Summary
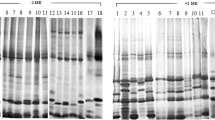
Proteins extracted from seed embryos of 29 different cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) and one wild rice (O. rufipogon Griff.) were compared by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis analysis. Among more than 300 protein spots on the gel we found some interesting variations in ten spots which were individually designated as proteins A-J. Protein E was observed in all indica cultivars but was not found in those of the subspecies japonica. In contrast, protein F was only detected in japonica cultivars. Protein A existed in all japonica cultivars but, with the exception of IR-36, could not be found in other indica cultivars. Therefore, proteins A, E and F can be used as markers for the identification of indica and japonica. Some so-called “Javanica” cultivars showed the characteristics of japonica subspecies with regard to proteins A and F, while one other cultivar of Javanica expressed a type intermediate between indica and japonica interms of proteins A and E. One feature discriminating between Javanica and japonica cultivars was found in the D, G, and J proteins which were expressed strongly in Javanica cultivars but were scarcely expressed in those of japonica. Expression of subspecies-specific proteins E and F in f1 hybrids was also investigated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauw G, De Loose M, Inze D, Van Montagu M, Vandekerck-hove J (1987) Alterations in the phenotype of plant cells studied by NH2-terminal amino acid-sequence analysis of proteins electroblotted from two-dimensional gel-separated total extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:4806–4810
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chowdhury MKU, Schaeffer GW, Smith RL, Matthews BF (1988) Molecular analysis of organelle DNA of different subspecies of rice and the genomic stability of mtDNA in tissue cultured cells of rice. Theor Appl Genet 76:533–539
Dallas JF (1988) Detection of DNA “fingerprints” of cultivated rice by hybridization with a human minisatellite DNA probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:6831–6835
Glaszmann JC (1987) Isozymes and classification of Asian rice varieties. Theor Appl Genet 74:21–30
Ishii T, Terachi T, Tsunewaki K (1986) Restriction endonuclease analysis of chloroplast DNA from cultivated rice species, Oryza sativa and O. glaberrima. Jpn J Genet 61:537–541
Khush GS, Gomez KA (1985) Parentage of IRRI crosses IR1-IR50,000. The International Rice Research Institute. Manila, Philippines
Ladizinsky G, Hymowitz T (1979) Seed protein electrophoresis in taxonomic and evolutionary studies. Theor Appl Genet 54:145–151
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Morishima H, Oka HI (1981) Phylogenetic differentiation of cultivated rice, XXII. Numerical evaluation of the Indica Japonica differentiation. Jpn J Breed 31:402–413
O'Farrell PH (1975) High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem 250:4007–4021
Oka HI (1988) Indica-Japonica differentiation of rice cultivars. In: Origin of cultivated rice. Japan Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo, pp 141–179
Ramagopal S (1990) Protein polymorphism in sugarcane revealed by two-dimensional gel analysis. Theor Appl Genet 79:297–304
Second G (1991) Molecular markers in rice systematics and the evaluation of genetic resources. In: Bajaj YPS (ed) Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry, vol 14, Rice. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 468–494
Takahashi N (1984) Differentiation of ecotypes in Oryza sativa L. In: Tsunoda S, Takahashi N (eds) Biology of rice. Japan Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo/Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 31–67
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. S. Khush
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saruyama, H., Shinbashi, N. Identification of specific proteins from seed embryos by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis for the discrimination between indica and japonica rice. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 84, 947–951 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227408
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227408