Summary
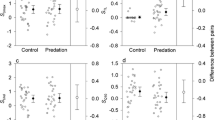
We used laboratory studies to examine the role of predation risk and cost of anti-predator behaviour in determining the behavioural response of several larval instars of Ischnura verticalis to a fish predator (Lepomis gibbosus). Smaller larvae were less susceptible to fish predation than larger larvae. Smaller larvae depressed movement to a greater degree in the presence of fish than did larger larvae; large larvae were generally less active than small larvae regardless of fish presence. Reduced feeding resulted in smaller larvae suffering more in terms of reduced growth than did large larvae. In general, our results tend to support the hypothesis that individuals that suffer high costs of anti-predator behaviour but little risk of predation may only exhibit anti-predator behaviours in the presence of predators, whereas individuals with a higher risk of predation and a lower cost of anti-predator behaviour may evolve anti-predator mechanisms that are in effect even in the absence of predators.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker RL (1981) Behavioural interactions and use of feeding areas by nymphs of Coenagrion resolutum (Coenagrionidae:Odonta). Oecologia (Berlin) 49:353–358
Brooks JL, Dodson SI (1965) Predation, body size, and composition of plankton. Science 150:28–35
Collins NC (1987) In-situ assessments of predation risk from benthivorous fish using time-lapse underwater video recordings. Abstracts 72nd Annual Meeting, Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio. Bull Ecol Soc Am 68:283
Daniel WW (1978) Applied nonparametric statistics, Houghton Mifflin, Boston, Mass, 510 p
Dixon SM, Baker RL (1987) Effects of fish on feeding and growth of larval Ischnura verticalis (Coenagrionidae: Odonata). Can J Zool 65:2276–2279
Heads PA (1985) The effect of invertebrate and vertebrate predators on the foraging movements of Ischnura elegans larvae (Odonata: Zygoptera), Freshw Biol 15:559–571
Heads PA (1986) The costs of reduced feeding due to predator avoidance: potential effects on growth and fitness in Ischnura elegans larvae (Odonata: Zygoptera). Ecol Entomol 11:369–377
Morin PJ (1984) The impact of fish exclusion on the abundance and species composition of larval odonates: Results of short-term experiments in a North Carolina farm pond. Ecology 65:53–60
Nilsson BI (1981) Susceptibility of some odonata larvae to fish predation. Verh Int Verein Limnol 21:1612–1615
Ringler NH (1979) Prey selection by benthic feeders. In: Stroud RH, Clepper H (eds) Predator-prey systems in fisheries management. Sport Fishing Institute, Washington, DC, 504 p
Shapiro SS, Wilk MB (1965) An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 52:591–611
Stein RA (1979) Behavioural response of prey to fish predators. In: Stroud RH, Clepper H (eds) Predator-prey systems in fisheries management. Sport Fishing Institute, Washington DC, 504 p
Thompson DJ (1978) Prey size selection by larvae of the damselfly, Ischnura elegans (Odonata). J Anim Ecol 47:769–785
Ware DM (1973) Risk of epibenthic prey to predation by rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J Fish Res Bd Can 30:787–797
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dixon, S.M., Baker, R.L. Effects of size on predation risk, behavioural response to fish, and cost of reduced feeding in larval Ischnura verticalis (Coenagrionidae: Odonata). Oecologia 76, 200–205 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00379953
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00379953