Abstract
Sprague-Dawley rats were made hypertensive by 6-week dietary salt loading with 8% NaCl in the diet and compared with control rats which had normal feed and water. At the end of this period, the salt-loaded group developed hypertension but the heart rate did not differ significantly from control.
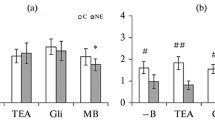
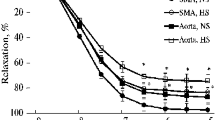
Serum taken from salt-loaded rats showed enhanced vasoconstrictor effect on normal rat's aorta when compared with controls. This enhanced vasoconstrictor effect was attenuated by adrenergic receptor blockers but not by serotoninergic blockers. Thus salt loading may induce accumulation of vasoactive agents in the blood of rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miyajima, E., Bunag, R. D.: Dietary salt loading produces baroreflex impairment and mild hypertension in rats. Am. J. Physiol, 1985: H278–H284.
Dina, T., Sofola, O.A., Egbe, P.E. et al: Cardiovascular responses to carotid chemoreceptor stimulation in rats during salt loading with hypertonic saline. IRCS Med. 1986; 14: 873.
Wright, G.L: Vascular sensitizing character of plasma from spontaneously hypertensive rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1981; 59:1111–1116.
Gavras, H.: How does salt raise blood pressure? A hypothesis. Hypertension 1986; 8: 83–88.
Ferrari, A.U., Mark, A.L.: Sensitization of aortic baroreceptors by high salt diet in Dahl Salt-sensitive rats. Hypertension 1987; 10: 55–60.
Luft,F. C.: Salt and hypertension: recent advances and perspectives. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1989; 114–215.
Nicholls, M.G., Kiowski, W., Zweifler, A.J., et al: Plasma Norepinephrine variations with dietary sodium intake. Hypertension 1980; 2: 29–32.
Julien, C., Barres., C., Sacquet, J. et al: Urinary catecholamines and blood pressure in genetically normotensive and hypertensive rats. Biog. Amine. 1989; 6: 525–534.
Obiefuna, O.A. Ebeigbe, A.B., Sofola, A.O., et al: Altered responses of aortic smooth muscle from Sprague-Dawley rats with salt-induced hypertension. Clin. Exp. physiol. Pharmacol. 1991; 18: 813–818.
Karaki H., Kubota, H, Urakawa, N.: Mobilisation of stored calcium for phasic contraction induced by norepinephrine in rabbit aorta. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1979; 56: 237–245.
DeChamplain, J., Farley, L., Causineau, D. et al: Circulating catecholamine levels in human and experimental hypertension Circ. Res. 1976; 38: 109–114.
Pang, P.K.T., Lewanczuk, R.Z., Benishin, C.G.: Parathyroid glands and cardiovascular functions. Contrib. Nephrol. Basel, Karger, 1991; 90: 65–71
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sofola, O.A., Obiefuna, P.C.M. & Adegunloye, B.J. Contractile response of normotensive rat aorta to serum from salt-loaded Sprague-Dawley rats. Pflugers Arch. 423, 161–163 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374976
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374976