Summary
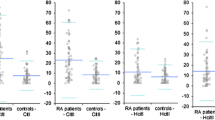
The presence of circulating IgG, IgA and IgM antibodies to native cartilage collagens in some patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) suggests that an autoimmune response to cartilage collagens may be involved in the pathogenesis of RA. However, the relevance of such antibodies to the pathological process remains unclear, and it is likely that many humoral and cellular derived factors combine to trigger events leading to the chronicity of the rheumatoid lesion. Since histological and biochemcal studies have suggested the involvement of mast cells in the rheumatoid joint, we have studied the frequency of IgE antibodies directed against the cartilage collagens type II, IX and XI in patients with active rheumatoid disease. Of the 91 patients' sera tested, 32 had significant levels of IgE anti-cartilage collagen antibodies when compared with non-arthritic controls. Total serum IgE levels did not correlate with the presence of IgE anti-collagen antibodies, nor were any patients positive for IgE antibodies to fibronectin, a widely distributed extracellular matrix component. These results are consistent with an allergic type I hypersensitivity reaction to cartilage antigens in RA involving mast cell and basophil degranulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trentham DE, Townes AS, Kang AH (1977) Autoimmunity to type II collagen: an experimental model of arthritis. J Exp Med 146:857–867
Clague RB, Moore LJ (1984) IgG and IgM antibody to native type II collagen in rheumatoid arthritis serum and synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum 27:1370–1377
Morgan K, Clague RB, Collins I, Ayad S, Phinn SD, Holt PJL (1987) Incidence of antibodies to native and denatured cartilage collagens (types II, IX and XI) and to type I collagen in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 46:902–907
Choi EK, Gatenby PA, McGill NW, Bateman JF, Cole WG, York JR (1988) Autoantibodies to type II collagen. Occurrence in rheumatoid arthritis, other arthritides, autoimmune connective tissue diseases and chronic inflammatory syndromes. Ann Rheum Dis 47:313–322
Londei M, Savill CM, Verhoff A, Brennan F, Leech ZA, Duance V, Maini R, Feldman M (1989) Persistence of collagen Type II specific T cell clones in the synovial membrane of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:636–640
Bromley M, Fisher WD, Woolley DE (1984) Mast cells at sites of cartilage erosion in the rheumatoid joint. Ann Rheum Dis 43:76–79
Crisp AJ, Chapman CM, Kirkham SE, Schiller AL, Krane SM (1984) Articular mastocytosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 27:845–851
Malone DG, Irani A, Schwartz LB, Barrett KE, Metcalfe DD (1986) Mast cell numbers and histamine levels in synovial fluids from patients with diverse arthritides. Arthritis Rheum 29:956–963
Ayad S, Abedin MZ, Grundy SM, Weiss JB (1981) Isolation and characterisation of an unusual collagen from hyaline cartilage and intervertebral disc. FEBS Lett 139:195–199
Ayad S, Abedin MZ, Weiss JB, Grundy SM (1982) Characterisation of another short chain disulphide-bonded collagen from cartilage, vitreous and intervetebral disc. FEBS Lett 139:300–304
Engvall E, Perlmann P (1972) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, ELISA 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzymelabelled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen coated tubes. J Immunol 109:129–145
Ramshaw JAR, Werkmeister JA (1988) Electrophoresis and electroblotting of native collagens. Anal Biochem 168:82–87
Hunder GG, Gleich GJ (1974) Immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels in serum and synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 17:955–963
O'Driscoll BR, Millburn HJ, Kemeny DM, Cochrane GM, Panayi GS (1985) Atopy and rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Allergy 15:547–553
Stuart JM, Huftstutter EH, Townes AS, Kang AH (1983) Incidence and specificity of antibodies to I, II, III, IV & V collagen in rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases as measured by I125 radioimmunoassay. Arthritis Rheum 26:832–840
Ishizaka TJ (1981) Analysis of triggering events in mast cells for release. J Allergy Clin Immunol 67:90–96
Yoffe JR, Taylor DJ, Woolley DE (1985) Mast-cell products and heparin stimulate the production of mononuclear-cell factor by cultured human monocyte/macrophages. Biochem J 230:83–88
Taylor DJ, Yoffe JR, Woolley DE (1983) Histamine H2 receptors on foetal-bovine articular chondrocytes. Biochem J 212:517–520
Yoffe JR, Taylor DJ, Woolley DE (1984) Mast cell products stimulate collagenase and prostaglandin E production by cultures of adherent rheumatoid synovial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 122:270–275
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bartholomew, J.S., Evanson, J.M. & Woolley, D.E. Serum IgE anti-cartilage collagen antibodies in rheumatoid patients. Rheumatol Int 11, 37–40 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00290249
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00290249