Summary
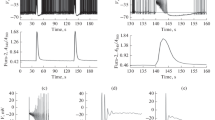
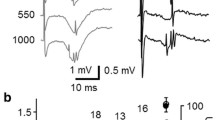
The Ca++-dependence of the repetitive firing of neostriatal neurons was studied in an in vitro slice preparation of the rat neostriatum. Neuronal firing was evoked by injecting depolarizing currents of 100–200 ms duration. In normal conditions, the mode of firing was tonic and showed very little adaptation. The frequency-current relation was linear over a wide range of frequencies. The repetitive firing was first enhanced and later suppressed by Co++, Mn++ and Cd++. These effects on the repetitive firing by the Ca++-channel blockers paralleled the suppression of the slow afterhyperpolarizing potential. The lowering (0.2 mM) of Ca++ had similar effects. In the presence of TEA (up to 10 mM), the cell fired both Na+ and Ca+ action potentials. The results suggest that, as in other CNS neurons of the vertebrate, in neostriatal neurons the slow afterhyperpolarizing potential (AHP) is due to a Ca++-activated K+-conductance, and that the AHP plays a crucial role in the repetitive firing of these neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams PR, Constanti A, Brown DA, Clark RB (1982) Intracellular calcium activates a fast voltage-sensitive K+ current in vertebrate sympathetic neurones. Nature 296: 746–749
Bargas J, Galarraga E, Aceves J (1984) Effects of tetraethylammonium on electrical properties of neostriatal neurons. Soc Neurosci Abstr 10: 348
Bargas J, Galarraga E, Aceves J (1988) Electrotonic properties of neostriatal neurons are modulated by extracellular potassium. Exp Brain Res 72: 390–398
Bargas J, Galarraga E, Aceves J (1989) An early outward conductance modulates the firing latency and frequency of neostriatal neurons of the rat brain. Exp Brain Res 75: 146–156
Barrett EF, Barrett JN (1976) Separation of two voltage-sensitive potassium currents and demonstration of a tetrodotoxin-resistant calcium current in frog motoneurons. J Physiol (Lond) 255: 737–774
Bourque CW, Randle JCR, Renaud LP (1985) Calcium dependent potassium conductance in rat supraoptic nucleus neurosecretory neurons. J Neurophysiol 54: 1375–1382
Brown DA, Griffith WH (1983) Calcium-activated outward current in voltage-clamped hippocampal neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol (Lond) 337: 287–301
Brown DA, Halliwell JV (1975) An in vitro preparation of the diencephalic interpeduncular nucleus. In: Kerkut GA, Wheal HV (eds) Electrophysiology of isolated mammalian CNS preparations. Academic Press, London, pp 285–308
Calabresi P, Mercuri N, Stanzione P, Stefani A, Bernardi G (1987a) Intracellular studies on the dopamine-induced firing inhibition of neostriatal neurons in vitro: evidence for D1 receptor involvement. Neuroscience 20: 757–771
Calabresi P, Misgeld U, Dodt HU (1987b) Intrinsic membrane properties of neostriatal neurons can account for their low level of spontaneous activity. Neuroscience 20: 293–303
Cherubini E, Lanfumey L (1987) An inward calcium current underlying regenerative calcium potentials in rat striatal neurons in vitro enhanced by BAY K 8644. Neuroscience 21: 997–1005
Connor JA (1985) Neural pacemakers and rhythmicity. Ann Rev Physiol 47: 17–28
Constanti A, Sim JA (1987) Calcium-dependent potassium conductance in guinea-pig olfactory cortex neurones in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 387: 173–194
Deitmer JW, Eckert R (1985) Two components of Ca-dependent potassium current in identified neurones of Aplysia californica. Pflügers Arch 403: 353–359
Dunlap K, Fischbach GD (1981) Neurotransmitters decrease the calcium conductance activated by depolarization of embryonic chick sensory neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 317: 519–535
Ewald DA, Levitan IB (1987) Ion channels regulated by calcium. In: Kaczmarek LK, Levitan IB (eds) Neuromodulation. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 138–158
Galarraga E, Bargas J, Aceves J (1984) Dendritic action potentials and calcium activated potassium conductance in neostriatal neurons. Soc Neurosci Abstr 10: 348
Galarraga E, Bargas J, Aceves J (1985) Slow sodium and IA currents in neostriatal neurons. Soc Neurosci Abstr 11: 202
Galvan M (1982) A transient outward current in rat sympathetic neurones. Neurosci Lett 31: 295–300
Galvan M, Adams PR (1982) Control of calcium current in rat sympathetic neurons by norepinephrine. Brain Res 244: 135–144
Galvan M, Sedlmeir C (1984) Outward currents in voltageclamped rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 356: 115–133
Goh JW, Pennefather PS (1987) Pharmacological and physiological properties of the after-hyperpolarization current of bullfrog ganglion neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 394: 315–330
Grace AA, Bunney BS (1984a) The control of firing pattern in nigral dopamine neurons: single spike firing. J Neurosci 4: 2866–2876
Grace AA, Bunney BS (1984b) The control of firing pattern in nigral dopamine neurons: burst firing. J Neurosci 4: 2877–2890
Gustafsson B, Wigström H (1981) Evidence for two types of afterhyperpolarization in CA1 pyramidal cells in the hippocampus. Brain Res 106: 462–468
Hille B (1984) Ionic channels of excitable membranes. Sinauer Assoc Inc. Sunderland Mass
Horn JP, McAffee (1980) Alpha-adrenergic inhibition of calcium-dependent potentials in rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 301: 191–204
Hotson JR, Prince DA (1980) A calcium-activated hyperpolarization follows repetitive firing in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol 43: 409–419
Jahnsen H, Llinás R (1984) Ionic basis for the electroresponsiveness and oscillatory properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 349: 227–247
Junge D (1981) Nerve and muscle excitation, 2nd edn. Sinauer Assoc Inc Sunderland Mass
Kita H, Kita T, Kitai ST (1985a) Active membrane properties of rat neostriatal neurons in an in vitro slice preparation. Exp Brain Res 60: 54–62
Kita H, Kita T, Kitai ST (1985b) Regenerative potentials in rat neostriatal neurons in an in vitro slice preparation. Exp Brain Res 60: 63–70
Kitai ST, Kita H (1984) Electrophysiological study of the neostriatum in brain slice preparation. In: Dingledine R (ed) Brain slices, Plenum Press, New York, pp 285–296
Krnjević K, Puil E, Werman R (1978) EGTA and motoneuronal after-potentials. J Physiol (Lond) 275: 199–223
Lancaster B, Adams PR (1986) Calcium-dependent current generating the afterhyperpolarization of hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol 55: 1268–1282
Lancaster B, Pennefather P (1987) Potassium currents evoked by brief depolarizations in bull-frog sympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol (Lond) 387: 519–548
Lanthorn T, Storm J, Andersen P (1984) Current-to-frequency transduction in CA1 hippocampal pyramidal cells: slow prepotentials dominate the primary range firing. Exp Brain Res 53: 431–443
Llinás R, Sugimori M (1980) Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell somata in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol (Lond) 305: 197–213
Madison DV, Nicoll RA (1984) Control of the repetitive discharge of rat CA1 pyramidal neurones in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 354: 319–331
Madison DV, Nicoll RA (1986a) Actions of noradrenaline recorded intracellularly in rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurones, in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 372: 221–244
Madison DV, Nicoll RA (1986b) Cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate mediates beta-receptor actions of noradrenaline in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol (Lond) 372: 245–259
Meech RW (1978) Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissue. Rev Biophys Bioeng 7: 1–18
Pennefather P, Lancaster B, Adams PR, Nicoll RA (1985) Two distinct Ca-dependent K currents in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 3040–3044
Reuter H (1983) Calcium channel modulation by neurotransmitters, enzymes and drugs. Nature 301: 569–574
Rudy B (1988) Diversity and ubiquity of K channels. Neuroscience 25: 729–749
Schwindt PC, Crill WE (1980) Properties of a persistent inward current in normal and TEA-injected motoneurons. J Neurophysiol 43: 1700–1723
Stafstrom CE, Schwindt PC, Chubb MC, Crill WE (1985) Properties of persistent sodium conductance and calcium conductance of layer V neurons from cat sensorimotor cortex in vitro. J Neurophysiol 53: 153–170
Stanfield PR (1983) Tetraethylammonium ions and the potassium permeability of excitable cells. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 97: 1–67
Stevens DR, Gallagher JP, Shinnick-Gallagher P (1984) Intracellular recordings from rat dorsolateral septal neurons, in vitro. Brain Res 305: 353–356
Storm JF (1987a) Action potential repolarization and a fast afterhyperpolarization in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol (Lond) 385: 733–759
Storm JF (1987b) Potassium currents underlying afterhyperpolarizations (AHPs) and spike repolarization in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells (CA1). Soc Neurosci Abstr 13: 176
Sugimori M, Preston RJ, Kitai ST (1978) Response properties and electrical constants of caudate nucleus neurons in the cat. J Neurophysiol 41: 1662–1675
Thompson SH (1977) Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 265: 465–488
Tokimasa T (1984) Calcium-dependent hyperpolarizations in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Neuroscience 12: 929–937
Yarom Y, Sugimori M, Llinás R (1985) Ionic currents and firing patterns of mammalian vagal motoneurons in vitro. Neuroscience 16: 719–737
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galarraga, E., Bargas, J., Sierra, A. et al. The role of calcium in the repetitive firing of neostriatal neurons. Exp Brain Res 75, 157–168 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248539
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248539