Abstract
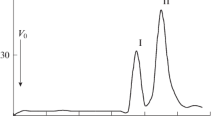
Lipopolysaccharides were isolated from the moderate halophilic Ectothiorhodospira shaposhnikovii slight to and Ectothiorhodospira mobilis and from the extremely halophilic Ectothiorhodospira halophila by the hot phenol-water and purified by the phenol-chloroform-petroleum ether methods. The isolated lipopolysaccharides of all three species contained 3-deoxy-d-manno-octulosonic acid and d-glycero-d-mannoheptose indicating the existence of a core. They contained additionally glucose and uronic acids (E. shaposhnikovii and E. mobilis) or glucose, uronic acids and threonine (E. halophila). Sodium deoxycholate gel-electrophoresis of the three lipopolysaccharides, each showing only one major band, indicated R-type character of the lipopolysaccharides of the three Ectothiorhodospira species.
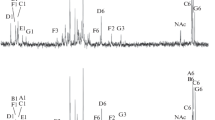
The lipid A fractions of the lipopolysaccharides from E. shaposhnikovii and E. mobilis represented phosphorylated “mixed” lipid A types with both 2,3-diamino-2,3-dideoxy-d-glucose and d-glucosamine. The lipid A from E. halophila contained also phosphate and 2,3-diamino-2,3-dideoxy-d-glucose but only traces of d-glucosamine, which would indicated lipid ADAG. The fatty acid spectra were characterized by amide-bound 3-OH-10:0 and 3-OH-12:0 (E. shaposhnikovii), 3-OH-10:0 (E. mobilis), or 3-OH-10:0,3-OH-14:0, and 3-oxo-14-0 (E. halophila). The predominant ester-bound fatty acids were 14:0 and 16:0 (E. shaposhnikovii and E. mobilis), or 12:0 and 14:1 (E. halophila).
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAG:
-
2,3-diamino-2,3-dideoxy-d-glucose
- Kdo:
-
3-deoxy-d-manno-octulosonic acid
- GlcA:
-
glucuronic acid
- GalA:
-
galacturonic acid
- GC-MS:
-
combined gas liquid chromatographymass spectrometry
- GlcN:
-
Glucosamine
- DOC:
-
sodium deoxycholate
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
- PAGE:
-
polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- PCP:
-
phenol-chloroform-petroleum ether
References
Brade H, Galanos C, Lüderitz O (1983) Differential determination of the 3-deoxy-d-mannooctulosonic acid residues in lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella minnesota rough mutants. Eur J Biochem 131: 195–200
Evers D, Weckesser J, Jürgens UJ (1986) Chemical analyses on cell envelope polymers of the halophilic, phototrophic Rhodospirillum salexigens. Arch Microbiol 145: 254–258
Galanos C, Lüderitz O, Westphal O (1969) A new method for extraction of R-lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem 9: 245–249
Hurlbert RE, Weckesser J, Mayer H, Fromme I (1976) Isolation and characterization of the lipopolysaccharide of Chromatium vinosum. Eur J Biochem 68: 365–371
Hurlbert RE, Hurlbert I (1977) Biological and physio-chemical properties of the lipopolysaccharide of Chromatium vinosum. Infect Immun 16: 983–994
Hurlbert RE, Weckesser J, Tharanathan RN, Mayer H (1978) Isolation and characterization of the lipopolysaccharide of Thiocapsa roseopersicina. Eur J Biochem 90: 241–246
Imhoff JF (1984) Reassignement of the genus Ectothiorhodospira Pelsh 1936 to a new family. Ectothiorhodospiraceae fam nov, and emended description of the Chromatiaceae Bavendamm 1924. Int J Syst Bacteriol 34: 338–339
Imhoff JF (1988) Anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria. In: Austin B (ed) Methods in aquatic bacteriology, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, pp 207–240
Imhoff JF (1989) Ectothiorhodospiraceae. In: Staley JT, Bryant MP, Pfennig N, Holt JG (eds) Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology, vol. 3. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 1654–1658
Imhoff JF, Ditandy T, Thiemann B (1991) Salt adaptation of Ectothiorhodospira. In: Rodriguez-Valera F (ed) General and applied aspects of halophilic microorganisms. Plenum Press, New York, pp 115–120
Ivanova TL, Turova TP, Antonov AS (1985) DNA-DNA and rRNA-DNA hybridization studies in the genus Ectothiorhodospira and other purple sulfur bacteria. Arch Microbiol 143: 154–156
Kandler O, Koenig H, Wiegel J, Claus D (1983) Occurrence of poly-gamma-d glutamic acid and poly-alpha-l glutamic acid in the genera Xanthobacter, Flexithrix, Sporosarcina and Planococcus. Syst Appl Microbiol 4: 34–41
Komuro T, Galanos C (1988) Analysis of Salmonella lipopolysaccharides by sodium deoxycholate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Chromatogr 450: 381–387
Masoud H, Urbanik-Sypniewska T, Lindner B, Weckesser J, Mayer H (1991) The structure of the lipid A component of Sphaerotilus natans. Arch Microbiol 156: 167–175
Mayer H, Campos-Portuguez SA, Busch M, Urbanik-Sypniewska T, Ramadas Bhat U (1990a) Lipid A variants — or how constant are the regions in lipopolysaccharides? In: Nowotny A, Spitzer JJ, Ziegler EJ (eds) Cellular and molecular aspects of endotoxin reactions. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 111–120
Maycr H, Krauss JH, Yokota A, Weckesser J (1990b) Natural variants of lipid A. In: Friedman H, Klein TW, Nakano M, Nowotny A (eds) Endotoxin. Plenum Publ., New York, pp 45–70
Meißner J, Borowiak D, Fischer U, Weckesser J (1988a) The lipopolysaccharide of the phototrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira vacuolata. Arch Microbiol 149: 245–248
Meißner J, Pfennig N, Krauss J, Mayer H, Weckesser J (1988b) Lipopolysaccharides of the Chromatiaceae species Thiocystis violacea, Thiocapsa pfennigii and Chromatium tepidum. J Bacteriol 170: 3267–3272
Moran AP, Zähringer U, Seydel U, Scholz D, Stütz P, Rietschel ETh (1991) Structural analysis of the lipid A component of Campylobacter jejuni CCUG 10936 (serotype O:2) lipopolysaccharide. Description of a lipid A containing a hybrid backbone of 2-amino-2-deoxy-d-glucose and 2,3-diamino-2,3-dideoxy-d-glucose. Eur J Biochem 198: 459–469
Raetz CRH (1987) Biosynthesis and pharmacological properties of Escherichia coli lipid A. In: Inouye M (ed) Bacterial outer membranes as model systems. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 229–245
Roppel J, Mayer H, Weckesser J (1975) Identification of a 2,3-diamino-2,3-dideoxyhexose in the lipid A component of lipopolysaccharides of Rhodopseudomonas viridis and Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Carbohydr Res 40: 31–40
Salimath VP, Tharanathan RN, Weckesser J, Mayer H (1984) The structure of the polysaccharide moiety of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides ATCC 17023 lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Biochem 144: 227–232
Stackebrandt E, Fowler VJ, Schubert W, Imhoff JF (1984) Towards a phylogeny of phototrophic purple sulfur bacteria — the genus Ectothiorhodospira. Arch Microbiol 137: 366–370
Stackebrandt E, Embley M, Weckesser J (1988) Phylogenetic, evolutionary, and taxonomic aspects of phototrophic eubacteria. In: Olson JM, Ormerod JG, Amesz J, Stackebrandt E, Trüper HG (eds) Green photosynthetic bacteria. Plenum Publ, New York, pp 201–215
Tharanathan RN, Salimath PV, Weckesser J, Mayer H (1985) The structure of lipid A from the lipopolysaccharide of Rhodopseudomonas gelatinosa 29/1. Arch Microbiol 141: 279–283
Tsai CM, Frasch CE (1982) A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 119: 115–119
Weckesser J, Drews G, Mayer H (1979) Lipopolysaccharides of photosynthetic prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol 33: 215–239
Weckesser J, Mayer H (1988) Different lipid A types in lipopolysaccharides of phototrophic and related non-phototrophic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 54: 143–154
Westphal O, Lüderitz O, Bister F (1952) Über die Extraktion von Bakterien mit Phenol/Wasser. Z Naturforsch 7b: 148–155
Woese CR (1987) Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev 51: 221–271
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahr, M., Fobel, B., Mayer, H. et al. Chemical composition of the lipopolysaccharides of Ectothiorhodospira shaposhnikovii, Ectothiorhodospira mobilis, and Ectothiorhodospira halophila . Arch. Microbiol. 157, 499–504 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276769
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276769