Summary
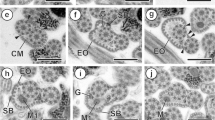
The primary spermatocytes of an Opilionid, Acanthopachylus aculeatus show (at least as a rule) two bodies which in longitudinal sections appear as integrated of up to 12 dark bands each about 300 Å wide, interlaced with one another by a curtain of thin filaments. The same bodies appear in transversal sections as formed by an hexagonal lattice the nodal points of which are the cross sections of the dark bands. The study of spermatocytes at early prophase demonstrated that at the inception these bodies are formed by association of several structures comparable to those observed in the axis of paired autosomes and called synaptinemal complexes.
The findings in this species are compared with their similar in other species, particularly with species of Gryllidae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brinkley, B. R., and J. H. D. Bryan: The ultrastructure of meiotic prophase chromosomes as revealed by silver-aldehyde staining. J. Cell Biol. 23, 14A (1964).
Coleman, J. R., and M. H. Moses: DNA and fine structure of synaptic chromosomes in the domestic rooster (Gallus domesticus). J. Cell Biol. 23, 63–78 (1964).
Fawcett, D. W.: The fine structure of chromosomes in the meiotic prophase of vertebrate spermatocytes. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 2, 405–406 (1956).
Meyer, G. F.: A possible correlation between submicroscopic structure of meiotic chromosomes and crossing-over. Publishing House of the Czechoslowak Academy of Sciences, Prague, 461–462 (1964).
—, O. Hess und W. Beermann: Phasenspezifische Funktionsstrukturen in Spermatocytenkernen von Drosophila melanogaster und ihre Abhängigkeit vom Y-Chromosom. Chromosoma (Berl.) 12, 676–716 (1961).
Moses, M. J.: Chromosomal structure in crayfish spermatocytes. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 2, 215–218 (1956);- The relation between the axial complex of meiotic prophase chromosomes and chromosome pairing in a salamander (Plethodon cinereus). J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 4, 633–635 (1958).
Nebel, B. R., and E. M. Coulon: The fine structures of chromosomes in pigeon spermatocytes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 13, 272–291 (1962).
Schin, K. S.: Meiotische Prophase und Spermatidenreifung bei Gryllus domesticus mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der Chromosomstruktur. Zellforsch. 65, 481–513 (1965).
Solari, A. J.: The morphology and ultrastructure of the sex vesicle in the mouse. Bxp. Cell Res. 36, 160–168 (1964).
Sotelo, J. R., and O. Trujillo-Cenóz: Submicroscopic structure of meiotic chromosomes during prophase. Exp. Cell Res. 74, 1–8 (1958); - Electron microscope study on chromosome structure during meiosis. Pathologie-Biologie 9, 762–768 (1961).
—, and R. Wettstein: Electron microscope study on meiosis. The sex chromosome in spermatocytes, spermatids and oocytes of Gryllus argentinus. Chromosoma (Berl.) 15, 389–415 (1964a); - Electron microscope study on the meiotic chromosomes of Acanthopachylus acukatus (Class Arachnida; Order Opiliones). XI International Congress of Cell Biology. Excerpt. Med. 77, 42 (1964b); - Fine structure of meiotic chromosomes of Gryllus argentinus. Experientia (Basel) 20, 610–612 (1964) ; - Fine structure of meiotic chromosomes. Symposium on Genes and Chromosomes. Structure and Function. Buenos Aires, 1964. J. of the Nat. Cancer Inst. 1965 (in press).
Watson, M. L.: Spermatogenesis in the adult albino rat as revealed by tissue sections in the electron microscope. The University of Rochester. Atomic Energy Project (unclassified) (1952).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This investigation was supported by United States Public Health Service Research Grant GM 08337 from the Research Grants Branch, Division of Medical Sciences, and partly by Grant RF 61034 from The Rockefeller Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wettstein, R., Sotelo, J.R. Electron microscope study on the meiotic cycle of Acanthopachylus aculeatus (Arachnida; Opiliones). Chromosoma 17, 246–257 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00283601
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00283601