Abstract
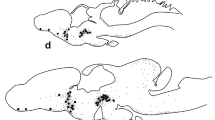
A study of prolactin-mRNA expression in the hypophysis of male and female Typhlonectes compressicaudus was carried out, using a quantitative in situ hybridization technique. In both males and females, an increase in the number of cells showing prolactin-like expression was observed at the beginning of the dry season. In the middle of the season, this number decreased. In pregnant females, mRNA expression remained constant during the first stages of gestation but, in the final stages, when embryos reached their maximum development, mRNA expression increased. In males and in sexually inactive females, prolactin-mRNA expression was the same throughout the year. We conclude that the activity of cells expressing prolactin could be related to hydromineral regulation and, in females, to the gestation process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhatta GK (1986) Some aspects of reproduction in the apodan Amphibia “Ichthyophis”. PhD Thesis, University of Karnatak, Darwad, India
Cooke NE, Coit D, Weiner RI, Baxter JD, Martial JA (1980) Structure of cloned DNA complementary to rat prolactin messenger RNA. J Biol Chem 255:6502–6510
Delsol M, Flatin J, Exbrayat J-M, Bons J (1981) Développement de Typhlonectes compressicaudus, Amphibien Apode vivipare. Hypothèses sur sa nutrition embryonnaire et larvaire par un ectotrophoblaste. C R Acad Sci III 293:281–285
Delsol M, Exbrayat J-M, Flatin J, Gueydan-Baconnier M (1986) Nutrition embryonnaire chez Typhlonectes compressicaudus (Duméril et Bibron 1841), Amphibien Apode vivipare. Mém Soc Zool Fr 43:39–54
Doerr-Schott J, Zuber-Vogeli M (1984) Immunohistochemical study of the adenohypophysis of Typhlonectes compressicaudus (Amphibia, Gymnophiona). Cell Tissue Res 235:211–214
Exbrayat J-M (1986) Quelques aspects de la biologie de la reproduction chez Typhlonectes compressicaudus (Duméril and Bibron 1841). Amphibien Apode. PhD thesis, Université Paris VI
Exbrayat j-M (1988) Croissance et cycle des voies génitales femelles de Typhlonectes compressicaudus (Duméril et Bibron 1841), Amphibien Apode vivipare. Amphibia-Reptilia 9:117–134
Exbrayat J-M (1989) The cytological modifications of the distal lobe of the hypophysis in Typhlonectes compressicaudus (Duméril and Bibron 1841), Amphibia Gymnophiona, during the cycles of seasonal activity. I. In adult males. Biol Struct Morphol 2:117–123
Exbrayat J-M (1992) Appareils génitaux et reproduction chez les Amphibiens Gymnophiones. Bull Soc Zool Fr 117:291–296
Exbrayat J-M, Collenot G (1983) Quelques aspects de l'évolution de l'ovaire de Typhlonectes compressicaudus (Duméril and Bibron 1841), Batracien Apode vivipare. Etude quantitative et histochimique des corps jaunes. Reprod Nutr Dev 23:889–898
Exbrayat J-M, Delsol M (1985) Reproduction and growth of Typhlonectes compressicaudus, a viviparous Gymnophione. Copeia 1985:950–955
Exbrayat J-M, Delsol M (1988) Oviparité et développement intrautérin chez les Gymnophiones. Bull Soc Herp Fr 45:27–36
Exbrayat J-M, Flatin J (1985) Les cycles de reproduction chez les Amphibiens Apodes. Influence des variations saisonnières. Bull Soc Zool Fr 110:301–305
Exbrayat J-M, Hraoui-Bloquet S (1992) La nutrition embryonnaire et les relations foeto-maternelles chez Typhlonectes compressicaudus, Amphibien Gymnophione vivipare. Bull Soc Herp Fr 61:51–59
Exbrayat J-M, Morel G (1990–1991) The cytological modifications of the distal lobe of the hypophysis in Typhlonectes compressicaudus (Duméril and Bibron 1841), Amphibia Gymnophiona, during the cycles of seasonal activity. II.In adult females. Biol Struct Morphol 3:129–138
Gabe M (1968) Techniques histologiques. Masson, Paris
Gabe M (1972) Contribution à l'histologie du complexe hypothalamo-hypophysaire d'Ichthyophis glutinosus (Batracien Apode). Acta Anat 2:253–269
Girod C (1983) Immunohistochemistry of the vertebrate adenohypophysis. In: Graumann W, Neumann K (eds) Handbuch der Histochemie, vol. VIII, suppl. Part 5. G. Fischer, Stuttgart New York, pp 1–536
Hemming FJ, Mesguish P, Morel G, Dubois PM (1983) Cryoultramicrotomy versus plastic embedding: comparative immunocytochemistry of rat anterior pituitary cells. J Microsc 131:26–34
Hraoui-Bloquet S, Exbrayat J-M (1994) Developpement des branchies chez les embryons de Typhlonectes compressicaudus, Amphibien Gymnophione vivipare. Ann Sci Nat Zool (Paris) 13éme sér 15:33–46
Masood Parveez U (1987) Some aspects of reproduction in the female apodan amphibian Ichthyophis. PhD Thesis, University of Karnatak, Darwad, India
Mazzi V, Vellano C, Toscano C (1967) Antigonadal effects of prolactin in adult male newt (Triturus cristatus carnifex Laur.) Gen Comp Endocrinol 8:320–324
Miller WL, Eberhardt NL (1983) Structure and evolution of the growth hormone gene family. Endocrinol Rev 4:97–130
Morel G, Dihl F, Gossard F (1989) Ultrastructural distribution of GH mRNA and GH intron 1 sequences in rat pituitary gland: effects of GH-releasing factor and somatostatin. Mol Cell Endocrinol 65:81–90
Oordt PGWJ van (1974) Cytology of the adenohypophysis. In: Lofts B (ed) Physiology of the Amphibia, vol 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 53–106
Pasteels JL, Herlant M (1962) Les différentes catégories de cellules chromophiles dans l'hypophyse des Amphibiens. Anat Anz 109:764–767
Pillay KV (1957) The hypothalamus-hypophyseal neurosecretory system of Gegenophis carnosus Beddome. Z Zellforsch 46:577–582
Sammouri R, Renous S, Exbrayat J-M, Lescure J (1990) Développement embryonnaire de Typhlonectes compressicaudus (Amphibia, Gymnophiona). Ann Sci Nat Zool (Paris), 13ème sér 11:135–163
Schubert C, Welsch U, Goos H (1977) Histological, immuno- and enzyme histochemical investigations on the adenohypophysis of the urodeles Mertensiella caucasica and Triturus cristatus and the caecilian Chthonerpeton indistinctum. Cell Tissue Res 185:339–349
Taylor EH (1968) The caecilians of the world. A taxonomic review. University of Kansas Press, Lawrence
Vlaming VL de (1979) Actions of prolactin among the vertebrates. In: Barrington EJW (ed) Hormones and evolution, vol 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 561–642
Wake MH (1968) Evolutionary morphology of the caecilian urogenital system. Part I. The gonads and the fat bodies. J Morphol 126:291–332
Wake MH (1970) Evolutionary morphology of the caecilian urogenital system. Part II. The kidneys and urogenital ducts. Acta Anat 75:321–358
Wake MH (1977) The reproductive biology of caecilians. An evolutionary perspective. In: Taylor DH, Guttman SI (eds) The reproductive biology of amphibians. Miami University, Oxford, Ohio, pp 73–100
Wake MH (1980) Reproduction, growth and population structure of the Central American caecilian Dermophis mexicanus. Herpetologica 36:244–256
Xavier F (1986) La reproduction de Nectophrynoides. In: Grassé PP, Delsol M (eds) Traité de Zoologie Batraciens, Tome IB. Masson, Paris, pp 497–513
Zuber-Vogeli M, Doerr-Schott J (1981) Description morphologique et cytologique de l'hypophyse de Typhlonectes compressicaudus (Duméril et Bibron) Amphibien Gymnophione de Guyane française. C R Acad Sci III 292:503–506
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Exbrayat, JM., Morel, G. Prolactin (PRL)-coding mRNA in Typhlonectes compressicaudus, a viviparous gymnophionan amphibian: an in situ hybridization study. Cell Tissue Res 280, 133–138 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00304518
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00304518