Abstract
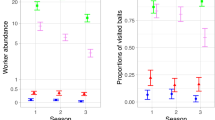
A series of experiments was conducted over 96 h in 240-mm-deep soil microcosms, to assess the effect of the presence and distribution of sheep manure over the soil surface on the vertical and horizontal distribution of burrows and numbers of the earthworms Aporrectodea trapezoides and Microscolex dubius. Within some microcosms the dung was placed on half of the soil surface and this caused aggregation, with over two-thirds of the earthworms being found in the soil directly under the manure. The presence of surface-applied sheep manure caused both species to aggregate in the surface soil. In contrast, without manure, A. trapezoides was evenly distributed throughout the soil profile while M. dubius aggregated in the deeper soil. The pattern of burrow construction was also influenced by the presence of surface manure. In the absence of manure, burrows of both species were evenly distributed through the soil, but in the presence of surface manure M. dubius constructed proportionally more burrows close to the surface. Both species constructed approximately twice the burrow area in the absence than in the presence of surface manure. For both species the daily rate of burrow construction decreased over the experimental period. From these data we inferred that there was more widespread and active foraging behaviour in both species when organic food material was scarce. M. dubius differed from A. trapezoides in that it more strongly concentrated foraging activity in the vicinity of the manure food source.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker GH, Barrett VJ, Grey-Gardner R, Buckerfield JC (1992) The life history and abundance of the introduced earthworms Aporrectodea trapezoides and A. caliginosa (Annelida: Lumbricidae) in pasture soils in the Mount Lofty Ranges, South Australia. Aust J Ecol 17:177–188
Barley KP (1959) The influence of earthworms on soil fertility. II. Consumption of soil and organic matter by earthworm Allolobophora caliginosa (Savigny). Aust J Agric 10:179–185
Buckerfield JC (1992) Earthworm populations in dryland cropping soils under conservation-tillage in South Australia. Soil Biol Biochem 24:1667–1672
Doube BM, Buckerfield JC, Barrett VJ, Baldock J, Oades M (1994a) Effects of lime, gypsum and organic matter on four species of earthworms in a red-brown earth in South Australia. Acta Zool Fenn 194 (in press)
Doube BM, Buckerfield JC, Kirkegaard J (1994b) Short term effects of tillage and stubble management on earthworm populations in New South Wales. Aust J Agric Res 45 (in press)
Doube BM, Ryder MH, Davoren CW, Meyer T (1994c) Earthworms: a down-under delivery service for biocontrol agents of root disease. Acta Zool Fenn 194 (in press)
Evans AC (1947) A method for studying the burrowing activities of earthworms. Ann Mag Nat Hist 14:643–650
Hendriksen NB (1991) Consumption and utilization of dung by detritivorous and geophagous earthworms in a Danish pasture. Pedobiol 35:65–70
Hughes MS, Bull CM, Doube BM (1994a) The use of resource patches by earthworms. Biol Fertil Soils 18:241–244
Hughes MS, Bull CM, Doube BM (1994b) The effects of sheep manure on the survival and growth of the earthworm Microscolex dubius (Annelida: Acanthodrilidae). Appl Soil Ecol 1:291–298
Lavelle P (1988) Earthworm activities and the soil system. Biol Fertil Soils 6: 237–251
Lawson LM (1993) The distribution and abundance of native and introduced earthworms in an area of pasture and native vegetation near Cape Jervis, South Australia. PhD thesis, Flinders University of South Australia
Lee KE (1985) Earthworms: their ecology and relationships with soils and land use. Academic Press, Sydney
Martin NA (1982) The interaction between organic matter in soil and the burrowing activity of three species of earthworm (Oligochaeta: Lumbricidae). Pedobiol 24:185–190
McCredie TA, Parker CA (1991) The potential of the exotic earthworms Aporrectodea trapezoides and Microscolex dubius for improving the physical condition of soil in the Western Australian wheatbelt. Report on Research during 1988/1990. Westfarmers Ltd and the Wheat Industry Research Council of Western Australia, Perth
McCredie TA, Parker CA, Abbott I (1992) Population dynamics of an exotic earthworm in a mediterranean pasture. Biol Fertil Soils 12:285–289
Tisdall JM (1978) Ecology of earthworms in irrigated orchards. In: Emerson WW, Bond RD, Dexter AR (eds) Modification of soil structure. Wiley, Chichester, pp 297–303
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hugnes, M.S., Bull, C.M. & Doube, B.M. Microcosm investigations into the influence of sheep manure on the behaviour of the geophagous earthworms Aporrectodea trapezoides and Microscolex dubuis . Biol Fert Soils 22, 71–75 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384435
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384435