Summary
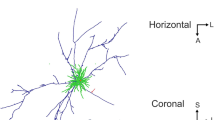
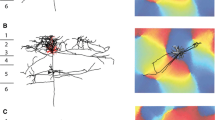
The intrinsic organization and interlaminar connections in neocortical layers I and II have been studied in adult hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) using the Golgi method. Layer I contains a dense plexus of horizontal fibers, the terminal dendritic bouquets of pyramidal cells of layer II and of underlying layers, and varieties of intrinsic neurons. Four main types of cells were found in layer I. Small horizontal cells represent most probably persisting foetal horizontal cells described for other mammals. Large horizontal cells, tufted cells, and spinous horizontal cells were also found in this layer.
Layer II contains primitive pyramidal cells representing the most outstanding feature of the neocortex of the hedgehog. Most pyramidal cells in layer II have two, three or more apical dendrites, richly covered by spines predominating over the basal dendrites. These cells resemble pyramidal cells found in the piriform cortex, hippocampus and other olfactory areas. It is suggested that the presence of these neurons reflects the retention of a primitive character in neocortical evolution.
Cells with intrinsic axons were found among pyramidal cells in layer II. These have smooth dendrites penetrating layer I and local axons forming extremely complex terminal arborizations around the bodies and proximal dendritic portions of pyramidal cells. They most probably effect numerous axo-somatic contacts resembling basket cells. The similarity of some axonal terminals with the chandelier type of axonal arborization is discussed. Other varieties of cells located in deep cortical layers and having ascending axons for layers I and II were also studied. It is concluded that the two first neocortical layers represent a level of important integration in this primitive mammal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbie AA (1940) Cortical lamination in the monotremata. J Comp Neurol 72:429–467
Ariëns Kappers CU, Huber GC, Crosby EC (1936) The comparative anatomy of the nervous system of vertebrates, including man, vol 3, Hafner Publ Comp, New York
Barón M, Gallego A (1971) Cajal cells of the rabbit cerebral cortex. Experientia 27:430–432
Berry M, Rogers AW (1965) The migration of neuroblasts in the developing cerebral cortex. J Anat 99:691–709
Bradford R, Parnavelas JG, Lieberman AR (1977) Neurons in layer I of the developing occipital cortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol 176:121–132
Brodmann K (1909) Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Großhirnrinde. Johann Ambrosius Barth, Leipzig, pp 193–197
Burton M (1969) The hedgehog. Andre Deutsch, London
Cajal SR (1890) Sobre la existencia de células nerviosas especiales en la primera capa de las circunvoluciones cerebrales. Gac Med Catal, December 15
Cajal SR (1891) Sur la structure de l'écorce cérébrale de quelques mammifères. Cellule 7:123–176
Cajal SR (1893) Neue Darstellung vom histologischen Bau des Centralnervensystems. Arch Anat Physiol, Anat Abtheil (Leipzig) 319–428
Cajal SR (1911) Histologie du système nerveux de l'homme et des vertébrés, vol. II. Maloine, Paris, Reimpress 1955, Instituto Cajal, CSIC, Madrid
Clark WE LeGros (1932) The brain of the insectivora. Proc Zool Soc (Lond) 102:975–1013
DeFelipe J, Fairén A (1982) A type of basket cell in superficial layers of the cat visual cortex. a Golgi-electron microscope study. Brain Res 244:9–16
DeFelipe J, Hendry SHC, Jones EG, Schmechel D (1985) Variability in the terminations of GABAergic chandelier cell axons on initial segments of pyramidal cell axons in the monkey sensorymotor cortex. J Comp Neurol 231:364–384
Diamond IT (1967) The sensory neocortex. In: Neff WD (ed) Contributions of sensory physiology, Vol. 2, Academic Press, New York pp 51–100
Diamond IT, Hall WC (1969) Evolution of neocortex. Science 164:251–262
Ebner FF (1969) A comparison of primitive forebrain organization in metatherian and eutherian mammals. Ann New York Acad Sci 167:241–257
Elliot Smith G (1902) Catalogue of the physiological series in the Hunterian Museum of Royal College of Surgeons, vol. 2, London
Elliot Smith G (1910) Some problems relating to the evolution of the brain. Lancet 1:1–6, 147–155, 221–227
Fairén A, DeFelipe J, Regidor J (1984) Nonpyramidal neurons: general account. In: Peters A, Jones EG (eds) Cerebral cortex, Vol. 1, Plenum Press, New York pp 201–253
Filimonoff IN (1964) Homologies of the cerebral formations of mammals and reptiles. J Hirnforsch 7:229–251
Flores A (1911) Die Myeloarchitektonik und die Myelogenie des Cortex Cerebri beim Igel (Erinaceus europaeus). J Psychol Neurol (Leipzig) 17:215–247
Fex MW, Inman O (1966) Persistence of Retzius-Cajal cells in developing dog brain. Brain Res 3:192–194
Freund TF, Martin KAC, Smith AD, Somogyi P (1983) Glutamate decarboxylase-immunoreactive terminals of Golgi-impregnated axoaxonic cells and of presumed basket cells in synaptic contact with pyramidal neurons of the cat's visual cortex. J Comp Neurol 221:263–278
Haberly LB (1983) Structure of the piriform cortex of the opossum. I. Description of neuron types with Golgi methods. J Comp Neurol 213:163–187
Haberly LB, Price JL (1978) Association and commissural fiber systems of the olfactory cortex of the rat. I. Systems originating in the piriform cortex and adjacent areas. J Comp Neurol 178:711–740
Heimer L (1969) The secondary olfactory connections in mammals, reptiles and sharks. Ann New York Acad Sci 167:129–146
Heimer L, Kalil R (1978) Rapid transneuronal degeneration and death of cortical neurons following removal of the olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol 178:559–609
Herrick CD (1921) A sketch of the origin of the cerebral hemispheres. J Comp Neurol 32:429–454
Johnston JB (1909) The morphology of the forebrain vesicle in vertebrates. J Comp Neurol 19:457–539
Johnston JB (1911) The telencephalon of selachians. J Comp Neurol 21:1–112
Jones EG, Hendry SHC (1984) Basket cells. In: Peters A, Jones EG (eds) Cerebral cortex, vol. 1 Plenum Press, New York pp 309–336
Kölliker A (1893) Handbuch der Gewebelehre des Menschen. Wilhelm Engelmann, Leipzig
König N, Valat J, Fulcrand J, Marty R (1977) The time of origin of Cajal-Retzius cells in the rat temporal cortex: an autoradiographic study. Neurosci Lett 4:21–26
Kuhlenbeck H (1965) Gehirn und Intelligenz. Confin Neurol 25:35–62
Lende RA (1969) A comparative approach to the neocortex: localization in monotremes, marsupials and insectivores. Ann New York Acad Sci 167:262–275
Lende RA, Sadler KM (1967) Sensory and motor areas in neocortex of hedgehog (Erinaceus). Brain Res 5:390–405
Loo YT (1931) The forebrain of the opossum, Didelphys virginiana. II. Histology. J Comp Neurol 52:1–148
Marin-Padilla M (1971) Early prenatal ontogenesis of the cerebral cortex (neocortex) of the cat (Felis domestica). A Golgi study. I. The primordial neocortical organisation. Z Anat Entwickl-Gesch 134:117–145
Marin-Padilla M (1984) Neurons of layer I. A developmental analysis. In: Perers A, Jones EG (eds) Cerebral cortex, Vol. 1, Plenum Press, New York pp 447–478
Marin-Padilla M, Marin-Padilla TM (1982) Origin, prenatal development and structural organization of layer I of the human cerebral (motor) cortex. Anat Embryol 164:161–206
Martin KAC (1984) Neuronal circuits in cat striate cortex. In: Peters A, Jones EG (eds) Cerebral cortex, Vol 2. Plenum Press, New York pp 241–284
Marty R, Pujol R (1966) Maturation post-natale de l'aire visuelle du cortex cérébral chez le chat. In: Hassler R, Stephan H (eds) Evolution of the forebrain, Georg Thieme, Stuttgart pp 405–418
McKenna MG (1969) The origin and early differentiation of therian mammals. Ann New York Acad Sci 167:217–240
Molliver ME, Van der Loos H (1970) The ontogenesis of cortical circuitry: the spatial distribution of synapses in somesthetic cortex of newborn dog. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 42(4):1–54
Noback CR, Purpura DP (1961) Postnatal ontogenesis of neurons in cat neocortex. J Comp Neurol 117:291–307
O'Leary JL (1937) Structure of the primary olfactory cortex of the mouse. J Comp Neurol 150:217–238
Oppermann K (1929) Cajal sche Horizontalzellen und Ganglienzellen des Marks. Z Neurol Psychiat 120:121–137
Parnavelas JG, Edmunds SM (1983) Further evidence that Retzius-Cajal cells transform to nonpyramidal neurons in the developing rat visual cortex. J Neurocytol 12:863–871
Peters A (1984) Chandelier cells. In: Peters A, Jones EG (eds) Cerebral cortex, Vol. 1, Plenum Press, New York pp 361–380
Raedler A, Sievers J (1975) The development of the visual system of the albino rat. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 50:1–88
Raedler E, Raedler A, Feldhaus S (1980) Dynamic aspects of neocortical histogenesis in the rat. Anat Embryol 158:253–269
Rakic P (1972) Mode of cell migration to the superficial layers of fetal monkey neocortex. J Comp Neurol 145:61–84
Reep R (1984) Relationship between prefrontal and limbic cortex: a comparative anatomical review. Brain Behav Evol 25:5–80
Retzius G (1893) Die Cajal'sche Zellen der Großhirnrinde beim Menschen und bei Säugethieren. Biol Untersuch 5:1–8
Rickmann M, Wolff JR (1976) on the earliest stages of glial differentiation in the neocortex of rat. Exp Brain Res Suppl 1:239–243
Rickmann M, Chronwall BM, Wolff JR (1977) On the development of non-pyramidal neurons and axons outside the cortical plate: the early marginal zone as a pallial anlage. Anat Embryol 151:285–307
Romer AS (1966) Vertebrate paleontology. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Sanides D, Sanides F (1974) A comparative Golgi study of the neocortex in insectivores and rodents. Z Mikr-Anat Forsch 88:957–977
Sanides F (1968) The architecture of the cortical taste nerve areas in squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus) and their relationships to insular, sensorimotor and prefrontal regions. Brain Res 8:97–124
Sanides F (1970) Functional architecture of motor and sensory cortices in primates in the light of a new concept of neocortex evolution. In: Noback CR, Montagna W (eds) Advances in primatology, Vol. 1, Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York pp 137–208
Sanides F, Sanides D (1972) The “extraverted neurons” of the mammalian cerebral cortex. Z Anat Entwickl-Gesch 136:272–293
Sas E, Sanides F (1970) A comparative Golgi study of Cajal foetal cells. Z Mikr-Anat Forsch 82:385–396
Simpson GG (1945) The principles of classification and a classification of mammals. Bull Am Mus Nat Hist 85:1–350
Somogyi P, Freund TF, Cowey A (1982) The axo-axonic interneuron in the cerebral cortex of the rat, cat and monkey. Neuroscience 7:2577–2607
Somogyi P, Kisvárday ZF, Martin KAC, Whitteridge D (1983) Synaptic connections of morphologically identified and physiologically characterized large basket cells in the striate cortex of cat. Neuroscience 10:261–294
Somogyi P, Freund TF, Hodgson AJ, Somogyi J, Beroukas D, Chubb IW (1985) Identified axo-axonic cells are immunoreactive for GABA in the hippocampus and visual cortex of the cat. Brain Res 332:143–149
Sousa-Pinto A, Paula-Barbosa M, Matos MC (1975) A Golgi and electron microscopical study of nerve cells in layer I of the cat auditory cortex. Brain Res 95:443–458
Stephan H (1956) Vergleichend-anatomische Untersuchungen an Insektivorengehirne. Gegenbaurs Morphol Jahr 97:123–142
Stephan H (1967) Zur Entwicklungshöhe der Insektivoren nach Merkmalen des Gehirns und die Definition der “Basale Insektivoren”. Zool Anz 179:177–199
Szentágothai J (1973) Synaptology of the visual cortex. In: Jung R (ed) Handbook of sensory physiology, Vol. VII/3, Central processing of visual information, part B, Visual centers in the brain. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York, pp 269–324
Valverde F (1965) Studies on the piriform lobe. Harvard University Press, Cambridge Mass
Valverde F (1970) The Golgi method: a tool for comparative structural analyses. In: Nauta WJH, Ebbesson SOE (eds) Contemporary research methods in neuroanatomy, Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York pp 12–31
Valverde F (1983) A comparative approach to neocortical organization based on the study of the brain of the hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus). In: Grisolía S, Guerri C, Samson F, Norton S, Reinoso-Suárez (eds) Ramón y Cajal's contribution to the neurosciences, Elsevier, Amsterdam pp 149–170
Valverde F (1985a) The organizing principles of the primary visual cortex in the monkey. In: Peters A, Jones EG (eds) Cerebral cortex, Vol. 3, Plenum Press, New York, pp 207–257
Valverde F (1985b) Intrinsic neocortical organization: some comparative aspects. Neuroscience (submitted)
Valverde F, López-Mascaraque L (1981) Neocortical endeavor: basic neuronal organization in the cortex of hedgehog. In: Vidrio EA, Fedoroff S (eds) Glial and neuronal cell biology, Eleventh Int Cong Anat, part A Alan R Liss, New York pp 281–290
Van Valen L (1967) New Paleocene insectivores and insectivore classification. Bull Am Mus Nat Hist 135:217–284
Westrum LE (1966) Electron microscopy of degeneration in the praepyriform cortex. J Anat (Lond) 100:683–685
Wolff JR (1978) Ontogenetic aspects of cortical architecture: lamination. In: Brazier MAB, Petsche H (eds) Architectonics of the cerebral cortex, Raven Press, New York pp 159–173
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valverde, F., Facal-Valverde, M.V. Neocortical layers I and II of the hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus). Anat Embryol 173, 413–430 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318926
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318926