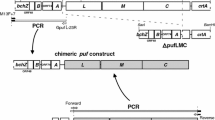
Abstract
The ribosomal protein gene rps4 was cloned and sequenced from the chloroplast genome of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The N-terminal 213 amino acid residues of the S4 protein are encoded in the single-copy region (SCR) of the genome, while the C-terminal 44 amino acid residues are encoded in the inverted repeat (IR). The deduced 257 amino acid sequence of C. reinhardtii S4 is considerably longer (by 51–59 residues) than S4 proteins of other photosynthetic species and Escherichia coli, due to the presence of two internal insertions and a C-terminal extension. A short conserved C-terminal motif found in all other S4 proteins examined is missing from the C. reinhardtii protein. In E. coli, mutations in the S4 protein suppress the streptomycin-dependent (sd) phenotype of mutations in the S12 protein. Because we have been unable to identify similar S4 mutations among suppressors of an sd mutation in C. reinhardtii S12 obtained using UV mutagenesis, we made site-directed mutations [Arg68 (CGT) to Len (CTG and CTT)] in the wild-type rps4 gene equivalent to an E. coli Gln53 to Len ribosomal ambiguity mutation (ram), which suppresses the sd phenotype and decreases translational accuracy. These mutants were tested for their ability to transform the sd S 12 mutation of C. reinhardtii to streptomycin independence. The streptomycin-independent isolates obtained by biolistic transformation all possessed the original sd mutation in rps12, but none had the expected donor Leu68 mutations in rps4. Instead, six of 15 contained a Gln73 (CAA) to Pro (CCA) mutation five amino acids downstream from the predicted mutant codon, irrespective of rps4 donor DNA. Two others contained six- and ten-amino acid, in-frame insertions at S4 positions 90 and 92 that appear to have been induced by the biolistic process itself. Eight streptomycin-independent isolates analyzed had wild-type rps4 genes and may possess mutations identical to previously isolated suppressors of sd that define at least two additional chloroplast loci. Cloned rps4 genes from streptomycin-independent isolates containing the Gln73 to Pro mutation and the 6-amino acid insertion in r-protein S4 transform the sd strain to streptomycin independence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen PN, Noller HF (1989) Mutations in ribosomal proteins S4 and S12 influence the higher order structure of 16S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol 208:457–468
Allen PN, Noller, HF (1991) A single base substitution in 16S ribosomal RNA suppresses streptomycin dependence and increases the frequency of translational errors. Cell 66:141–148
Bedwell D, Davis G, Gosink M, Post L, Nomura M, Kestler H, Zengel JM, Lindahl L (1985) Nucleotide sequence of the alpha ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res 13:3891–3903
Ben Tahar S, Bottomley W, Whitfeld PR (1986) Characterization of the spinach chloroplast genes for the S4 ribosomal protein, tRNAThr (UGU) and tRNASer (GGA). Plant Mol Biol 7:63–70
Birge EA, Kurland CG (1970) Reversion of a streptomycin-dependent strain of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet 109:356–369
Boynton JE, Gillham NW (1993) Chloroplast transformation in Chlamydomonas. Meth Enzymol 27:510–536
Deusser E, Stöffler G, Wittmann HG (1970) Ribosomal proteins XVI. Altered S4 proteins in Escherichia coli revertants from streptomycin dependence to independence. Mol Gen Genet 109:298–302
Donner D, Kurland CG (1972) Changes in the primary structure of a mutationally altered ribosomal protein S4 of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet 115:49–53
Douglas SE, Durnford DG (1990) Nucleotide sequence of the genes for ribosomal protein S4 and tRNAArg from the chlorophyll c-containing alga Cryptomonas F. Nucleic Acids Res 18:1903
Funatsu G, Wittmann HG (1972) Location of amino acid replacements in protein S12 isolated from Escherichia coli mutants resistant to streptomycin. J Mol Biol 68:547–550
Funatsu G, Nierhaus K, Wittmann HG (1972a) Ribosomal proteins XXXVII. Determination of allele types and amino acid exchanges in protein S12 of three streptomycin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta 287:282–291
Funatsu G, Puls W, Schiltz E, Reinbolt J, Wittmann HG (1972b) Ribosomal proteins XXXI. Comparative studies on altered proteins S4 of six Escherichia coli revertants from streptomycin dependence. Mol Gen Genet 115:131–139
Gorini L (1974) Streptomycin and misreading of the genetic code. In: Nomura M, Tissières A, Lengyel P (eds) Ribosomas. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, pp 791–803
Gray MW (1992) The endosymbiont hypothesis revisited. Int Rev Cytol 141:233–357
Gruissem W, Schuster G (1993) Control of mRNA degradation in organelles. In: Brawerman G, Belasco J (eds) Control of messenger RNA stability. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 329–365
Grundy FJ, Henkin TM (1990) Cloning and analysis of the Bacillus subtilis rpsD gene, encoding ribosomal protein S4. J Bacteriol 172:6372–6379
Hallick RB, Hong L, Drager RG, Favreau MR, Monfort A, Orsat B, Spielmann A, Stutz E (1993) Complete sequence of Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 21:3537–3544
Harris EH (1989). The Chlamydomonas sourcebook. Academic Press, San Diego
Harris EH, Burkhart BD, Gillham NW, Boynton JE (1989) Antibiotic resistance mutations in the chloroplast 16S and 23S rRNA genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: correlation of genetic and physical maps of the chloroplast genome. Genetics 123:281–292
Harris EH, Boynton JE, Gillham, NW (1994) Chloroplast ribosomes and protein synthesis. Microbiol Rev 58:700–754
Hasenbank R, Guthrie C, Stöffler G, Wittmann HG, Rosen L, Apirion D (1973) Electrophoretic and immunological studies on ribosomal proteins of 100 Escherichia coli revertants from streptomycin dependence. Mol Gen Genet 127:1–18
Hauser CR, Randolph-Anderson BL, Hohl TM, Harris EH, Boynton JE, Gillham NW (1993) Molecular genetics of chloroplast ribosomes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. In: Nierhaus KH, Franceschi F, Subramanian AR, Erdmann VA, Wittmann-Liebold B (eds) The translational apparatus. Structure, function, regulation, evolution. Plenum Press, New York-London, pp 545–554
Hiratsuka J, Shimada H, Whittier R, Ishibashi T, Sakamoto M, Mori M, Kondo C, Honji Y, Sun C-R, Meng B-Y, Li Y-Q, Kanno A, Nishizawa Y, Hirai A, Shinozaki K, Sugiura M (1989) The complete sequence of the rice (Oryza sativa) chloroplast genome: intermolecular recombination between distinct tRNA genes accounts for a major plastid DNA inversion during the evolution of the cereals. Mol Gen Genet 217:185–194
Hoffman DW, Davies C, Gerchman SE, Kycia JH, Porter SJ, White SW, Ramakrishnan V (1994) Crystal structure of prokaryotic ribosomal protein L9: a bi-lobed RNA binding protein. EMBO J 13:205–212
Itoh T, Wittmann HG (1973) Amino acid replacements in proteins S5 and S12 of two Escherichia coli revertants from streptomycin dependence to independence. Mol Gen Genet 127:19–32
Kreider G, Brownstein BL (1971) A mutation suppressing streptomycin dependence. II. An altered protein on the 30S ribosomal subunit. J Mol Biol 61:135–142
Levinson G, Gutman GA (1987) Slipped-strand mispairing: a major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Mol Biol Evol 4:203–221
Lindahl L, Zengel JM (1986) Ribosomal genes in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet 20:297–326
Liu X-Q, Gillham NW, Boynton JE (1989). Chloroplast ribosomal protein gene rps12 of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Wild-type sequence, mutation to streptomycin resistance and dependence, and function in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 264:16100–16108
Newman SM, Boynton JE, Gillham NW, Randolph-Anderson BL, Johnson AM, Harris EH (1990) Transformation of chloroplast ribosomal RNA genes in Chlamydomonas. Molecular and genetic characterization of integration events. Genetics 126:875–888
Noller HF, Moazed D, Stern S, Powers T, Allen PN, Robertson JM, Weiser B, Triman K (1990) Structure of rRNA and its functional interactions in translation. In: Hill W, Dahlberg A, Garrett RA, Moore PB, Schlessinger D, Warner JR (eds) The ribosome. Structure, function and evolution. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 73–92
Palmer JD (1985) Comparative organization of chloroplast genomes. Annu Rev Genet 19:325–354
Palmer JD (1992) Comparisons of chloroplast and mitochondrial genome evolution in plants. In: Herrmann RG (ed) Plant gene research: organelles. Springer-Verlag, Wien, pp 99–133
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Sanford JC, Smith FD, Russell JA (1993) Optimizing the biolistic process. Meth Enzymol 27:510–536
Schmidt RJ, Richardson CB, Gillham NW, Boynton JE (1983) Sites of synthesis of chloroplast ribosomal proteins in Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol 96:1451–1463
Shinozaki K, Ohme M, Tanaka M, Wakasugi T, Hayashida N, Matsubayashi T, Zaita N, Chunwongse J, Obokata J, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Ohto C, Torazawa K, Meng BY, Sugita M, Deno H, Kamogashira T, Yamada K, Kusuda J, Takaiwa F, Kato A, Tohdoh N, Shimada H, Sugiura M (1986a) The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J 5:2043–2049
Shinozaki K, Ohme M, Tanaka M, Wakasugi T, Hayashida N, Matsubayashi T, Zaita N, Chunwongse J, Obokata J, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Ohto C, Torazawa K, Meng BY, Sugita M, Deno H, Kamogashira T, Yamada K, Kusuda J, Takaiwa F, Kato A, Tohdoh N, Shimada H, Sugiura M (1986b) The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome. Plant Mol Biol Rep 4:111–147
Stern DB, Kindle KL (1993) 3′ end maturation of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast atpB mRNA is a two-step process. Mol Cell Biol 13:2272–2285
Subramanian AR, Steinmetz A, Bogorad L (1983) Maize chloroplast DNA encodes a protein sequence homologous to the bacterial ribosome assembly protein S4. Nucl Acids Res 11:5277–5286
Umesono K, Inokuchi H, Shiki Y, Takeuchi M, Chang Z, Fukuzawa H, Kohchi T, Shirai H, Ohyama K, Ozeki H (1988) Structure and organization of Marchantia polymorpha chloroplast genome. II. Gene organization of the large single copy region from rps12 to atpB. J Mol Biol 203:299–331
van Acken U (1975) Proteinchemical studies on ribosomal proteins S4 and S12 from ram (ribosomal ambiguity) mutants of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet 140:61–68
Wang S, Liu X-Q (1991) The plastid genome of Cryptomonas phi encodes an hsp 70-like protein, a histone-like protein, and an acyl carrier protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10783–10787
Wittmann HG, Wittmann-Liebold B (1974) Chemical structure of bacterial ribosomal proteins. In: Nomura M, Tissieres A, Lengyel P (eds) Ribosomes. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, pp 115–140
Wolfe KH, Morden CW, Palmer JD (1992a) Function and evolution of a minimal plastid genome from a nonphotosynthetic plant. Proe Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10648–10652
Wolfe KH, Morden CW, Ems SC, Palmer JD (1992b) Rapid evolution of the plastid translational apparatus in a nonphotosynthetic plant: loss or accelerated sequence evolution of tRNA and ribosomal protein genes. J Mol Evol 35:304–317
Yoshinaga K, Ohta T, Suzuki Y, Sugiura M (1988). Chlorella chloroplast DNA sequence containing a gene for the large subunit of ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase and a part of a possible gene for the beta' subunit of RNA polymerase. Plant Mol Biol 10:245–250
Zhou D-X, Quigley F, Massenet O, Mache R (1989) Cotranscription of the S10- and spc-like operons in spinach chloroplasts and identification of three of their gene products. Mol Gen Genet 216:439–445
Zimmerman RA (1980) Interactions among protein and RNA components of the ribosome. In: Hill W, Dahlberg A, Garrett RA, Moore PB, Schlessinger D, Warner JR (eds) The ribosome. Structure, function and evolution. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 135–169
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by R. G. Herrmann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Randolph-Anderson, B.L., Boynton, J.E., Gillham, N.W. et al. The chloroplast gene encoding ribosomal protein S4 in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii spans an inverted repeat — unique sequence junction and can be mutated to suppress a streptomycin dependence mutation in ribosomal protein S12. Molec. Gen. Genet. 247, 295–305 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293197
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293197