Summary
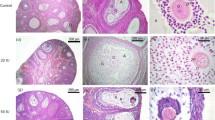
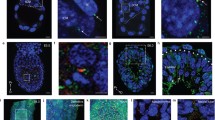
Both the hormone dependency and the morphological details of estrogen-dependent ciliogenesis in the shell gland of the chick oviduct were investigated. Ciliogenesis was initiated on day 3 of estrogen treatment, and progressively more cells became differentiated until, on day 10, ∼ 55% ciliation occurred with 17β-estradiol (1 mg/day) and ∼75% ciliation occurred with diethylstilbestrol (1 mg/day). Simultaneous administration of progesterone with diethylstilbestrol (1 mg each/day for 10 days) caused a 50% depression in the number of ciliated cells on day 10. The rate of ciliogenesis was found to be affected by progesterone and the type of estrogen administered. The minimum stimulatory dose of estradiol was found to be between 0.01 mg/day and 0.05 mg/day. Ciliogenic cells were first recognized by the appearance of pro-basal bodies in the apical portion of the cell. Pro-basal body maturation and cilium formation were the same as those described for the chick trachea. Ciliogenesis in the chick was found to be homologous to estrogen-dependent ciliogenesis in various mammalian oviducts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aderson, R.G.W., Brenner, R.M.,: The formation of basal bodies (centrioles) in the rhesus monkey oviduct. J. Cell Biol. 50, 10–34 (1971)
Anderson, R.G.W., Brenner, R.M.: Estrogen-stimulated oviduct of the rhesus monkey in organ culture. Electron microscopic concepts of secretion, edit. by M. Hess pp. 85–97. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1975
Brenner, R.M., Anderson, R.G.W.: Endocrine control of ciliogenesis in the primate oviduct. Handbook of physiology, Sect, on Endocrinology, Vol. II, Part 2, edit. by R.O. Greep and E.B. Astwood, pp. 123–140. Washington: American Physiological Society, 1973
Brenner, R.M., Resko, J.A., West, N.B.: Cyclic changes in oviductal morphology and residual cytoplasmic estradiol binding capacity induced by sequential estradiol-progesterone treatment of spayed rhesus monkeys. Endocrinology 95, 1094–1104 (1974)
Dirksen, E.R.: Ciliogenesis in the mouse oviduct. A scanning electron microscope study. J. Cell Biol. 62, 899–904 (1974)
Dirksen, E.R., Crocker, T.T.: Centriole replication in differentiating ciliated cells of mammalian respiratory epithelium. An electron microscope study. J. Microsc. 5, 629–644 (1966)
Kalnins, V.I., Porter, K.R.: Centriole replication during ciliogenesis in the chick tracheal epithelium. Z. mikr.-anat. Forsch. 100, 1–30 (1969)
Laugier, C., Brard, E., Sandoz, D., Boisvieux-Ulrich, E.: Interactions du benzoate d'oestradiol et de la progesterone sur le développement de l'oviducte de Caille (Coturnix coturnix japonica). I. Etude Pondérale et histologique. Gen. comp. Endocr. 26, 285–300 (1975)
Oka, T., Schimke, R.T.: Interaction of estrogen and progesterone in chick oviduct development. I. Antagonistic effect of progesterone on estrogen induced proliferation and differentiation of tubular gland cells. J. Cell Biol. 41, 816–831 (1969)
Palmiter, R.D., Wrenn, J.T.: Interaction of estrogen and progesterone in chick oviduct development. III. Tubular gland cell cytodifferentiation. J. Cell Biol. 50, 598–615 (1971)
Segal, S.J.: The primary effects of gonadal steroids on target cells. Recent progress in reproductive endocrinology, edit. by P.G. Crosignani and V. H.T. James, pp. 1–26. London: Academic Press 1974
Sorokin, S.P.: Reconstruction of centriole formation and ciliogenesis in mammalian lungs. J. Cell Sci. 3, 207–229 (1968)
Steinmann, R.: An electron microscopic study of ciliogenesis in developing epidermis and trachea in Xenopus laevis. Amer. J. Anat. 122, 19–55 (1968)
Verhage, H.G., Abel, J.H., Tietz, W.J., Barrau, M.D.: Estrogen-induced differentiation of the oviductal epithelium in prepubertal dogs. Biol. Reprod. 9, 475–488 (1973)
Verhage, H.G., Brenner, R.M.: Estradiol-induced differentiation of the oviductal epithelium in ovariectomized cats. Biol. Reprod. 13, 104–111 (1975)
Verhage, H.G., West, N.B., Brenner, R.M.: Progesterone antagonism of estrogen-driven ciliogenesis in the oviduct of the cat. Abst., Seventh Annual Meeting, Society for the Study of Reproduction, p. 128, Hawn, Canada (1974)
Wrenn, J.T.: An analysis of tubular gland morphogenesis in chick oviduct. Develop. Biol. 26, 400–415 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We would like to thank Dr. Frederick Grinnell for his helpful comments on the manuscript. This project was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health — HD 08987
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anderson, R.G.W., Hein, C.E. Estrogen dependent ciliogenesis in the chick oviduct. Cell Tissue Res. 171, 459–466 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220238
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220238