Abstract
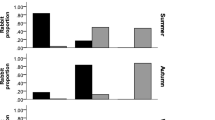
A case of local feeding specialization in the European badger (Meles meles), a carnivore species with morphological, physiological and behavioural traits proper to a trophic generalist, is described. For the first time, we report a mammalian species, the European rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus), as the preferred prey of badgers. Secondary prey are consumed according to their availability, compensating for temporal fluctuations in the abundance of rabbit kittens. We discuss how both predator (little ability to hunt) and prey (profitability and predictability) features, may favour the observed specialization, as predicted by foraging theory. Badgers show a trend to specialize on different prey in different areas throughout the species range. It is suggested that changes in prey features can reverse the badger feeding strategy at the population level. Such dynamic behavioural responses make difficult to label badgers as generalists or specialists at the species level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allier C, González-Bernáldez F, Ramírez-Díaz L (1974) Mapa ecológico de la Reserva Biológica de Doñana. Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Sevilla
Ashby KR, Elliot K (1983) The diet of the badger (Meles meles L.) in Castle Eden, County Durham. Acta Zool Fenn 174: 205–207
Begon M, Harper JL, Townsend CR (1990) Ecology: individuals, populations and communities. 2nd edn. Blackwell, Oxford
Ciampalini B, Lovari S (1985) Food habits and trophic niche overlap of the badger (Meles meles L.) and the red fox (Vulpes vulpes L.) in a Mediterranean coastal area. Z Säugetierk 50: 226–234
Delibes M, Calderón J (1979) Datos sobre la reprodución del conejo, Oryctolagus cuniculus (L.), en Doñana, S.O. de España, durante un año seco. Doñana Acta Vert 6: 91–99
Font I (1983) Climatología de España y Portugal. Instituto Nacional de Meteorología, Madrid
Fox LR, Morrow PA (1981) Specialization: species property or local phenomenon? Science 211: 887–893
Futuyma DJ (1986) Evolutionary biology, 2nd edn. Sinauer, Sunderland
Futuyma DJ, Moreno G (1988) The evolution of ecological specialization. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 19: 207–233
Hanski I, Hansson L, Henttonen H (1991) Specialist predators, generalist predators, and the microtine rodent cycle. J Anim Ecol 60: 353–367
Harris S (1984) Ecology of badgers Meles meles: distribution in Britain and habitat selection, persecution, food and damage in the city of Bristol. Biol Conserv 28: 349–375
Henry C (1983) Position trophique du blaireau européen (Meles meles L.) dans une fôret du Centre de la France. Acta Oecol Oecol Gener 4: 345–358
Kruuk H (1978) Spatial organization and territorial behaviour of the European badger Meles meles. J Zool Lond 184: 1–19
Kruuk H (1989) The social badger. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Kruuk H, Kock L de (1981) Food and habitat of badgers (Meles meles L.) on Monte Baldo, northern Italy. Z Säugetierk 46: 295–301
Kruuk H, Parish T (1981) Feeding specialization of the European badger Meles meles in Scotland. J Anim Ecol 50: 773–788
Kruuk H, Parish T (1983) Seasonal and local differences in the weight of European badgers (Meles meles, L.) in relation to food supply. Z Säugetierk 48: 45–50
Kruuk H, Parish T (1985) Food, food avalilability and weight of badgers (Meles meles) in relation to agricultural changes. J Appl Ecol 22: 705–715
Lockie JD (1961) The food of the pine marten Martes martes in west Ross-Shire, Scotland. Proc Zool Soc Lond 136: 187–195
Lüps P, Roper TJ, Stocker G (1987) Stomach contents of badgers (Meles meles L.) in central Switzerland. Mammalia 51: 559–569
Mellgren RL, Roper TJ (1986) Spatial learning and discrimination of food patches in the European badger (Meles meles L.). Anim Behav 34: 1129–1134
Morse DJ (1980) Behavioral mechanisms in ecology. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Murdoch WW (1969) Switching in general predators: experiments on predator specificity and stability of prey populations. Ecol Monogr 39: 335–354
Myers K (1971) The rabbit in Australia. Dynamics of populations. In: Boer PG den, Gradwell GR (eds) Dynamics of numbers in populations. Centre of Agricultural Publishing and Documentation. Wageningen, pp 478–506
Neal E (1986) The natural history of badgers. Croom Helm, Beckenham
Partridge L, Green, P (1985) Intraspecific feeding specialization and population dynamics. In: Sibly RM, Smith RH (eds) Behavioural ecology: ecological consequences of adaptive behaviour. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 207–226
Pigozzi G (1989) Digging behaviour while foraging by the European badger, Meles meles, in a Mediterranean habitat. Ethology 83: 121–128
Pigozzi G (1991) The diet of the European badger in a Mediterranean coastal area. Acta Theriol 36: 293–306
Raw F (1959) Estimating earthworm populations by using formaling. Nature 186: 1661–1662
Rodríguez A, Delibes M (1992) Food habits of badgers (Meles meles) in an arid habitat. J Zool Lond 227: 347–350
Rogers PM, Myers K (1979) Ecology of the European wild rabbit, Oryctolagus cuniculus (L.), in Mediterranean habitats. J Appl Ecol 16: 691–703
Sanderson SL (1991) Functional stereotypy and feeding performance correlated in a trophic specialist. Funct Ecol 5: 795–803
Schoener TW (1971) Theory of feeding strategies. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 2:369–404
Skinner CA, Skinner PJ (1988) Food of badgers (Meles meles) in an arable area of Essex. J Zool Lond 215: 360–362. Skoog P (1970) The food of the Swedish badger (Meles meles L.). Viltrevy 7: 1–120
Soriguer RC (1984) Biología y dinámica de una población de conejos Oryctolagus cunïculus (L.) en Andalucía occidental. Doñana Acta Vert (vol espec):1–379
Soriguer RC, Myers K (1986) Morphological, physiological and reproductive features of a wild rabbit population in Mediterranean Spain under different habitat management. Mammál Rev 16: 197
Stark R, Roper TJ, Chivers DJ, Maclarnon A (1987) Gastrointestinal anatomy of the European badger Meles meles L.: a comparative study. Z Säugetierk 52: 88–96
Stephens DW, Lynch JF, Sorensen AE, Gordon C (1986) Preference and profitability: theory and experiment. Am Nat 127: 533–553
Valverde JA (1957) Notes écologiques sur le lynx d'Espagne Felis lynx pardina Temminck. Terre Vie 1: 51–67
Valverde JA (1967) Estructura de una comunidad de vertebrados terrestres. Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Madrid
Villafuerte R (1994) Riesgo de predación y estrategias defensivas del conejo, Oryctolagus cuniculus, en el Parque Nacional de Doñana. Ph D Thesis, Universidad de Córdoba
Zar JH (1984) Biostatistical analysis, 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martín, R., Rodríguez, A. & Delibes, M. Local feeding specialization by badgers (Meles meles) in a mediterranean environment. Oecologia 101, 45–50 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00328898
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00328898