Summary
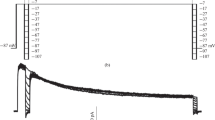
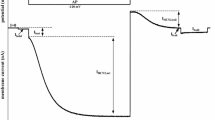
The ionic mechanisms underlying inward or anomalous rectification have been studied in the marine hypotrichous ciliate Euplotes vannus. Inward-current pulses of moderate amplitude elicited time-dependent rectification that started from a hyperpolarization peak and was expressed as a depolarizing sag towards rest. Voltage-clamp analysis showed that this depolarization is caused by the activation of a complex inward current that does not inactivate with time. The current is carried by a major Na and a minor K component. The Na-current component has been identified by its concentration-dependent reduction in low extra-cellular Na solutions and the capability of Li2+ as Na substitute to carry the current, though with a slightly reduced amplitude. The K-current component has been isolated from the total current after the replacement of Na2+ within the experimental solution. It was blocked in media that contained 10 mmol/liter TEA, a well-known blocker for K inwardly rectifying currents. TEA was only effective at membrane potentials close to or negative to the potassium equilibrium potential. The inward current was reduced after the injection of the Ca chelator EGTA into the cell. Also the elimination of the ciliary membrane, by deciliating cells with ethanol, reduced the amplitude of the inwardly rectifying currents. Both experiments indicate a regulatory function of Ca22+ in inward rectification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angstadt, J.D., Calabrese, R.L. 1989. A hyperpolarization-activated inward current in heart interneurons of the medicinal leech. J. Neurosci. 9:2846–2857
Ballanyi, K., Deitmer, J.W. 1984. Concentration-dependent effects of Ba22+ on action potential and membrane currents in the ciliate Stylonychia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 78A:575–581
De Peyer, J.E., Machemer, H. 1978. Hyperpolarizing and depolarizing mechanoreceptor potentials in Stylonychia. J. Comp. Physiol. 127:255–266
Deitmer, J.W. 1981. Voltage and time characteristics of the potassium mechanoreceptor current in the ciliate Stylonychia. J. Comp. Physiol. 141:173–182
Deitmer, J.W. 1982. The effects of tetraethylammonium and other agents on the potassium mechanoreceptor current in the ciliateStylonychia. J. Exp. Biol. 96:239–249
DiFrancesco, D., Torotora, P. 1991. Direct activation of cardiac pace-maker channels by intracellular cyclic AMP. Nature 351:145–147
Kamondi, A., Reiner, P.B. 1991. Hyperpolarization-activated inward current in histaminergic tuberomammillary neurons of the rat hypothalamus. J. Neurophysiol. 66:1902–1911
Krüppel, T., Lueken, W. 1988. Membrane excitability and membrane currents in the marine ciliate Euplotes vannus. Eur. J. Protistol. 24:11–21
Krüppel, T., Lueken, W. 1990. Calcium-dependent sodium current in the marine ciliate Euplotes vannus. J. Membrane Biol. 116:79–86
Latorre, R., Miller, C. 1983. Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels. J. Membrane Biol. 71:11–30
Lueken, W., Gaertner, M., Breer, H. 1983. Mating-type-specific loss of conjugation competence by irritation in Euplotes vannus. J. Exp. Zool. 226:11–17
Machemer, H., Ogura, A. 1979. Ionic conductances of membranes in ciliated and deciliated Paramecium. J. Physiol. 296:49–60
Matsuda, H., Saigusa, A., Irisawa, H. 1987. Ohmic conductance through the inwardly rectifying K channel and blocking by internal Mg22+. Nature 325:156–159
McCormick, D.A., Pape, H-C. 1990. Properties of a hyperpolarization-activated cation current and its role in rhythmic oscillation in thalamic relay neurones. J. Physiol. 431:291–318
Mukai, M., Kyogoku, L, Kuno, M. 1992. Calcium-dependent inactivation of inwardly rectifying K2+ channel in a tumor mast cell line. Am. J. Physiol. 256:C84-C90
Naitoh, Y., Eckert, R. 1968. Electrical properties of Paramecium caudatum: Modifications by bound and free cations. Z. vergl. Physiologie 61:427–452
Naitoh, Y., Eckert, R. 1973. Sensory mechanisms in Paramecium II. Ionic basis of the hyperpolarizing mechanoreceptor potential. J. Exp. Biol. 59:53–65
Oertel, D., Schein, S.J., Kung, C. 1978. A potassium conductance activated by hyperpolarization in Paramecium. J. Membrane Biol. 43:169–185
Ogura, A., Machemer, H. 1980. Distribution of mechanoreceptor channels in the Paramecium surface membrane. J. Comp. Physiol. 135:233–242
Partridge, L.D., Swandulla, D. 1988. Calcium-activated non-specific cation channels. TINS 11:69–72
Phillips, C.L., Bacigalupo, J., O'Day, P.M. 1992. Inward rectification in Limulus photoreceptors. Visual Neurosci. 8:19–25
Preston, R., Saimi, Y., Kung, C. 1990. Evidence for two K2+ currents activated upon hyperpolarization of Paramecium tetraurelia. J. Membrane Biol. 115:41–50
Preston, R.R., Saimi, Y., Kung, C. 1992a. Calcium current activated upon hyperpolarization of Paramecium tetraurelia. J.Gen. Physiol. 100:233–251
Preston, R.R., Saimi, Y., Kung, C. 1992b. Calcium-dependent inacti vation of the calcium current activated upon hyperpolarization of Paramecium tetraurelia. J. Gen. Physiol. 100:253–268
Rudy, B. 1988. Diversity and ubiquity of K channels. Neuroscience 25:729–749
Saimi, Y. 1986. Calcium-dependent sodium currents in Paramecium: mutational manipulations and effects of hyper and depolarization. J. Membrane Biol. 92:227–236
Saimi, Y., Kung, C. 1980. A Ca-induced Na-current in Paramecium. J. Exp. Biol. 88:305–325
Satow, Y., Kung, C. 1974. Genetic dissection of active electrogenesis in Paramecium aurelia. Nature 247:69–71
Satow, Y., Kung, C. 1977. A regenerative hyperpolarization in Paramecium. J. Comp. Physiol. 119:99–110
Spain, W.J., Schwindt, P.C., Crill, W.E. 1987. Anomalous rectification in neurons from cat sensorimotor cortex in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 57:1555–1576
Thompson, H., Aldrich, W. 1980. Membrane potassium channels. In: The Cell Surface and Neuronal Function. C.W. Cotman, G. Poste, and G.L. Nicolson, editors, pp. 49–85. Elsevier North-Holland, Amsterdam
Tokimasa, T., Akasu, T. 1990. Cyclic AMP regulates an inward rectifying sodium-potassium current in dissociated bull-frog sympathetic neurones. J. Physiol. 420:409–429
Valbonesi, A., Ortenzi, C., Luporini, P. 1988. An integrated study of the species problem in the Euplotes crassus-minutavannus group. J. Protozool. 35:38–45
Valbonesi, A., Ortenzi, C., Luporini, P. 1992. The species problem in a ciliate with a high multiple mating type system, Euplotes crassus. J. Protozool. 39:45–54
Vandenberg, C.A. 1987. Inward rectification of a potassium channel in cardiac ventricular cells depends on internal magnesium ions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:2560–2564
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The author is grateful to Harald Mikoleit for technical assistance and preparing the figures and to Prof. W. Lueken for his critical comments. This work was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, SFB 171, C7.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krüppel, T. Inward rectification by hyperpolarization-activated Na current in the marine ciliate Euplotes vannus . J. Membarin Biol. 133, 263–270 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232025
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232025