo measurement of chlorophyll fluorescence. This technique is capable of detecting a response to a 10-6 M enrichment under most conditions. The time sequence of the response varied with the amino acid used and with the enantiomeric form of the amino acid. Ammonia and carbon dioxide were liberated before the increase in chlorophyll fluorescence occurred. Liberation of ammonia in a dark bottle from L-arginine was from 75 to 85% of the theoretical yield. Microautoradiography using 14C L-arginine or L-glutamic acid at 10-7 M showed heavy labeling associated with fecal pellets and detrital aggregates. Phytoplankton cells were not appreciably labeled. The evidence suggests that bacteria are important in the cycling of these compunds.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Andrews, P. and P.J. LeB. Williams: Heterotrophic utilization of dissolved organic compounds in the sea. III. Measurements of the oxidation rates and concentrations of glucose and amino acids in seawater. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 51, 111–125 (1971)
Bada, J.L.: Kinetics of nonbiological decomposition and racemization of amino acids in natural waters. Adv. Chem. Ser. 106, 309–331 (1971)
Brock, M.L. and T.D. Brock: The application of microautoradiographic techniques to ecological studies. Mitt. int. Verein. theor. angew. Limnol. 15, 1–29 (1968)
Carpenter, E.J., C.C. Remsen and S.W. Watson: Utilization of urea by some marine phytoplankters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17, 265–269 (1972)
Concver, R.J.: Feeding on large particles by Calanus hyperboreus (Kroyer). In: Some contemporary studies in marine science, pp 187–194. Ed. by H. Barnes. London: Allen and Unwin 1966
Conover, S.M.: Nitrate, ammonium and urea as nitrogen sources for marine diatoms in culture and in spring blooms, Ph.D. thesis, Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S., Canada 1974
Degens, E.T.: Molecular nature of nitrogenous compounds in sewater and recent marine sediments. Occ. Publs Inst. mar. Sci. Univ. Alaska Coll. 1, 77–106 (1970)
Derenbach, J.B. and P.J. LeB. Williams: Autotrophic and bacterial production: fractionation of plankton populations by differential filtration of samples from the English Channel. Mar. Biol. 25, 263–269 (1974)
Guillard, R.R.L. and J.H. Ryther: Studies on marine plankton diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea (Cleve) Gran. Can. J. Microbiol. 8, 229–239 (1962)
Hobbie, J.J., C.C. Crawford and K.L. Webb: Amino acid flux in an estuary. Science, N.Y. 159, 1463–1464 (1968)
Hoshaw, R.W. and J.R. Rosowski: Methods for microscopic algae. In: Handbook of phycological methods, Chapter 3. pp 53–67. Ed. by J.R. Stein. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press 1973
McCarthy, J.J.: The uptake of urea by natural populations of marine phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17, 738–748 (1972)
Munro, A.L.S. and T.D. Brock: Distinction between bacterial and algal utilization of soluble substances in the sea. J. gen. Microbiol. 51, 35–42 (1968)
Neilson, A.H. and R.A. Lewin: The uptake and utilization of organic carbon by algae: an essay in comparative biochemistry. Phycologica 13, 227–264 (1974)
North, B.B.: Primary amines in California coastal waters: utilization by phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 20, 20–27 (1975)
Otsuki, A. and T. Hanya: Production of dissolved organic matter from dead green algal cells. I. Aerobic microbial decomposition. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17, 248–257 (1972)
Paerl, H.W.: Bacterial uptake of dissolved organic matter in relation to detrital aggregation in marine and freshwater systems. Limnol. Oceanogr. 19, 966–972 (1974)
Pugh, P.R.: An evaluation of liquid scintillation counting techniques for use in aquatic primary production studies. Limnol. Oceanogr. 18, 306–310 (1973)
Schell, D.M.: Uptake and regeneration of free amino acids in marine waters of southeast Alaska, Limnol. Oceanogr. 19, 260–270 (1974)
Solorzano, L.: Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenol-hypochlorite method. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 799–801 (1969)
Strickland, J.D.H. and T.R. Parsons: A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Bull. Fish. Res. Bd Can 167, 1–311 (1968)
Thomas, W.H.: Phytoplankton nutrient experiments off Baja California and in the eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 26, 1133–1145 (1969)
—: On nitrogen deficiency in tropical Pacific Ocean phytoplankton: photosynthetic parameters in poor and rich water. Limnol. Oceanogr. 15 380–385 (1970a)
—: Effect of ammonium and nitrate concentration on chlorophyll increase in natural tropical Pacific phytoplankton populations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 15, 386–394 (1970b)
Wheeler, P.A., B.B. North and G.C. Stephens: Amino acid uptake by marine phytoplankters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 19, 249–259 (1974)
Williams, P.J. LeB.: Heterotrophic utilization of dissolved organic compounds in the sea. I. Size distribution of population and relationship between respiration and incorporation of growth substrates. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 50, 859–870 (1970)
— and R.W. Gray: Heterotrophic utilization of dissolved organic compounds in the sea. II. Observations on the responses of heterotrophic marine populations to abrupt increases in amino acid concentration. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 51, 871–881 (1970)
Wright, R.T. and J.E. Hobbie: Use of glucose and acetate by bacteria and algae in aquatic ecosystems. Ecology 47 (1966)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M.R. Tripp, Newark
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hollibaugh, J.T. The biological degradation of arginine and glutamic acid in seawater in relation to the growth of phytoplankton. Marine Biology 36, 303–312 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389191
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389191