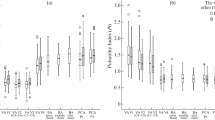
Summary
In 33 human subjects with a sound circulatory system regional cerebral blood flow changes, following intracarotid injection of sodium methylglucamine diatrizoate (Angiografin, Urografin 76%) during cerebral angiography, were investigated. Angiografin®, at the start of recording 1 and 3 min after intracarotid injection, caused an increase of rCBF of 15.7% and 7.8% respectively. Urografin®, 3 min after completion of intracarotid injection, brought about an increase of rCBF of 23.0%. Under the action of both X-ray radiopaque materials at the start of rCBF-measurement, 5 and 8 min after completed intracarotid injection, there no longer was a significant difference from the resting values. Changes in haemodynamics (blood pressure, pulse rate) during carotid cerebral angiography with sodium-methylglucamine diatrizoate (Angiografin, Urografin 76%) were not observed in this study.
Résumé
Chez 33 sujets humains avec un système cireulatoire régional normal, les auteurs ont étudié les répercussions de l'injection intra-carotidienne du sodium méthylglucamine diatrizoate (Angiografine, Urografine 76%) sur le flux sanguin cérébral régional au cours de l'angiographie cérébrale. Dans le cas de l'Angiografine, on notait une augmentation du flux sanguin cérébral régional de 15.7% et 7.8% respectivement 1 et 3 min après l'injection intra-carotidienne. Avec l'Urografine 76%, l'augmentation du flux sanguin cérébral régional était de 23.0%. Les mesures pratiquées 5 et 8 min après la fin de l'injection ne montraient pas de différence sensible entre les deux produits de contraste. Chez ces malades il n'y a pas eu de modifications hémodynamiques (pression sanguine, pouls) sous l'influence du sodium méthylglucamine diatrizoate (Angiografine, Urografine 76%) au cours de l'angiographie carotidienne.
Zusammenfassung
Bei 33 kreislaufgesunden Patienten wurden die Veränderungen der regionalen Hirndurchblutung nach Injektion von Angiografin bzw. Urografin 76% in die A. carotis interna untersucht. Dabei fand sich nach Angiografin bei Beginn der Durchblutungs-messung im zeitlichen Abstand von 1 bzw. 3 Min. nach erfolgter Injektion des Kontrastmittels eine Zunahme des rCBF um 15,7% bzw. 7,8%. Urografin rief bei Meßbeginn im zeitlichen Abstand von 3 Min. nach erfolgter Injektion des Kontrastmittels einen rCBF-Anstieg von 23% hervor. Bei Meßbeginn im zeitlichen Abstand von 5 und 8 Min. nach der Injektion war eine signifikante Differenz von der Ausgangslage nicht mehr erkennbar. Die Verfasser konnten keine Veränderungen der Kreislaufparameter (Blutdruck, Pulsfrequenz) während der Angiographie feststellen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelola, A., Oduntan, S.A.: Changes in haemodynamics and blood gases during carotid cerebral angiography with sodium-methylglucamine diatrizoate urografin 60%). Brit. J. Radiol. 44, 528, 949 (1971)
Aurup, L., Aurup, R.: Blood pressure variations during cerebral arteriography. Dan. med. Bull. 12, 185 (1965)
Bloor, B.M., Wrenn, F.R., Margolis, G.: Effect of intracarotid iodopyracet (Diodrast) on cerebral blood flow. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. 71, 358 (1954)
Brown, A.S., Donaldson, A.A.: The effect of x-ray contrast medium (angiografin) on regional cerebral blood flow. In: Brain and blood flow, p. 289. London: Pitman Medical 1971
Fischer, H.W., Cornell, S.H.: The toxicity of the sodium and methylgucamine salts of diatrizoate, iothalamate and metrizoate. — An experimental study of their circulatory effects following intracarotid injection. Radiology 85, 1013 (1965)
Fischer, H.W., Eckstein, J.W., Perret, G.: Comparison of the cardiovascular effect of contrast media in cerebral angiography in man. J. Neurosurg. 19, 943 (1962)
Foltz, E.L., Thomas, L.B., Ward, A.A.: The effects of intracarotid diodrast. J. Neurosurg. 9, 68 (1952)
Geddes, I.C.: Anaesthesia for cerebral angiography. Brit. J. Anaesth. 24, 252 (1952)
Greitz, T.: Dilatation of cerebral veins during cerebral angiography with water soluble contrast media. Acta Radiol. 4, 625 (1966)
Greitz, T.: A radiological study of the brain circulation by rapid serial angiography of the carotid artery. Acta Radiol. (Suppl.) 140, 123 (1956)
Greitz, T., Tornell, G.: Bradycardial reactions during cerebral angiography. A comparison of isopaque sodium, Isopaque B, hypaque and urografin. Acta Radiol. (Suppl.) 270, 75 (1967)
Herrschaft, H., Gleim, F.: Relationship between circulation time and cerebral blood flow in cerebrovascular disease. Neuroradiol. 3, 199 (1972)
Herrschaft, H., Schmidt, H.: Die quantitative Messung der örtlichen Hirndurchblutung in Allgemeinnarkose unter Normo-, Hypo- und Hypercapnie. Anaesthesist 22, 442 (1973)
Herrschaft, H., Schmidt, H., Duus, P.: Cerebral blood flow in man under general anaesthesia with regard to several narcotics. Europ. Neurol. 6, 373 (1972)
Huber, P., Handa, J.: Effect of contrast material, hypercapnia, hyperventilation, hypertonic glucose and papaverine on the diameter of the cerebral arteries. Angiographic determination in man. Invest. Radiol. 2, 17 (1967)
Huber, P., Handa, J.: Der Einfluß von Kontrastmittel auf Hirngefäße und Hirndurchblutung. Schweiz. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. 97, 282 (1966)
Hilal, S.K.: Hemodynamic responses in the cerebral vessels to angiographic contrast media. Acta Radiol. 5, 211 (1966)
Hilal, S.K.: Hemodynamic changes associated with the intra-arterial injection of contrast media. Radiology 86, 615 (1966)
Ingvar, D.H., Soderberg, U.: Cerebral vasomotor tone and EEG during injections of umbradil. — An experimental study with a new method. Acta Radiol 47, 185 (1957)
Jørgensen, P.B., Karle, A., Rosenklint, A.: Changes in blood pressure and cardiac rhythm induced by arterial contrast injection. Neuroradiol. 5, 215 (1973)
Kagstrom, E., Lindgren, P., Tornell, G.: Changes in cerebral circulation during carotid angiography with sodium acetrizoate triurol) and sodium diatrizoate (hypaque). Acta Radiol. 50, 151 (1958)
Kagstrom, E., Lindgren, P., Tornell, G.: Circulatory disturbances during cerebral angiography. — An experimental evaluation of certain contrast media. Acta Radiol. 54, 3 (1960)
Kagstrom, E., Lindgren, P., Tornell, G.: Circulatory changes during cerebral angiography. Acta Radiol. 54, 3 (1960)
Klingler, M., Stricker, F., Hunzinger, W.: Kreislaufwirkungen angiographischer Kontrastmittel am Tier und am Mensch. Zbl. Neurochir. 16, 57 (1956)
Lin, J.P., Kricheff, I.I., Chase, N.E.: Comparative blood pressure changes in angiography with meglumine iothalamate (60% Conray) and 50% sodium diatrizoate (50% Hypaque). Radiology 85, 1033 (1965)
Lindgren, P., Tornell, G.: Blood pressure and heart rate responses in carotid angiography with sodium acetrizoate (Triurol). An experimental study in cats. Acta Radiol. 50, 160 (1958)
Lundervold, A., Engeset, A.: Polygraphic recording of EEG, ECG and blood pressure during cerebral angiography with isopaque B. Acta Radiol. (Suppl.) 270, 87 (1967)
Potchen, E.J.: The effect of cerebral arteriography on regional cerebral blood flow measurement. In: Cerebral blood flow. Fischgold, H., Taveras, J.M. (eds.). Springfield, Ill.: Charles C. Thomas 1970
Schmidt, H.W.: The behavior of the pial vessels and after the intracarotid injection of roentgen contrast media. Acta Radiol. 44, 100 (1955)
Tindall, G.T., Greenfield, J.D., Dillingham, W., Lee, J.F.: Effect of 50 per cent sodium diatrizoate (hypaque) on blood flow in the internal carotid artery of man. Amer. Heart J. 69, 215 (1965)
Ulano, H.B., Ascanio, G., Rice, W., O'Hern, R., Houmas, E., Oppenheimer, J.M.: Effects of angiographic contrast media and hypertonic saline solutions on cerebral venous outflow in autoregulating brains. Invest. Radiol. 5, 518 (1970)
Vogel, H., Hakim, A., Pflüger, G.: Rückatmung bei Verwendung von Ruben-Ventilen. Anaesthesist 18, 247 (1969)
Warelius, T.: Effects of contrast medium injection on haemodynamics in cerebral angiography. Brit. J. Radiol. 40, 538 (1967)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herrschaft, H., Gleim, F. & Schmidt, H. Effects of angiographic contrast media on regional cerebral blood flow and haemodynamics in man. Neuroradiology 7, 95–103 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00341877
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00341877