Summary
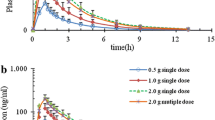
The pharmacokinetic behaviour of cefadroxil was dose-dependent in healthy male volunteers following the oral administration of single doses of 5, 15, and 30 mg · kg−1.
As the dose of cefadroxil increased from 5 to 15 and 30 mg · kg−1, the peak plasma concentrations, normalized to 5 mg · kg−1, decreased significantly from 15.1 to 10.7 and 7.6 mg·l−1, while the corresponding normalized areas under the plasma concentration-time curves from 0 to 2 h decreased significantly from 1258 to 946 and 801 min·mg·l−1.
When the same subjects were given 5 mg·kg−1 of cefadroxil together with 45 mg·kg−1 of cephalexin, the absorption of cefadroxil was slowed to a similar or greater extent than with the high dose of cefadroxil.
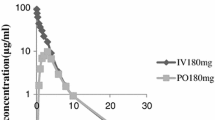
Although the absorption rate decreased as the dose increased, the systemic availability of cefadroxil was essentially complete at all doses, as judged by the 24 h urinary recoveries of the antibiotic. Kinetic analysis of the plasma concentration-time curves gave the best fit with a zero-order followed by a first-order absorption process, consistent with saturable intestinal absorption of cefadroxil.
The elimination rate of cefadroxil was directly related to dose and plasma concentrations, and the clearance at the dose of 5 mg·kg−1 was significantly increased by the simultaneous administration of high-dose cephalexin.
The renal clearance of cefadroxil ranged from 98 ml·min·l−1 at total plasma cephalosporin (cefadroxil + cephalexin) concentrations less than 2.5 mg·l−1 to 156 mg·l−1 at concentrations greater than 40 mg·l−1. These findings are consistent with saturable active gastrointestinal absorption and renal tubular reabsorption of cefadroxil, with competitive inhibition of both processes by cephalexin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike A (1976) An information criterion (AIC). Math Sci 14: 5–9
Antonin KK, Bieck P, Schick C, Steidle B (1982) Vergleichende chemische und radiologische Bestimmung der intestinalen Passagzeit Mund-Zoekum. Z Gastroenterol 20: 554–555
Arvidsson A, Borg» O, Alván G (1979) Renal excretion of cephapirin and cephaloridine: evidence for saturable tubular reabsorption. Clin Pharmacol Ther 25: 870–876
Hirtz J (1985) The gastrointestinal absorption of drugs in man: a review of current concepts and methods of investigation. Br J Clin Pharmacol 19: 77–83S
Kennedy M, Chinwah P, Wade DN (1979) A pharmacological method of measuring mouth-caecal transit in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 8: 372–373
Kimura T, Yamamoto T, Mizuno M, Suga Y, Kitade S, Sezaki H (1983) Characterization of aminocephalosporin transport across rat intestine. J Pharmacobio Dyn 6: 246–253
La Rosa F, Ripa S, Prenna M, Ghezzi A, Pfeffer M (1982) Pharmacokinetics of cefadroxil after oral administration in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 21: 320–322
Mariño EL, Domínguez-Gil A, Muriel C (1982) Influence of dosage form and administration route on the pharmacokinetic parameters of cefadroxil. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 20: 73–77
Nakashima E, Tsuji A, Kagatami S, Yamana T (1984) Intestinal absorption mechanisms of amino-beta-lactam antibiotics. III. Kinetics of carrier-mediated transport across the rat small intestine in situ. J Pharmacobio Dyn 7: 452–464
Sánchez-Picó A, Peris-Ribera JE, Toledano C, Torres-Molina F, Casabó VG, Martín-Villodre A, Plá-Delfina JM (1989) Non-linear intestinal absorption kinetics of cefadroxil in the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol 41: 179–185
Sjövall J, Alván G, Westerlund D (1985) Oral cyclacillin interacts with the absorption of oral ampicillin, amoxycillin, and bacampicillin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 29: 495–502
Tsuji A, Nakashima E, Kagami I, Yamana T (1981) Intestinal absorption of amphoteric beta-lactam-antibiotics. I. Comparative absorption and evidence for saturable transport of amino-beta-lactam antibiotics by in situ rat small intestine. J Pharm Sci 70: 768–772
Wagner JG (1979) Fundamentals of clinical pharmacokinetics. Drug Intelligence Publications, Hamilton, pp 174–201 and 136–143
Yamaoka K, Tanagawara Y, Nakagawa T, Uno T (1981) A pharmacokinetic analysis program (MULTI) for microcomputer. J Pharmacobio Dyn 4: 879–885
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garrigues, T.M., Martin, U., Peris-Ribera, J.E. et al. Dose-dependent absorption and elimination of cefadroxil in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 41, 179–183 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265914
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265914