Abstract
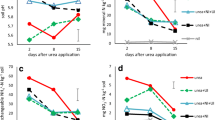
A laboratory experiment was conducted on an Aquic Udifluvent Belgian soil in order to study the movement of urea and its hydrolysis products. This study was carried out at two moisture levels (10 and 20%) upon the addition of three types of urease inhibitors: hydroquinone, phenylphosphorodiamidate (PPDA), and N-(n-butyl)phosphorothioic triamide (NBPT). The results clearly show the effects of the inhibitors in retarding the hydrolysis of urea. The highest effect was observed with NBPT, followed by hydroquinone, and PPDA. The effect was more pronounced at 10% than at 20% moisture content. It was clear that subsequent nitrification of the NH sup+inf4 formed was inhibited at the lower moisture level. At 10% moisture, from the 7th day of incubation on, some NH sup+inf4 moved about 3 cm and reached the top of the soil column. At 20% moisture, no NH sup+inf4 reached the surface as it was quickly nitrified. After 17 days of incubation and at 20% moisture, the total mineral N was more or less homogeneously distributed within the soil column. In contrast, at 10% moisture, the remaining urea and the hydrolysis products were still concentrated at the place of application. The distribution of urea and its hydrolysis products was comparable with 7 days of incubation at 20% moisture and 17 days at 10%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beyrouty CA, Sommers LE, Nelson DW (1988) Ammonia volatilization from surface-applied urea as affected by several phosphoroamide compounds. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52:1173–1178
Bouwmeester RJB, Vlek PL, Stumpe JM (1985) Effect of environmental factors on ammonia volatilization from a urea-fertilized soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49:376–381
Bremner JM (1965) Inorganic forms of nitrogen. In: Black CA, Evans DD, White JL, Ensminger LE, Clarke FE (eds) Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2, Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wisc. 1179–1237
Bremner JM, Chai HS (1989) Effects of phosphoroamides on ammonia volatilization and nitrite accumulation in soils treated with urea. Biol Fertil Soils 8:227–230
Bundy JG, Bremner JM (1974) Effect of urease inhibitors on nitrification in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 6:27–30
Bymes BH (1988) The degradation of the urease inhibitor phenylphosphorodiamidate in soil systems and the performance of N-(n-butyl)phosphorotioic triamide in flooded rice culture. PhD thesis, Technical University of Munich, Germany
Christianson CB, Byrnes BH, Carmona G (1990) A comparison of the sulfur and oxygen analogs of phosphoric triamide urease inhibitors in reducing urea hydrolysis and ammonia volatilization. Fert Res 26:21–27
Gould WD, Hagedorn C, McCready RGL (1986) Urea transformations and fertilizer efficiency in soil. Adv Agron 40:209–238
Hendrickson LL, O'Connor MJ (1987) Urease inhibition by decomposition products of phenylphosphorodiamidate. Soil Biol Biochem 19:595–597
Mulvaney RL, Bremner JM (1979) A modified diacetyl monoxime method for colorimetric determination of urea in soil extracts. Commun. Soil Sci Plant Anal 10:1163–1170
Stumpe JM, Vlek PLG, Lindsay WL (1984) Ammonia volatilization from urea and urea phosphates in calcareous soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48:921–927
Wang Zhengping, Van Cleemput O, Baert L (1990) Effect of urease inhibitors on nitrification in soil. Soil Use Manage 6:41–43
Wang Zhengping, Van Cleemput O, Demeyer P, Baert L (1991) Effect of urease inhibitors on urea hydrolysis and ammonia volatilization. Biol Fertil Soils 11:43–47
Watson CJ (1990) The influence of soil properties on the effectiveness of phenylphosphorodiamidate (PPD) in reducing ammonia volatilization from surface-applied urea Fert Res 24:1–10
Yeomans JC, Bremner JM (1986) Effects of urease inhibitors on denitrification in soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 17:63–73
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhengping, W., Van Cleemput, O. & Baert, L. Movement of urea and its hydrolysis products as influenced by moisture content and urease inhibitors. Biol Fert Soils 22, 101–108 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384440
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384440