Summary
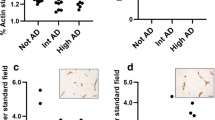
It was the aim of this study to determine, qualitatively and quantitatively, alterations in the blood vessels of brains removed postmortem from patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD), and to compare these findings with the appearance of cerebral blood vessels in a group of individuals without brain disorders. Celloidin sections of brain tissue from four cerebral areas, pre-frontal (Brodmann's area 9), basal forebrain, sensorimotor, and hippocampus, were subjected to an alkaline phosphatase reaction to facilitate the evaluation of the vascular distribution. The vascular density in five sections was determined by counting the number of vascular intersections with a microscopic test grid of 100 squares; ten fields per section were examined in this manner. Analysis of 16 AD and 6 control brains, showed that there was a striking and statistically significant reduction in the vascular net density specifically in the basal forebrain region and the hippocampus of AD brains. In addition, vessels in the AD brains exhibited extensive topographical changes, such as kinking and looping. These results indicate that modifications in vascular density are present in AD brains with a marked regional specificity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akima M, Nonaka H, Kagesawa M, Tanaka K (1986) A study on the microvasculature of the cerebral cortex. Lab Invest 55:482–489
Bell MA, Ball MJ (1981) Morphometric comparison of hippocampal microvasculature in aging and demented people: diameters and densities. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 53:299–318
Bell MA, Scarrow WG (1984) Staining for microvascular alkaline phosphatase in thick celloidin sections of nervous tissue: morphometric and pathologic applications. Microvasc Res 27:189–203
Blessed G, Tomlinson BE, Roth M (1968) The association between quantitative measures of dementia and of senile changes in the cerebral grey matter of elderly subjects. Br J Psychiatr 114:797–811
Haug H (1987) Brain sizes, surfaces, and neuronal sizes of the cortex cerebri: a stereological investigation of man and his variability and a comparison with some mammals (primates, whales, marsupials, insectivores, and one elephant). Am J Anat 180:126–142
Coleman PD, Flood DG (1987) Neuron numbers and dendritic extent in normal aging and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 8:521–545
Creasey H, Rapoport SI (1985) The aging human brain. Ann Neurol 17:2–10
Fang CH (1974) The studies of cerebral arterioles and capillaries in normal and pathologic states in man. In: Cervós-Navarro J (ed) Pathology of cerebral microcirculation. De Gruyter, Berlin, pp 431–441
Glenner GG (1985) On causative theories in Alzheimer's disease. Hum Pathol 16:433–435
Hassler O (1965) Vascular changes in senile brains. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 5:40–53
Hunziker O, Abdel'Al S, Schulz U (1979) The aging human cerebral cortex: a stereological characterization of changes in the capillary net. J Gerontol 34:345–350
Khachaturian ZS (1985) Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 42:1097–1104
Pickworth FA (1934) A new method of study of the brain capillaries and its application to the regional localization of mental disorder. J Anat 69:62–71
Prohovnik I, Mayeux R, Sackeim HA, Smith G, Stern Y, Alderson PO (1988) Cerebral perfusion as a diagnostic marker of early Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 38:931–937
Ravens JR (1978) Vascular changes in the human senile brain. In: Cervós-Navarro J (ed) Advances in neurology, vol 20. Raven Press, New York, pp 487–501
Scheibel AB, Duong T, Tomiyasu U (1987) Denervation microangiopathy in senile dementia, Alzheimer type. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 1:19–37
Selkoe DJ (1989) Aging, amyloid, and Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med 320:1484–1487
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by the St. Louis Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders Association and the Department of Community Medicine. St. Louis University Medical Center
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischer, V.W., Siddiqi, A. & Yusufaly, Y. Altered angioarchitecture in selected areas of brains with Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 79, 672–679 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294246
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294246