Abstract
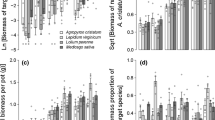
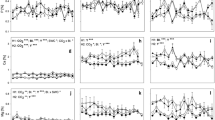
Leaf expansion, population dynamics and reproduction under elevated CO2 were studied for two dominant and four subdominant species in a high alpine grassland (2500 above sea level, Swiss Central Alps). Plots of alpine heath were exposed to 335 μl l-1 and 680 μl l-1 CO2 in open-top chambers over three growing seasons. Treatments also included natural and moderately improved mineral nutrient supply (40 kg N ha-1 year-1 in an NPK fertilizer mix). Seasonal dynamics of leaf expansion, which was studied for the dominant graminoid Carex curvula only, were not affected by elevated CO2 during two warm seasons or during a cool season. Improved nutrient supply increased both the expansion rate and the duration of leaf growth but elevated CO2 did not cause any further stimulation. Plant and tiller density (studied in all species) increased under elevated CO2 in the codominant Leontodon helveticus and the subdominant Trifolium alpinum, remained unchanged in two other minor species Poa alpina and Phyteuma globulariifolium, and decreased in Carex curvula. In Potentilla aurea elevated CO2 compensated for a natural decline in shoot number. By year 3 the number of fertile shoots in Leontodon and individual seed weight in Carex were slightly increased under elevated CO2, indicating CO2 effects on sexual reproduction in these two dominant species. The results suggest that the effects of elevated CO2 on the population dynamics of the species studied were not general, but species-specific and rather moderate effects. However, the reduction of tiller density in Carex curvula, in contrast to the increases observed in Leontodon helveticus and Trifolium alpinum, indicates that elevated CO2 may negatively affect the abundance of the species most characteristic of this alpine plant community.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arp WJ, Drake BG (1991) Increased photosynthetic capacity of Scirpus olneyi after 4 years of exposure to elevated CO2. Plant Cell Environ 14:1003–1006
Bazzaz FA, Garbutt K (1988) The response of annuals in competitive neighborhoods: effects of elevated CO2. Ecology 69:937–946
Bazzaz FA, Ackerly DD, Woodward FI, Rochefort L (1992) CO2-enrichment and dependence of reproduction on density in an annual plant and a simulation of its population dynamics. J Ecol 80:643–651
Cipollini ML, Drake BG, Whigham D (1993) Effects of elevated CO2 on growth and carbon/nutrient balance in the deciduous woody shrub Lindera benzoin (L.) Blume. Oecologia 96:339–346
Coleman JS, Bazzaz FA (1992) Effects of CO2 and temperature on growth and resource use of co-occurring C3 and C4 annuals. Ecology 73:1244–1259
Curtis PS, Drake BG, Leadley PW, Arp WJ, Whigham DF (1989) Growth and senescence in plant communities exposed to elevated CO2 concentrations on an estuarine marsh. Oecologia 78:20–26
Diemer MW (1994) Mid-season gas exchange of an alpine grassland under elevated CO2. Oecologia 98:429–435
Fajer ED, Bowers MD, Bazzaz FA (1992) The effect of nutrients and enriched CO2 environments on production of carbon based allelochemicals in Plantago: a test of the carbon/nutrient balance hypothesis. Am Nat 140:707–723
Hilbert TW, Prudhomme TI, Oechel WC (1987) Response to tussock tundra to elevated carbon dioxide regimes: analysis of ecosystem CO2 flux through nonlinear modeling. Oecologia 72:466–472
Körner Ch, Wieser G, Cernusca A (1989) Der Wasserhaushalt waldfreier Gebiete in den österreichischen Alpen zwischen 600 und 2600 m Höhe. In: Cernusca A (ed) Struktur und Funktion von Graslandökosystemen im Nationalpark Hohe Tauern (Veröffentlichungen des österreichischen MAB-Programmes, Band 13). Universitätsverlag Wagner, Innsbruek
Körner Ch, Diemer M, Schäppi B, Zimmermann L (1996) The response of alpine vegetation to elevated CO2. In: Koch GW, Mooney HA (eds) Carbon dioxide and terrestrial ecosystems. Physiological ecology series. Academic Press, San Diego. 177–195
Nijs I, Impens I, Behaege T (1988) Effects of elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide on gas exchange and growth of white clover. Photosynth Res 15:163–176
Overdieck D (1986) Long-term effects on an increased CO2 concentration on terrestrial plants in model ecosystems. Morphology and reproduction of Trifolium repens L. and Lolium perenne L. Int J Biometeorol 30:323–332
Owensby CE, Coyne PI, Ham JM, Auen LM, Knapp AK (1993) Biomass production in a tall grass prairie ecosystem exposed to ambient and elevated CO2. Ecol Appl 3:644–653
Ryle GJA, Powell CE, Davidson IA (1992) Growth of white clover, dependent on N2 fixation in elevated CO2 and temperature. Ann Bot 70:221–228
Schäppi B, Körner Ch (1996) Growth responses of an alpine grassland to elevated CO2. Oecologia 105:43–52
Schanz F, Keller M, Niederhauser P (1994) Einfluß von Umweltfaktoren auf den Diatomeen-Aufwuchs von Hochgebirgsseen der Zentralalpen (Gotthardgebiet). Verh Ges Ökol 23:57–62
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1981) Biometry. Freeman, San Francisco
Steinger T, Körner Ch, Schmid B (1996) Long-term persistence in a changing climate: DNA analysis suggests very old ages of clones of Carex curvula. Oecologia 105:94–99
Tissue DT, Oechel WC (1987) Response of Eriophorum vaginatum to elevated CO2 and temperature in the Alaskan tussock tundra. Ecology 68:401–410
Wilkinson L, Hill MA, Vang E (1992) Systat: statistics. Systat Evanston
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schäppi, B. Growth dynamics and population development in an alpine grassland under elevated CO2 . Oecologia 106, 93–99 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00334411
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00334411