Abstract
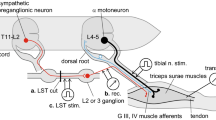
1. A shivering-like state of tremor was induced, in steroid-anesthetized cats, by perfusing the brain ventricles with a solution of d-tubocurarine in artificial spinal fluid. The behaviour of spinal α- and γ-motor systems and of muscle spindle afferents, belonging to hindlimb extensor and flexor muscles, was investigated by electrophysiological methods.
2. During the tremor state, a marked predominance of flexor muscle activity prevailed, as proved both by mechanical and electromyographical records. Sporadic grouped activity bursts of extensor units were usually related reciprocally to the maintained flexor bursts.
3. During curare perfusion, a progressively increasing background activity of fusimotor neurones was observed, leading to enhanced background activity of the muscle spindles through intact γ loops. No sign of any rhythmic pacemaker activity that was synchronous with the tremor frequencies was found in the fusimotor units.
4. With interrupted γ-spindle loops, rhythmic discharge grouping was also absent in the α units. In this condition, tonic α motoneurone stretch reflexes, as well as monosynaptic ventral root reflexes, were still enhanced by curare action.
5. The results indicate that intraventricular curare perfusion activates descending facilitatory pathways towards spinal α as well as γ motoneurones. The possibility is discussed that the fusimotor effects are mainly concentrated upon the γ2-component.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Beer, A. G.: Beiträge zur Pharmakologie des extrapyramidalen Systems. I. Mitt.: Die Wirkung des Harmins bei Katzen mit intaktem Nervensystem. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 193, 377–392 (1939).
Birzis, L., and A. Hemingway: Efferent brain discharge during shivering. J. Neurophysiol. 20, 156–166 (1957).
Boyd, I. A.: The motor innervation of mammalian muscle spindles. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 159, 7–9P (1961).
— The structure and innervation of the nuclear bag muscle fibre system and the nuclear chain muscle fibre system in mammalian muscle spindles. Phil. Trans. B 245, 81–136 (1962).
Bruggencate, H. G. ten, H. D. Henatsch u. H. Bossmann: Spinalmotorische Systeme bei experimentellem Tremor durch Curare-Perfusion der Hirnventrikel. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 279, R 20 (1964).
Carmichael, E. A., W. Feldberg, and K. Fleischhauer: The site of origin of the tremor produced by tubocurarine acting from the cerebral ventricles. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 162, 539–554 (1962).
Decima, E. E., R. George, W. L. Haslett jr., and R. W. Rand: Rhythmic activity of gastrocnemius motor pool induced by oxotremorine. Fed. Proc. 23, 560 (1964).
Eccles, J. C., P. Fatt, and K. Koketsu: Cholinergic and inhibitory synapses in a pathway from motor-axon collaterals to motoneurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 126, 524–562 (1954).
Eccles, R. M., and A. Lundberg: Synaptic actions in motoneurones by afferents which may evoke the flexion reflex. Arch. ital. Biol. 97, 199–221 (1959).
Feldberg, W.: A pharmacological approach to the brain from its inner and outer surface. London: E. Arnold 1963.
—, and K. Fleischhauer: The site of origin of the seizure discharge produced by tubocurarine acting from the cerebral ventricles. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 160, 258–283 (1962).
Folkerts, J. F., and E. A. Spiegel: Tremor on stimulation of the midbrain tegmentum. Confin. neurol. (Basel) 13, 193–202 (1953).
Granit, R.: Receptors and sensory perception. New Haven: Yale Univ. Press 1955.
—, and B. R. Kaada: Influence of stimulation of central nervous structures on muscle spindles in cat. Acta physiol. scand. 27, 130–160 (1952).
Halliday, A. M., and J. W. T. Redefearn: An analysis of the frequencies of finger tremor in healthy subjects. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 134, 600–611 (1956).
— Finger tremor in tabetic patients and its bearing on the mechanism producing the rhythm of physiological tremor. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 21, 101–108 (1958).
Hemingway, A.: Schivering. Physiol. Rev. 43, 397–422 (1963).
Jansen, J. K. S., and P. B. C. Matthews: The central control of the dynamic response of muscle spindle receptors. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 161, 357–378 (1962).
Jung, R.: Physiologische Untersuchungen über den Parkinsontremor und andere Zitterformen beim Menschen. Z. ges. Neurol. Psychiat. 175, 262–332 (1941).
--, and R. Hassler: The extrapyramidal motor system. In: Handbook of Physiology; Section I, Neurophysiology, Vol. II, edit. J. Field. American Physiol. Soc. Wash. D.C., p. 863–927, 1960.
Kaelber, W. W.: Tremor at rest from tegmental lesions in the cat. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol. 22, 695–701 (1963).
—, and E. G. Hamel: Drug (Tremorine)-induced tremor in the cat. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.) 2, 338–340 (1960).
— Observations on rest-type tremor in the cat. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol. 20, 263–274 (1961).
Klussmann, F. W.: Der Einfluß der Temperatur auf die Aktivität der α- und γ-Motoneurone des Rückenmarks. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 279, R 42 (1964).
Laporte, Y., et P. Bessou: Modifications d'excitabilité de motoneurones homonymes provoquées par l'activation physiologique de fibres afférentes d'origine musculaire du groupe II. J. Physiol. (Paris) 51, 897–908 (1959).
Lippold, O. C. J., J. W. T. Redfearn, and J. Vučo: The rhythmical activity of groups of motor units in the voluntary contraction of muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 137, 473–487 (1957).
— The influence of afferent and descending pathways on the rhythmical and arrhythmical components of muscular activity in man and the anaesthetized cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 146, 1–9 (1959).
Loeschcke, H. H.: Persönliche Mitteilung (1963).
Luschnat, K.-D.: Die Eigenreflexerregbarkeit des menschlichen Rückenmarks als Schwingungsvorgang. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 258, 431–451 (1954).
— Schwingungsfähigkeit im zentralen Teil des Eigenreflexbogens. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 262, 502–516 (1956).
Matthews, B. H. C.: Nerve endings in mammalian muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 78, 1–53 (1933).
Matthews, P. B. C., The differentiation of two types of fusimotor fibre by their effects on the dynamic response of muscle spindle primary endings. Quart. J. exp. Physiol. 47, 324–333 (1962).
Mitchell, R. A., H. H. Loeschcke, W. H. Massion, and J. W. Severinghaus: Respiratory responses mediated through superficial chemosensitive areas on the medulla. J. appl. Physiol. 18, 523–533 (1963).
Nash, J. B., and G. A. Emerson: Studies on the mode of action of Tremorine (1,4 Dipyrrolidino-2-butyne). Fed. Proc. 18, 426 (1959).
Spuler, H., E. G. Szekely, and E. A. Spiegel: Stimulation of the ventrolateral region of the thalamus. Its effect upon tremor induced by midbrain stimulation in cats. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.) 6, 208–219 (1962).
Steg, G.: Efferent muscle innervation and rigidity. Acta physiol. scand. 61, Suppl. 225, 1–53 (1964).
Stuart, D. G., and R. W. Porter: Proprioceptive contributions to shivering. Fed. Proc. 23, 567 (1964).
Stuart, D. G., and R. W. Porter: Proprioceptive contributions to shivering. Fed. Proc. 23, 567 (1964).
Szekely, E. G., and G. V. Jacoby: Tremor induced by autostimulation in cats. Physiologist 6, 283 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit 6 Textabbildungen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ten Bruggencate, H.G., Henatsch, H.D. & Bossmann, H. Tremor und spinalmotorische α- und γ-Systeme der Katze bei Curareperfusion der Hirnventrikel. Pflügers Archiv 282, 102–118 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00363212
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00363212