Summary
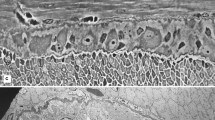
Turtle's retinae were incubated in isotonic Ringer and then studied with the electron microscope in order to determine if in these conditions an extracellular space appeared. In the incubated retinae, as in the normal ones no extracellular space was observed. The distance between adjacent membranes is of 120–250 Å and is filled with a cementing material.
The Müller cell of the turtle's retina is described. The existence, at the choroidal end of this cell, of villous projections filled with vesicles and the accumulation of mitochondria under these projections would suggest that a process of micropinocytosis takes place in this site, and that it may be metabolically more active. After incubation, Müller cells showed no appreciable changes, in contrast with what happens to astrocytes in incubated slices of CNS (Gerschenfeld et al. 1959).
The addition of sodium-l-glutamate to the incubation medium determined a marked swelling of the nervous endings in the inner synaptic layer and a similar though less pronounced change in the ganglion cells. This would indicate that the surcharge of water, sodium and chloride produced by glutamate (Ames 1956) is localized in this layer.
The selective action of glutamate on the inner synaptic layer, in contrast with the excellent preservation of the outer synaptic layer, is probably linked to differences in biochemistry and physiology of synapses in these two strata.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, J.N.: Extracellular space in central nervous system. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat (Chicago) 73, 241 (1955).
Ames, A. III: Studies in water and electrolytes in nervous tissue. II. Effect of glutamate and glutamine. J. Neurophysiol. 19, 213 (1956).
Ames, A. III: and A.B. Hastings: Studies in water and electrolytes in nervous tissue. I. Rabbit retina: Methods and interpretation of data. J. Neurophysiol. 19, 201 (1956).
Curtis, D.R., J.W. Phillis and J.C. Watkins: Chemical excitation of spinal neurons. Nature (Lond.) 183, 611 (1959).
Davson, H.: Some aspects of the relationship between the cerebrospinal fluid and the central nervous system. In: Ciba Foundation. Symposium on Cerebrospinal Fluid, p. 189. London: Churchill 1958.
—, and E. Spaziani: The blood brain barrier and the extracellular space of the brain. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 149, 135 (1959).
Francis, C.M.: Cholinesterase in the retina. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 120, 435 (1953).
Gerebtzoff, M.A.: Cholinesterases: A histochemical contribution to the solution of some functional problems. London: Pergamon Press 1959.
Gerschenfeld, H.M., F. Wald, J.A. Zadunaisky and E.D.P. De Robertis: Function of astroglia in the water-ion metabolism of the central nervous system. Neurology (Minneap.) 9, 412 (1959).
Horstmann, E., u. H. Meves: Die Feinstruktur des molekulären Rindengraues und ihre physiologische Bedeutung. Z. Zellforsch. 49, 569 (1959).
Kolmer, W.: Die Netzhaut. In: W. v. Möllendorffs Handbuch der mikroskopischen Anatomie des Menschen, Bd. 3/2, S. 295. 1936.
Krebs, H.A., L.V. Eggleston and R. Hems: Distribution of glutamine and glutamic acid in animal tissues. Biochem. J. 44, 159 (1949).
Lowry, O.H., N. Roberts and C. Lewis: The quantitative biochemistry of the retina. J. biol. Chem. 220, 880 (1956).
Lucas, D.R., and J.P. Newhouse: The toxic effect of sodium l-glutamate on the inner layers of the retina. A.M.A. Arch. Ophthal. 58, 193 (1957).
Manery, J.F., and L.F. Haege: Extent to which radioactive chloride penetrates tissues and its significance. Amer. J. Physiol. 134, 83 (1941).
—, and A.B. Hastings: The distribution of electrolytes in mammalian tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 127, 657 (1939).
Marchesani, O.: Cit. by S. L. Polyak in The Retina, p. 364. Chicago: University Chicago Press 1941.
McIllwain, A.: Biochemistry and the central nervous system, p. 38. Boston: Little Brown & Co. 1955.
Noell, W.K., and A. Lasansky: Effects of electrophoretically applied drugs and electrical currents on the ganglion cells of the retina. Fed. Proc. 115, 18 (1959).
- - Personal communication.
Pappius, A.H., and K.A.C. Elliott: Water distribution in incubated slices of brain and other tissues. Canad. J. Biochem. 34, 1007 (1956).
Robertis, E.D.P. De, and C.M. Franchi: Electronmicroscope observations on synaptic vesicles in synapses of the retinal rods and cones. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 2, 307 (1956).
—, and H.M. Gerschenfeld: Submicroscopic morphology and function of glial cells. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 3, 1 (1961).
Sjöstrand, F.S.: Ultrastructure of retinal rod synapses of the guinea pig eye as revealed by threedimensional reconstruction from serial sections. J. ultrastruct. Res. 2, 122 (1958).
—: Electron microscopy of the retina. In: The structure of the eye, edit. G.K. Smelser, p. I. New York: Academic Press 1961.
Stern, J.R., L.V. Eggleston, R. Hems and H.A. Krebs: Accumulation of glutamic acid in isolated brain tissues. Biochem. J. 44, 410 (1949).
Terner, C., L.V. Egglerton and H.A. Krebs.: The role of glutamic acid in the transport of potassium in brain and retina. Biochem. J. 47, 139 (1950).
Villegas, G.M.: Electron-microscopic study of the vertebrate retina. J. gen. Physiol. 43, 15 (1960).
Yamada, E.: The fine structure of the paraboloid in the turtle retina as revealed by electron-microscopy. Abstract of the Symposium of Fine Structure of Eye (in press). 1960.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Work supported by a research grant from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (5–60), U.S.A.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wald, F., de Robertis, E. The action of glutamate and the problem op the “extracellular space” in the retina. Z.Zellforsch 55, 649–661 (1961). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384504
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384504