Abstract
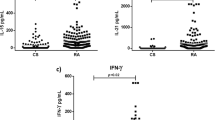
The measurement of serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R), a sensitive marker of lymphocyte activation, has been proposed as an indicator of disease activity and “outcome” in patients with inflammatory diseases characterized by the activation of immune cells. Serum sIL-2R levels have been reported higher in rheumatoid patients than in controls. Using an enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay (ELISA), we evaluated soluble IL-2R levels in the serum of 34 patients with RA and in the synovial fluid of 25 of these patients and we compared it with levels found in the serum of 13 healthy controls. Serum sIL-2R levels were significantly elevated in RA patients compared with the healthy agematched control group (P<0.005). The mean level of soluble IL-2R in synovial fluids was significantly higher than the mean sera levels in RA patients (P<0.0001). Moreover, we examined the correlation between serum and synovial fluid sIL-2R levels and disease activity measures. Serum sIL-2R correlated only with ESR (P<0.04). The synovial fluid sIL-2R correlated with ESR (P<0.02) and a visual analogue scale (VAS) pain score (P<0.04). Both serum and synovial fluid sIL-2R levels correlated with the chronic arthritis systemic index (CASI; P<0.04 and P<0.005, respectively). Our data suggested that in RA the measurement of sIL-2R may certainly mirror the degree of chronic inflammation and the continuous activation of the immune cells in the joint, although the role of this molecule in the immune response is still unclear.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weissman AM, Harford JB, Svetlik PB, Leonard WL, Depper JM, Waldmann TA, Greene WC, Klausner RD (1986) Only high-affinity receptors for interleukin 2 mediate internalization of ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:1463–1466
Rubin LA, Kurman CC, Fritz ME, Biddison WE, Boutin B, Yarchoan R, Nelson DL (1985) Soluble interleukin-2 receptors are released from activated human lymphoid cells in vitro. J Immunol 135:3172–3177
Robb RJ, Kutny RM (1987) Structure-function relationships for the IL-2 receptor system. IV. Analysis of the sequence and ligand binding properties at the soluble Tac protein. J Immunol 139:855–862
Reske-Kunz AB, Osawa H, Josimovic-Alasevic O, Rüde E, Diamantstein T (1987) Soluble interleukin 2 receptors are released by long term-cultured insulin-specific T cell transiently after contact with antigen. J Immunol 138:192–196
Smith KA (1980) T-cell growth factor. Immunol Rev 51:337–357
Rubin LA, Snow KM, Kurman CC, Nelson DL, Keystone EC (1990) Serial levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptor in the peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: correlation with disease activity. J Rheumatol 17:597–602
Keystone EC, Snow KM, Bombardier C, Chang CH, Nelson DL, Rubin LA (1988) Elevated soluble interleukin-2 receptor levels in the sera and synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:844–849
Campen DH, Horwitz DA, Quismorio P Jr, Ehresmann GR, Martin WJ (1988) Serum levels of interleukin-2 receptor and activity of rheumatic diseases characterized by immune system activation. Arthritis Rheum 31:1358–1364
Wolf R, Brelsford WG (1988) Soluble interleukin-2 receptors in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 31:729–735
Wagner PK, Kiwanuka J, Magrath IT, Edwards BK, Rubin LA, Nelson DL (1987) Soluble interleukin-2 receptor levels in undifferentiated and lymphoblastic lymphoma patients. J Clin Oncol 8:1262–1274
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane JF, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS, Medger JT, Mitchell DM, Neustadt DH, Pinals RS, Schaller JG, Sharp JT, Wilder RL, Hunder GG (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Ritchie DM, Boyle JA, McInnes JM, Jasani MK, Dalakos TG, Grievson P, Buchanan WW (1968) Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med 37:393–406
Thompson PW, Silman AJ, Kirwan JR, Currey HLF (1992) Articular indices of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation with the acute-phase response. Arthritis Rheum 30:618–623
Salaffi F, Ferraccioli GF Carotti M, Blasetti P, Cervini C (1992) Disability in rheumatoid arthritis: predictive role of age and depression. Rec Progr Med 83:675–679
Hochberg MC, Chang RW, Dwosh I, Lindsey S, Pincus T, Wolfe F (1992) The American College of Rheumatology 1991 revised criteria for the classification of global functional status in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 35:498–502
Larsen A, Dale K, Eek M (1977) Radiographic evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis and related conditions by standard reference films. Acta Radiol Diagn 18:481–491
Ferraccioli GF, Bartoli E, Salaffi F, Peroni M (1993) Chronic arthritis systemic index (CASI). A nomogram to assess activity and severity of chronic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 36:1180–1181
Scott DL, Dacre JE, Greenwood A, Treasure L, Huskisson EC (1990) Can we develop simple response criteria for slow-acting anti-rheumatic drugs? Ann Rheum Dios 49:196–198
Rubin LA, Kurman CC, Biddison WE, Goldman ND, Nelson DL (1985) A monoclonal antibody, 7G7/B6, binds to an epitope on the human interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor that is distinct from that recognized by IL-2 or anti-Tac. Hybridoma 4:91–102
Symons JA, Wood NC, Di Giovine FS, Duff GW (1988) Soluble IL-2 receptor rheumatoid, arthritis. Correlation with disease activity, IL-1 and IL-2 inhibition. J Immunol 141:2612–2618
Tung KSK, Umland E, Matzner P, Nelson K, Schauf V, Rubin LA, Wagner D, Scollard D, Prakong V, Vithayasai V, Worobec S, Smith T, Suriyanond V (1987) Soluble serum interleukin-2 receptor levels in leprosy patients. Clin Exp Immunol 68:10–15
Sethi KK, Nather H (1986) Elevated titers of cell-free interleukin-2 receptor in serum and cerebrospinal fluid specimens of patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Immunol Lett 13:179–184
Vaisberg M, Sancez ML, Sheinberg MA (1987) Lymphocyte activation in the peripheral blood and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 5:233
Vaisberg M, Scheinberg MA (1990) Simultaneous evaluation of membrane bound and soluble interleukin-2 receptor expression in the blood and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 8:579–582
Wood NC, Symons JA, Dutz GW (1988) Serum interleukin-2 receptor in rheumatoid arthritis: a prognostic indicator of disease activity? J Autoimmun 1:353–361
Sox HC Jr, Liang MH (1986) The erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Ann Intern Med 104:515–523
Kitas GD, Salmon M, Farr M, Gaston JSH, Bacon PA (1988) Deficient interleukin 2 production in rheumatoid arthritis: association with active disease and systemic complications. Clin Exp Immunol 73:242–249
Miossec P, Kashiwado K, Ziff M (1987) Inhibitor of interleukin-2 in rheumatoid synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum 30:121–129
Rubin LA, Jay G, Nelson DA (1986) The released interleukin 2 receptor binds interleukin 2 efficiently. J Immunol 137:3841–3844
Crilly A, Madhok R, Watson J, Capell HA (1993) Serum concentrations of soluble interleukin 2 receptor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: effect of second line drugs. Ann Rheum Dis 52:58–60
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carotti, M., Salaffi, F., Ferraccioli, G.F. et al. Soluble interleukin-2 receptor in sera and synovial fluids of rheumatoid patients: correlations with disease activity. Rheumatol Int 14, 47–52 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300246
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300246