Summary
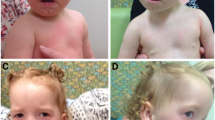
Comparative molecular analysis of chromosome 15, sub-band q11.2 of patients with the Prader-Willi or Angelman syndromes demonstrates that they have a similar deletion. An hypothesis is presented that attempts to explain the tremendous degree of clinical heterogeneity in these diverse deletion-associated syndromes based on abnormal haplotypes present on the cytogenetically normal homolog. This hypothesis also addresses genetic similarities between patients who have deletion and those who have the inv dup (15) by postulating that these syndromes are caused by relative dosage ratios of normal versus abnormal alleles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldridge J, Kunkel L, Bruns G, Tantravahi U, Lalande M, Brewster T, Moreau E, Wilson M, Bromley W, Roderick T, Latt SA (1984) A strategy to reveal high frequency RFLPs along the human X chromosome in human XX males. Am J Hum Genet 36:546–564
Artzt K, Shin HS, Bennett D (1982) Gene mapping within the T/t complex of the mouse. II. Anomalous position of the H-2 complex in t haplotypes. Cell 28:471–476
Baraitser M, Patton M, Lam STS, Brett EM, Wilson J (1987) The Angelman (Happy Puppet) syndrome: is it autosomal recessive? Clin Genet 31:323–330
Brookwell R, Veleba A (1987) Proximal 15q variant with normal phenotype in three unrelated individuals. Clin Genet 31:311–314
Buckton KE, Spowart G, Newton MS, Evans HJ (1985) Forty four probands with an additional “marker” chromosome. Hum Genet 69:353–370
Burke CM, Kouseff BG, Gleeson M, O'Connell BM, Devlin JG (1987) Familial Prader-Willi syndrome. Arch Intern Med 147: 673–675
Butler MG, Meaney FJ, Palmer CG (1986) Clinical and cytogenetic survey of 39 individuals with Prader-Labhart-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet 23:793–809
Cohen DM, Green JG, Miller J, Gorlin RJ, Reed JA (1987) Acrocephalopolysyndactyly type II — Carpenter syndrome: clinical spectrum and an attempt at unification with Goodman and Summitt syndromes. Am J Med Genet 28:311–324
Cohen MM Jr, Hall BD, Smith DW, Graham CB, Lampert KJ (1973) A new syndrome with hypotonia, obesity, mental deficiency, and facial, oral, ocular, and limb anomalies. J Pediatr 83:280–284
Donlon TA, Lalande M, Wyman A, Bruns G, Latt SA (1986) Instability of molecular probes associated with the chromosome 15 instability in the Prader-Willi syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4408–4412
Donlon TA, Lalande M, Bruns G, Wharton R, Latt SA (1987) Paracentromeric mapping of 11 cloned DNA segments from chromosome 15. (9th International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping) Cytogenet Cell Genet 46:607
Endo M, Tasaka Y, Matsuura N, Matsuda I (1976) Laurence-Moon-Biedl syndrome (?) and Prader-Willi syndrome (?) in a single family. Eur J Pediatr 123:269–276
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Fornace AJ, Cummings DE, Comeau CM, Kant JA, Crabtree GR (1984) Single-copy inverted repeats associated with regional genetic duplications in gamma fibrinogen and immunoglobulin genes. Science 224:161–164
Fraccaro M, Zuffardi O, Bühler E, Schinzel A, Simoni G, Witkowski R, Bonifaci E, Caufin D, Cignacco G, Delendi N, Gargantini L, Losanowa T, Marca L, Ullrich E, Vigi V (1983) Deficiency, transposition, and duplication of one 15q region may be alternatively associated with Prader-Willi (or a similar) syndrome. Analysis of seven cases after varying ascertainment. Hum Genet 64:388–394
France HF de, Beemer FA, Ippel PF (1984) Duplication in chromosome 15q in a boy with the Prader-Willi syndrome; further cytogenetic confusion. Clin Genet 26:379–382
Führmann-Rieger A, Kohler A, Führmann W (1984) Duplication or insertion in 15q11-13 associated with mental retardation — short stature and obsity — Prader-Willi or Cohen syndrome? Clin Genet 25:347–353
Greenberg F, Ledbetter DH (1987) Deletions of proximal 15q without Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet 28:813–820
Greenberg F, El-Hibri H, Ledbetter DH (1983) A jumping translocation of chromosome 15: a clue to the etiology of Prader-Willi syndrome? Pediatr Res 17: 211A (abstr)
Herrmann B, Bucan M, Mains PE, Frischauf AM, Silver LM, Lehrach H (1986) Genetic analysis of the proximal portion of the mouse t complex: evidence for a second inversion within t haplotypes. Cell 44:469–476
Hood OJ, Rouse BM, Lockhart LH, Bodensteiner JB (1986) Proximal duplications of chromosome 15: clinical dilemmas. Clin Genet 29:234–240
Jennings MW, Jones RW, Wood WG, Weatherall DJ (1985) Analysis of an inversion within the human beta globin gene cluster. Nucleic Acids Res 13:2897–2906
Kaplan LC, Wharton R, Elias E, Mandell F, Donlon T, Latt S (1987) Clinical heterogeneity associated with deletions in the long arm of chromosome 15: report of 3 new cases and their possible genetic significance. Am J Med Genet 28:45–53
Lalande M, Dryja TP, Schreck RR, Shipley J, Flint A, Latt SA (1984) Isolation of human chromosome 13-specific DNA sequences cloned from flow sorted chromosomes and potentially linked to the retinoblastoma locus. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 13:283–295
Lalande M, Schreck RR, Hoffman R, Latt SA (1985) Identification of inverted duplicated no. 15 chromosomes using bivariate flow cytometric analysis. Cytometry 6:1–6
Ledbetter DH, Riccardi VM, Airhart SD, Strobel RJ, Keenan BS, Crawford JD (1981) Deletions of chromosome 15 as a cause of the Prader-Willi syndrome. N Engl J Med 304:325–329
Ledbetter DH, Mascarello JT, Riccardi VM, Harper VD, Airhart SD, Strobel RJ (1982) Chromosome 15 abnormalities and the Prader-Willi syndrome: a follow-up report of 40 cases. Am J Hum Genet 34:278–285
Lehrman MA, Russell DW, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1986) Exon-Alu recombination deletes 5 kilobases from the low density lipoprotein receptor gene, producing a null phenotype in familial hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:3679–3683
Lejeune J, Maunory C, Prieur M (1979) Translocation sauteuse (5p;15q),(8q;15q)(12q;15q). Ann Génét (Paris) 22:210–213
Lubinsky M, Zellweger H, Greenswag L, Larson G, Hansmann I, Ledbetter D (1987) Familial Prader-Willi syndrome with apparently normal chromosomes. Am J Med Genet 28:37–43
Magenis RE, Brown MG, Lacey DA, Budden S, LaFranchi S (1987) Is Angelman syndrome an alternate result of del(15)(q11q13)? Am J Med Genet 28:829–828
Mattei JF, Mattei MG, Giraud F (1983) Prader-Willi syndrome and chromosome 15. Hum Genet 64:356–363
Mattei MG, Souiah N, Mattei JF (1984) Chromosome 15 anomalies and the Prader-Willi syndrome: cytogenetic analysis. Hum Genet 66:313–334
McKusick VA (1983) Mendelian inheritance in man, 6th edn. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Pettigrew AL, Gollin SM, Greenberg F, Riccardi VM, Ledbetter DH (1987) Duplication of proximal 15q as a cause of Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet 28:791–802
Prader A, Labhart A, Willi H (1956) Ein Syndrom von Adipositas, Kleinwuchs, Kryptorchismus und Oligophreni nach myatonieartigem Zustand im Neugeborenenalter. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 86:1260–1261
Protter AA, Levy-Wilson B, Miller J, Bencen G, White T, Seilhawer J (1984) Isolation and sequence-analysis of the human apolipoprotein CIII gene and the intergenic region between the Apo-AI and Apo-CIII genes. DNA 3:449–456
Richards JE, Gilliam AC, Shen A, Tucker PW, Blattner FR (1983) Unusual sequences in the murine immunoglobulin μ-δ heavy-chain region. Nature 306:483
Rouyer F, Simmler M, Page DC, Weissenbach J (1987) A sex chromosome rearrangement in a human XX male caused by Alu-Alu recombination. Cell 51:417–425
Sarvetnick N, Fox HS, Mann EA, Mains PE, Elliot RW, Silver LM (1986) Nonhomologous pairing in mice heterozygous for a t haplotype can produce recombinant chromosomes with duplications and deletions. Genetics 113:723–734
Schreck RR, Breg WR, Erlanger BF, Miller OJ (1977) Preferential derivation of abnormal human G-group-like chromosomes from chromosome 15. Hum Genet 36:1–12
Schwartz S, Max SR, Panny SR, Cohen MM (1985) Deletions of proximal 15q and non-classical Prader-Willi syndrome phenotypes. Am J Med Genet 20:255–263
Shin HS, Flaherty L, Artzt K, Bennett D, Ravetch J (1983) Inversion in the H-2 complex of t-haplotypes in mice. Nature 306:380–383
Silver LM (1985) Mouse t haplotypes. Annu Rev Genet 19:179–208
Smith A, Noel M (1980) A girl with the Prader-Willi syndrome and Robertsonian translocation 45,XX,t(14;15)(p11;q11) which was present in three normal family members. Hum Genet 55:271–273
Smith D (1982) Recognizable patterns of human malformation. Saunders, Philadelphia
Stetten G, Sroka-Zaczek B, Corson VL (1981) Prenatal detection of an accessory chromosome identified as an inversion duplication (15). Hum Genet 57:357–359
Tantravahi U, Kirschner DA, Beauregard L, Page L, Kunkel L, Latt SA (1983) Cytologic and molecular analysis of 46,XXq- cells to identify a DNA segment that might serve as a probe for a putative human X chromosome inactivation center. Hum Genet 64:33–38
Willems PJ, Kijkstra I, Brouwer OF, Smit GPA (1987) Recurrence risk in the Angelman (“Happy Puppet”) syndrome. Am J Med Genet 27:773–780
Wisniewski LP, Hassold T, Heffelfinger J, Higgins JV (1979) Cytogenetic and clinical studies in five cases of inv dup(15). Hum Genet 50:259–270
Wisniewski LP, Witt ME, Ginsberg-Fellner F, Wilner J, Desnick RJ (1980) Prader-Willi syndrome and a bisatellited derivative of chromosome 15. Clin Genet 18:42–47
Zellweger H, Soper RT (1979) The Prader-Willi syndrome. Med Hyg 37:3338–3345
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donlon, T.A. Similar molecular deletions on chromosome 15q11.2 are encountered in both the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes. Hum Genet 80, 322–328 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00273644
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00273644