Abstract
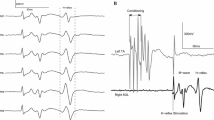
To evaluate functional change in the spinal reflex pathway with ageing, we studied heteronymous Ia facilitation from the quadriceps to soleus muscle in 30 normal volunteers (aged 24–68 years). The size of the test H-reflex of the soleus muscle was adjusted to 25% that of the maximal M-response. The conditioning stimulus was adjusted to 1.5-fold the motor threshold to stimulate all the Ia fibres in the femoral nerve. Facilitation was quantified as the slope of the very early part of facilitation, within 0.8 ms of onset. This procedure enabled us to evaluate the extent of monosynaptic Ia facilitation without contamination by other effects. The extent of facilitation decreased linearly with age. This decrease in facilitation could reflect a decrease in the number of Ia fibres and in their conduction velocities, and an increase in presynaptic inhibition on Ia terminals. The increase in presynaptic inhibition may be an adaptive phenomenon in the ageing of the neuromuscular system or, alternatively, a deteriorating process with decreasing flexible supraspinal modulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araki T, Eccles JC, Ito M (1960) Correlation of the inhibitory post-synaptic potential of motoneurones with the latency and time course of inhibition of monosynaptic reflexes. J Physiol (Lond) 154:354–377
Bertoni-Freddari C, Fattoretti P, Casoli T, Meier-Ruge W, Ulrich J (1990) Morphological adaptive response of the synaptic junctional zones in the human dentate gyrus during aging and Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 517:69–75
Boxer PA, Morales FR, Chase MH (1988) Alterations of group Iamotoneuron monosynaptic EPSPs in aged cats. Exp Neurol 100:583–595
Brooke JD, Singh R, Wilson MK, Yoon P, McIlroy WE (1989) Ageing of human segmental oligosynaptic reflexes for control of leg movement. Neurobiol Aging 10:721–725
Burke D, Gandevia SC, McKeon B (1983) The afferent volleys responsible for spinal proprioceptive reflexes in man. J Physiol (Lond) 339:535–552
Burke JR, Kamen G, Koceja DM (1989) Long-latency enhancement of quadriceps excitability from stimulation of skin afferents in young and old adults. J Gerontol 44:158–163
Corbin KB, Gardner ED (1937) Decrease in number of myelinated fibers in human spinal roots with age. Anat Rec 68:63–74
Crone C, Hultborn H, Mazières L, Morin C, Nielsen J, PierrotDeseilligny E (1990) Sensitivity of monosynaptic test reflexes to facilitation and inhibition as a function of the test reflex size: a study in man and the cat. Exp Brain Res 81:35–45
Delwaide PJ (1973) Human monosynaptic reflexes and presynaptic inhibition. An interpretation of spastic hyperreflexia. In: Desmedt JE (ed) Human reflexes, pathophysiology of motor systems, methodology of human reflexes. (New developments in electromyography and clinical neurophysiology, vol 3) Karger, Basel, pp 508–522
Dorfman LJ, Bosley TM (1979) Age-related changes in peripheral and central nerve conduction in man. Neurology 29:38–44
Eccles JC (1977) The understanding of the brain, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Engelhardt JK, Morales FR, Yamuy J, Chase MH (1989) Cable properties of spinal cord motoneurons in adult and aged cats. J Neurophysiol 61:194–201
Fetz EE, Jankowska E, Johannisson T, Lipski J (1979) Autogenetic inhibition of motoneurones by impulses in group Ia muscle spindle afferents. J Physiol (Lond) 293:173–195
Hultborn H, Meunier S, Pierrot-Deseilligny E, Shindo M (1987) Changes in presynaptic inhibition of Ia fibers at the onset of voluntary contraction in man. J Physiol (Lond) 389:757–772
Katz R, Meunier S, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (1988) Changes in presynaptic inhibition of Ia fibers in man while standing. Brain 111:417–437
Kuno M (1959) Excitability following antidromic activation in spinal motoneurones supplying red muscles. J Physiol (Lond) 149:374–393
Meunier S, Penicaud A, Pierrot-Deseilligny E, Rossi A (1990) Mo-nosynaptic Ia excitation and recurrent inhibition from quadriceps to ankle flexors and extensors in man. J Physiol (Lond) 423:661–675
Morales FR, Boxer PA, Fung SJ, Chase MH (1987) Basic electrophysiological properties of spinal cord motoneurons during old age in the cat. J Neurophysiol 58:180–194
Morita H, Shindo M, Yanagawa S, Yanagisawa N (1993a) Neuromuscular response in man to repetitive nerve stimulation. Muscle Nerve 16:648–654
Morita H, Shindo M, Yanagawa S, Yanagisawa N (1993b) Decrease of presynaptic inhibition in patients with Parkinson's disease. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 87:S34
Pierrot-Deseilligny E, Katz R, Morin C (1979) Evidence for Ib inhibition in human subjects. Brain Res 166:176–179
Sabbahi MA, Sedgwick EM (1982) Age-related changes in monosynaptic reflex excitability. J Gerontol 37:24–32
Swallow M (1966) Fibre size and content of the anterior tibial nerve of the foot. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 29:205–213
Taylor PK (1984) Non-linear effects of age on nerve conduction in adults. J Neurol Sci 66:223–234
Trillo L, Gonzalo LM (1992) Ageing of the human entorhinal cortex and subicular complex. Histol Histopathol 7:17–22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morita, H., Shindo, M., Yanagawa, S. et al. Progressive decrease in heteronymous monosynaptic la facilitation with human ageing. Exp Brain Res 104, 167–170 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00229867
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00229867