Summary
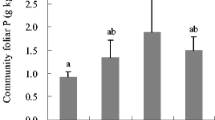
Plant nutrient status and physiological processes were examined in relation to soil nutrient characteristics under individuals of five species colonizing a young cinder deposit in Hawaii Volcanoes National Park. Two exotic species, Buddeleja asiatica and Myrica faya, had high photosynthetic rates and high nitrogen concentrations and relatively easily decomposed leaves; soils under them had high concentrations of nitrogen, cations, and organic matter and high rates of net nitrogen mineralization. At the other extreme, the natives Metrosideros polymorpha and Vaccinium reticulatum had low plant concentrations and photosynthetic rates, and low concentrations and turnover rates of N in the soil. Thus, a strong correlation exists between soil processes and plant processes, suggesting a positive feedback cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bazzaz D (1983) Characteristics of population in relation to disturbance in natural and man-modified ecosystems. In: Mooney HA and Godron M (eds) Disturbance and Ecosystems: Components of Response, Springer, New York, pp 259–275
Chapman HO (1965) Cation Exchange Capacity. In: Black CA (ed). Methods of Soil Analysis. Am. Soc. of Agronomy, Madison WI, USA, pp 891–901
Field C, Mooney HA (1986) The photosynthesis-nitrogen relationship in wild plants. In: Givnish TS (ed) On the Economy of Plant Form and Function. Cambridge University Press
Jenkinson DS, Powlson DS (1976) The effects of biocidal treatments on metabolism in soil. I. Fumigation with chloroform. Soil Biol Biochem 8:167–177
Matson PA, Waring RH (1984) Effects of nutrient and light limitation on mountain hemlock: Susceptibility to laminated root rot. Ecology 65(5):1517–1524
Mueller-Dombois D, Whiteaker LD (1990) Plants associated with Myrica faya and two other pioneer trees on a recent volcanic surface in Hawaii Volcanoes National Park. Phytocoenologia (in press)
Scientific Instruments Corporation (1981) Digestion and sample preparation for the analysis of total kjeldahl nitrogen and/or phosphorus in water samples. Pleasanton, NY
Smathers GA, Mueller-Dombois D (1974) Invasion and recovery of vegetation after a volcanic eruption in Hawaii. National Park Service Scientific Monograph Series No. 5, Government Printing Office, Washington, DC p 129
Technicon Instrument Corporation (1973) Nitrite and nitrate in water and wastewater, Ind. Method 100-70 W, Tarrytown, NY
Technicon Instrument Corporation (1977) Individual/simultaneous determinations of nitrogen and/or phosphorus in BD acid digests, Ind. Method 329-70 W, Tarrytown, NY
Vitousek PM, Matson PA (1988) Nitrogen transformations in a range of tropical forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 20(3):361–367
Vitousek PM, Walker LR (1989) Biological invasion by Myrica faya in Hawaii: Plant demography, nitrogen fixation, and ecosystem effects. Ecol Monog 59(3):247–265
Vitousek PM, Walker LR, Whiteaker LD, Muller-Dombois D, Matson PA (1987) Biological invasion by Myrica faya alters ecosystem development in Hawaii. Science 238:802–804
Voroney RP, Paul E (1984) Determination of Kc and Kn in situ for calibration of the chloroform fumigation-incubation method. Soil Biol Biochem 16:9–14
Walker TW, Syers JK (1976) The fate of phosphorus during pedogenesis. Geoderma 14:1–19
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matson, P. Plant-soil interactions in primary succession at Hawaii Volcanoes National Park. Oecologia 85, 241–246 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319408
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319408